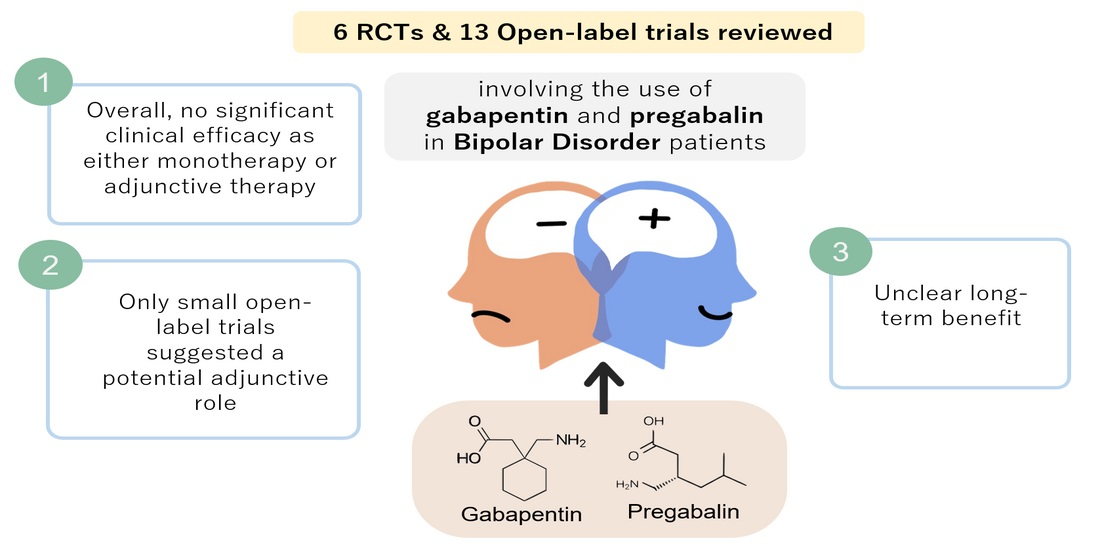
Consider consulting your doctor before using Lyrica to manage bipolar disorder symptoms. While it’s not FDA-approved for this specific purpose, research suggests potential benefits in certain cases, particularly for managing neuropathic pain often associated with bipolar disorder.
Studies show Lyrica may reduce the intensity of nerve pain, a common comorbidity in bipolar disorder. This pain relief can improve sleep quality and overall mood, indirectly benefiting mood stabilization. However, always discuss potential risks and interactions with your prescribing physician, especially given potential side effects like drowsiness and weight gain.
Remember, Lyrica is not a standalone treatment for bipolar disorder. It should be used in conjunction with other proven treatments, such as mood stabilizers or antidepressants, as determined by your psychiatrist. A personalized treatment plan is key; individual responses to medication vary greatly.
Specific considerations: Close monitoring for potential side effects is imperative. Report any unusual changes in mood, behavior, or physical health to your healthcare provider immediately. Regular blood tests may also be recommended to monitor liver function and other potential issues.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of bipolar disorder or any medical condition.
- Lyrica and Bipolar Disorder: A Detailed Overview
- Managing Symptoms with Lyrica
- Potential Side Effects and Interactions
- Lyrica’s Mechanism of Action and Potential Benefits in Bipolar Disorder
- Managing Specific Bipolar Symptoms
- Important Considerations and Further Research
- Lyrica’s Potential Risks and Side Effects in Bipolar Patients
- Cognitive Effects
- Other Potential Risks
- Monitoring and Management
- Lyrica’s Use in Bipolar Disorder: Current Clinical Guidelines and Best Practices
- Important Considerations for Patients Considering Lyrica for Bipolar Disorder
Lyrica and Bipolar Disorder: A Detailed Overview
Lyrica (pregabalin) isn’t FDA-approved to treat bipolar disorder. However, some clinicians prescribe it off-label to manage specific symptoms.
Managing Symptoms with Lyrica
Research suggests Lyrica might help alleviate certain bipolar symptoms, particularly neuropathic pain and anxiety, which frequently co-occur with bipolar disorder. Its effectiveness in this context varies significantly among individuals. Always discuss potential benefits and risks with your doctor before starting Lyrica.
While Lyrica may offer some symptom relief, it does not address the underlying causes of bipolar disorder. It’s crucial to remember that Lyrica is not a substitute for mood stabilizers or other medications typically used to treat bipolar disorder. Using it alongside these other treatments should be guided by a psychiatrist.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions
Lyrica carries potential side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, weight gain, and swelling in the extremities. Furthermore, it can interact with other medications, including some commonly used for bipolar disorder. Thorough monitoring of any potential interactions is required.
Always inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking before starting Lyrica. Open communication with your doctor is paramount for safe and effective treatment.
Careful consideration of potential risks and benefits is vital before using Lyrica to manage symptoms associated with bipolar disorder. This decision should be made in close consultation with your healthcare provider, who can create a personalized treatment plan based on your specific needs and medical history.
Lyrica’s Mechanism of Action and Potential Benefits in Bipolar Disorder
Lyrica, or pregabalin, primarily works by binding to voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system. This reduces the release of neurotransmitters like glutamate and norepinephrine, impacting pain signaling and nerve excitability. In bipolar disorder, this mechanism offers several potential benefits. Reduced glutamate release might help manage mood swings associated with manic episodes, by modulating excessive neuronal activity. Simultaneously, the effects on norepinephrine may help alleviate depressive symptoms.
