Considering Propecia? Start with a clear understanding of your hair loss. Consult a dermatologist or trichologist for a proper diagnosis – this crucial step determines the best treatment approach. They’ll assess your hair type, the extent of your hair loss, and underlying health conditions.
Finasteride, the active ingredient in Propecia, works by inhibiting the production of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that contributes significantly to male pattern baldness. Clinical trials show a significant improvement in hair growth for many men. However, remember that results vary, and consistent use is vital for maintaining improvements.
Beyond the prescription route, explore alternative therapies. Minoxidil, a topical solution, can stimulate hair growth in some individuals. Lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet rich in protein and a stress-reduction plan, may also contribute to scalp health. Remember: discuss these options with your doctor to create a personalized strategy that’s right for you.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment.
- Propecia (Finasteride): A Detailed Guide
- Understanding Finasteride
- Dosage and Administration
- Potential Side Effects
- Long-Term Use and Discontinuation
- Alternative Treatments
- Important Considerations
- Finding a Doctor
- Understanding Propecia’s Mechanism of Action
- Targeting DHT: The Key to Hair Growth
- Propecia’s Effectiveness in Treating Male Pattern Baldness
- Factors Influencing Results
- Understanding the Limitations
- Realistic Expectations
- Specific Recommendations
- Alternative Treatments
- Potential Side Effects and Risks Associated with Propecia
- Sexual Side Effects
- Other Potential Side Effects
- Important Considerations Before Using Propecia
- Who is a Suitable Candidate for Propecia Treatment?
- How to Properly Use Propecia and Follow Dosage Instructions
- Understanding the Treatment Timeline
- Important Considerations
- Missed Dose?
- Alternative Treatments for Male Pattern Baldness
- Comparing Propecia to Other Hair Loss Medications
- Topical Treatments
- Other Oral Medications
- Hair Transplant Surgery
- Lifestyle Changes
- The Cost of Propecia and Insurance Coverage Options
- Factors Affecting Propecia Cost
- Insurance Coverage
- Comparing Costs
- Patient Assistance Programs
- Seeking Information
- Long-Term Effects and Discontinuation of Propecia
- Potential Long-Term Effects
- Discontinuation Guidance
- Hair Regrowth After Discontinuation
- Monitoring for Side Effects
- Alternative Treatment Options
Propecia (Finasteride): A Detailed Guide
Consult your doctor before starting Propecia or any medication. They can assess your suitability and discuss potential side effects.
Understanding Finasteride
Propecia, containing finasteride, is an oral medication used to treat male pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia). It works by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase, which converts testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT). High DHT levels contribute significantly to hair loss.
- Reduces DHT: Finasteride directly targets this hormone, slowing hair loss.
- Promotes Hair Growth: In many men, it stimulates new hair growth.
- Maintenance Therapy: Continued use is generally needed to maintain results.
Dosage and Administration
The typical dose is one 1mg tablet daily. Consistent daily use is key. Never exceed the prescribed dosage.
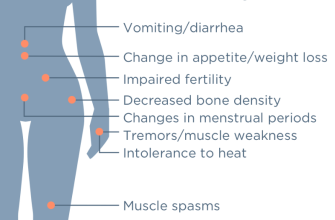
Potential Side Effects
While generally well-tolerated, some men experience side effects. These are usually mild and temporary, but you should report any concerns to your doctor immediately.
- Decreased Libido
- Erectile Dysfunction
- Ejaculation Problems
- Breast Tenderness or Enlargement
These side effects are usually infrequent and often resolve upon cessation of treatment. However, it is important to monitor your health closely.
Long-Term Use and Discontinuation
Hair loss may resume if you stop taking finasteride. Discuss long-term treatment options with your doctor. Gradual discontinuation might be advised to assess your body’s response.
Alternative Treatments
Other hair loss treatments exist, including minoxidil (topical application) and hair transplants. Your doctor can help determine the best approach for your specific needs.
Important Considerations
- This information is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice.
- Always discuss your medical history with your doctor before starting any new medication.
- Regular monitoring is recommended to check for potential side effects and treatment efficacy.
Finding a Doctor
Use online resources to locate a dermatologist or healthcare professional specializing in hair loss. They can provide a personalized assessment and recommend the appropriate treatment plan.
Understanding Propecia’s Mechanism of Action
Propecia, containing finasteride, works by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase. This enzyme converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone responsible for hair follicle miniaturization in male pattern baldness. By reducing DHT levels in the scalp, Propecia helps slow down or stop hair loss.
Targeting DHT: The Key to Hair Growth
The reduction in DHT is key. Lower DHT levels allow hair follicles to remain active and produce hair, thus improving hair growth and potentially thickening existing hairs. It’s important to understand that Propecia doesn’t regrow hair already lost; it primarily focuses on preventing further hair loss and promoting hair growth in affected areas.
Results vary individually. Many men experience improvement in hair loss, but the effects are not permanent. Discontinuing Propecia often results in a return to the previous hair loss pattern. Consult a doctor to discuss the appropriate treatment plan and potential side effects.
Propecia’s Effectiveness in Treating Male Pattern Baldness
Finasteride, the active ingredient in Propecia, demonstrably slows hair loss in many men. Studies show it can prevent further hair thinning and even promote some hair regrowth in approximately 60-80% of users. This improvement isn’t dramatic for everyone; results vary significantly based on individual factors.
Factors Influencing Results
Genetic predisposition plays a major role. Men with a strong family history of male pattern baldness often see better results. Age at treatment initiation also matters; younger men generally respond better. Consistent medication use is paramount; stopping Propecia usually leads to the resumption of hair loss.
Understanding the Limitations
Propecia primarily addresses hair loss on the crown and mid-scalp. It’s less effective for receding hairlines or hair loss already significantly advanced. Furthermore, it only works while you’re taking it; hair loss will likely return if you discontinue treatment.
Realistic Expectations
Expect gradual improvement over several months. Significant changes may not be visible immediately. While it’s a valuable tool for many, Propecia isn’t a guaranteed cure for male pattern baldness. A consultation with a dermatologist is recommended to discuss individual suitability and potential side effects.
Specific Recommendations
Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. Maintain a consistent dosage schedule. Discuss potential side effects, which, though infrequent, include sexual dysfunction. Be patient; results take time. Consider combining Propecia with Minoxidil for potentially better results.
Alternative Treatments
Hair transplants offer a permanent solution for those not satisfied with medication, providing a more immediate and noticeable result. However, this is a surgical procedure with its own set of considerations.
Potential Side Effects and Risks Associated with Propecia
Propecia, while effective for many, carries potential side effects. Understanding these risks is key to making an informed decision.
Sexual Side Effects
- Decreased Libido: This is a common side effect, reported by a significant percentage of users. It usually resolves upon cessation of treatment.
- Erectile Dysfunction: Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection can occur. Again, this often subsides after stopping Propecia.
- Ejaculation Disorders: Changes in ejaculate volume or the ability to ejaculate may be experienced by some men.
The frequency of these sexual side effects varies, and they aren’t experienced by everyone. However, open communication with your doctor is vital if you notice any changes.
Other Potential Side Effects
- Gynecomastia (breast enlargement): Although rare, this is a possible side effect.
- Prostate cancer risk: Studies have shown conflicting results regarding the impact of Propecia on prostate cancer risk. Consult your physician for a thorough risk assessment.
- Allergic reactions: Skin rashes, itching, or swelling are possible, requiring immediate medical attention.
- Depression: A link between Propecia use and depression has been suggested in some studies, though more research is needed to establish causality.
Important Considerations Before Using Propecia
- Pre-existing conditions: Discuss your medical history, including any liver or prostate problems, with your doctor before starting Propecia.
- Drug interactions: Certain medications may interact negatively with Propecia. Provide your physician with a complete list of your current medications.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Propecia is not for women, particularly those who are pregnant or breastfeeding. Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you are exposed to it during pregnancy.
- Regular monitoring: Regular check-ups with your doctor are recommended to monitor your overall health and assess any side effects.
This information is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your physician before starting any medication.
Who is a Suitable Candidate for Propecia Treatment?
Generally, men experiencing male pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia) are prime candidates. This includes men with noticeable hair thinning on the crown or receding hairline.
Age plays a role; Propecia is most effective in younger men, generally between 18 and 41. Older men may still benefit, but results may vary.
Medical history is key. Discuss any existing health conditions, especially liver problems, with your doctor before starting treatment. Propecia isn’t suitable for women or children.
Specific expectations are vital. Propecia slows hair loss, but it doesn’t guarantee hair regrowth for everyone. Some may experience minimal changes, while others see significant improvement.
Regular follow-up appointments with your doctor are necessary to monitor progress and address any side effects. Consistent use is essential for optimal results.
Ultimately, a consultation with a dermatologist or healthcare professional will determine your suitability. They will assess your individual needs and guide you on the best course of action.
How to Properly Use Propecia and Follow Dosage Instructions
Take one 1mg tablet of Propecia daily, with or without food. Consistency is key; take it around the same time each day to maintain consistent blood levels of the active ingredient, finasteride.
Understanding the Treatment Timeline
Results vary, but you should see some improvement in hair growth within three to six months of consistent use. Don’t expect overnight miracles; patience and adherence to the prescribed regimen are paramount. Hair growth is gradual and may continue to improve over time. Continue taking Propecia as directed by your doctor even if you see initial results.
Important Considerations
Propecia is intended for long-term use. Stopping treatment will likely result in a return of hair loss. Discuss your treatment plan with your physician to determine the best course for your individual needs. Inform your doctor about all medications you are currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to avoid potential drug interactions. Never share your medication with others.
Missed Dose?
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for your next dose. Don’t double up on doses. Consistent daily intake is more effective than sporadic dosing.
Alternative Treatments for Male Pattern Baldness
Consider minoxidil (Rogaine). This over-the-counter topical solution slows hair loss and may stimulate regrowth. Apply it directly to the scalp as directed.
Explore low-level laser therapy (LLLT). Devices like laser combs or caps emit low-level lasers that can promote hair follicle growth. Research suggests this approach can be beneficial, but individual results vary.