Managing Specific Bipolar Symptoms
Studies suggest Lyrica may prove helpful in managing certain bipolar symptoms. For instance, some research points to its potential for reducing anxiety and improving sleep, both common challenges for individuals with bipolar disorder. This is especially significant, as sleep disruption often exacerbates mood instability. However, it’s vital to note that Lyrica isn’t a first-line treatment for bipolar disorder and should be used under strict medical supervision.
Important Considerations and Further Research
While promising, existing research on Lyrica’s effectiveness in bipolar disorder is limited. Further, large-scale, well-designed clinical trials are needed to definitively establish its efficacy and identify optimal dosing strategies. Always discuss potential benefits and risks with a qualified psychiatrist before using Lyrica to manage bipolar disorder symptoms. They can assess your individual needs and determine if Lyrica is an appropriate addition to your treatment plan. Furthermore, potential side effects, such as weight gain and dizziness, require careful monitoring.
Lyrica’s Potential Risks and Side Effects in Bipolar Patients
Consult your doctor immediately if you experience significant weight gain, swelling in your ankles or feet, or unusual breathing difficulties. These can be signs of serious side effects. Lyrica, while sometimes used off-label for bipolar disorder symptom management, carries potential risks. Weight gain is a common side effect, often significant, potentially exacerbating existing health problems.
Cognitive Effects
Drowsiness and dizziness are frequently reported. These can impair concentration and coordination, impacting daily life and potentially increasing the risk of accidents. Some patients experience difficulty with memory or thinking clearly. Monitor your cognitive function closely and inform your physician of any concerning changes.
Other Potential Risks
Lyrica can increase the risk of blurred vision. Always prioritize safety and avoid driving or operating machinery if affected. Skin reactions like rash or itching are also possible. Rarely, more severe allergic reactions can occur, necessitating immediate medical attention. Changes in mood or worsening of bipolar symptoms are also possibilities. Open communication with your psychiatrist is crucial for managing these risks.
Monitoring and Management
Regular monitoring of your weight, blood pressure, and overall health is vital. Your doctor will likely adjust your dosage based on your response and any side effects. Do not stop taking Lyrica abruptly without consulting your doctor; this can lead to withdrawal symptoms. Report any new or worsening symptoms promptly to ensure safe and effective management of your treatment.
Lyrica’s Use in Bipolar Disorder: Current Clinical Guidelines and Best Practices
Currently, Lyrica (pregabalin) lacks FDA approval for bipolar disorder treatment. However, some clinicians consider it off-label for managing certain symptoms.
Off-label use often targets neuropathic pain associated with mood episodes, particularly in bipolar II disorder. Research suggests potential benefit in reducing pain and improving sleep, though evidence remains limited.
Clinical guidelines generally do not recommend Lyrica as a first-line treatment for bipolar disorder. Instead, they prioritize mood stabilizers, antipsychotics, and antidepressants, depending on the specific presentation of the illness.
If considering Lyrica off-label, clinicians should carefully weigh potential benefits against risks. Close monitoring for side effects such as dizziness, weight gain, and sedation is vital. Regular assessment of mood symptoms is necessary to determine treatment efficacy.
Always prioritize patient safety and informed consent. Open communication about potential benefits, risks, and alternative treatments is paramount.
Specific dosage and duration should be individualized based on patient response and tolerance. Gradual tapering is recommended when discontinuing Lyrica to minimize withdrawal symptoms.
Collaboration with a psychiatrist specializing in bipolar disorder is strongly advised for appropriate diagnosis and management. They can help develop a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to individual needs.
Important Considerations for Patients Considering Lyrica for Bipolar Disorder
Talk openly with your psychiatrist. They can assess your specific needs and determine if Lyrica is appropriate for you, given your bipolar disorder history and other medications you’re taking.
Understand that Lyrica isn’t a first-line treatment for bipolar disorder. It’s sometimes used to manage certain symptoms, like nerve pain or mood swings, but not the core illness itself. Your doctor will explain its role in your treatment plan.
- Monitor for side effects: Common side effects include dizziness, drowsiness, and weight gain. Report any concerning side effects immediately to your doctor. Less common but serious side effects exist; prompt medical attention is critical.
- Gradual dosage adjustments: Your doctor will likely start you on a low dose and gradually increase it. This minimizes the risk of side effects.
- Potential for interactions: Lyrica can interact with other medications. Provide your doctor with a complete list of everything you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
- Withdrawal symptoms: Stopping Lyrica abruptly can lead to withdrawal symptoms. Always follow your doctor’s instructions when adjusting or stopping the medication.
- Regular monitoring: Your psychiatrist will want to regularly monitor your progress and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
Explore alternative treatments. Many effective treatments for bipolar disorder exist, including mood stabilizers, antidepressants, and antipsychotics. Lyrica might be a supplemental medication, but it shouldn’t replace a comprehensive treatment strategy.
- Discuss your concerns and preferences with your doctor. Active participation in your treatment decisions is key to success.
- Seek support. Joining a support group or talking to a therapist can help you manage the challenges of bipolar disorder.
Remember, managing bipolar disorder is a long-term process that requires ongoing care and attention. Open communication with your healthcare team is crucial for optimal results.