Consult a dermatologist about platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy. This procedure involves injecting your own platelet-rich plasma into your scalp, potentially stimulating hair follicle activity and encouraging hair growth.
Investigate hair transplantation. This surgical procedure involves moving hair follicles from a donor area to areas experiencing hair loss. It provides permanent results, but it’s a more invasive and costly option.
Maintain a healthy diet. Nutrients like protein, iron, zinc, and biotin are crucial for hair health. A balanced diet supports overall well-being, which may positively impact hair growth.
Manage stress levels. Chronic stress can contribute to hair loss. Incorporate stress-reducing techniques like exercise, yoga, or meditation into your routine.
Talk to your doctor. They can help you understand the cause of your hair loss and recommend appropriate treatment options. They can also rule out any underlying medical conditions contributing to hair loss.
Comparing Propecia to Other Hair Loss Medications
Propecia (finasteride) targets DHT, a hormone contributing to hair loss. Other medications offer different approaches.
Topical Treatments
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): A topical solution or foam, minoxidil stimulates hair growth but doesn’t address DHT. Many men use it alongside Propecia for synergistic effects. Expect gradual results, typically within several months. Regular use is crucial.
- Other topical agents: Some newer topical treatments are emerging, often combining minoxidil with other ingredients. Research their safety and efficacy thoroughly before use.
Other Oral Medications
- Dutasteride (Avodart): Similar to finasteride, dutasteride blocks DHT. It’s often stronger, but also carries potentially higher side effects. Discuss this option carefully with your doctor.
Hair Transplant Surgery
- Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): These surgical procedures involve moving hair follicles from areas with robust growth to thinning areas. Results are permanent but require significant investment of time and money.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP injections use your own blood platelets to stimulate hair follicle growth. This is often used in conjunction with other treatments, not as a standalone solution.
Choosing the right treatment depends on individual factors like hair loss severity, budget, and tolerance to side effects. Consult a dermatologist or hair loss specialist for personalized recommendations.
Lifestyle Changes
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in protein and essential nutrients supports hair health.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can exacerbate hair loss. Explore relaxation techniques.
Remember, results vary. Patience and consistent treatment are key. Don’t hesitate to discuss your options with a medical professional.
The Cost of Propecia and Insurance Coverage Options
Propecia’s price varies depending on dosage, pharmacy, and location. Expect to pay between $50 and $150 per month for a 1mg daily dose. Generic finasteride, the same active ingredient, is significantly cheaper, often costing under $30 monthly.
Factors Affecting Propecia Cost
Several factors influence the final price. Mail-order pharmacies usually offer lower prices than local pharmacies. Using discount coupons or patient assistance programs can also lower your out-of-pocket expenses. The brand name Propecia tends to be more expensive than generic finasteride.
Insurance Coverage
Many insurance plans cover Propecia or generic finasteride, but coverage specifics depend on your policy. Check your plan’s formulary – a list of covered medications – to verify coverage and any associated copays or deductibles. If your plan doesn’t cover Propecia, consider using a generic alternative or exploring patient assistance programs.
Comparing Costs
| Option | Approximate Monthly Cost | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Brand-name Propecia | $50 – $150 | Price varies significantly |
| Generic Finasteride | Under $30 | Generally much cheaper |
| Mail-order Pharmacy | Variable | Often offers discounts |
Patient Assistance Programs
Manufacturer programs and independent foundations may offer financial assistance for those who qualify based on income. Research available options to find a suitable program. Contact your doctor or pharmacist for guidance and resources.
Seeking Information
Always consult your physician or pharmacist for personalized advice on medication costs and coverage options available to you. They can provide the most accurate and up-to-date information tailored to your specific situation and insurance plan.
Long-Term Effects and Discontinuation of Propecia
Consult your doctor before stopping Propecia. Sudden cessation may lead to rapid hair loss reversal. Gradual reduction under medical supervision is usually recommended.
Potential Long-Term Effects
While generally safe, long-term Propecia use may be associated with sexual side effects in some men, such as decreased libido or erectile dysfunction. These are usually temporary and resolve upon discontinuation. However, persistent issues warrant immediate medical attention.
Some studies suggest a potential link between long-term finasteride use and prostate cancer, though this remains an area of ongoing research and is not definitively proven. Open communication with your doctor is key to addressing any concerns.
Discontinuation Guidance
Your doctor will personalize a discontinuation plan based on individual factors. This may involve gradually decreasing dosage over several weeks or months. Monitoring hair growth and any side effects is a vital part of this process.
Hair Regrowth After Discontinuation
| Time After Stopping | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|
| Within the first few months | Some individuals may experience minimal hair loss. |
| After 6-12 months | Hair loss may become more noticeable for some. |
| Long term | Hair loss patterns typically revert to the pre-treatment state. Individual results vary greatly. |
Monitoring for Side Effects
Regular check-ups with your doctor are crucial during and after treatment. Report any unusual symptoms immediately. Early detection of potential problems allows for timely intervention and management.
Alternative Treatment Options
Discuss alternative therapies with your doctor if Propecia is unsuitable or ineffective. Several other treatments exist, and your doctor can help determine which approach is best suited to your specific needs.