Experiencing a rash after taking Flagyl (metronidazole)? Don’t panic. Rashes are a relatively common side effect, though their severity varies. This information aims to help you understand what to expect and what steps you can take.
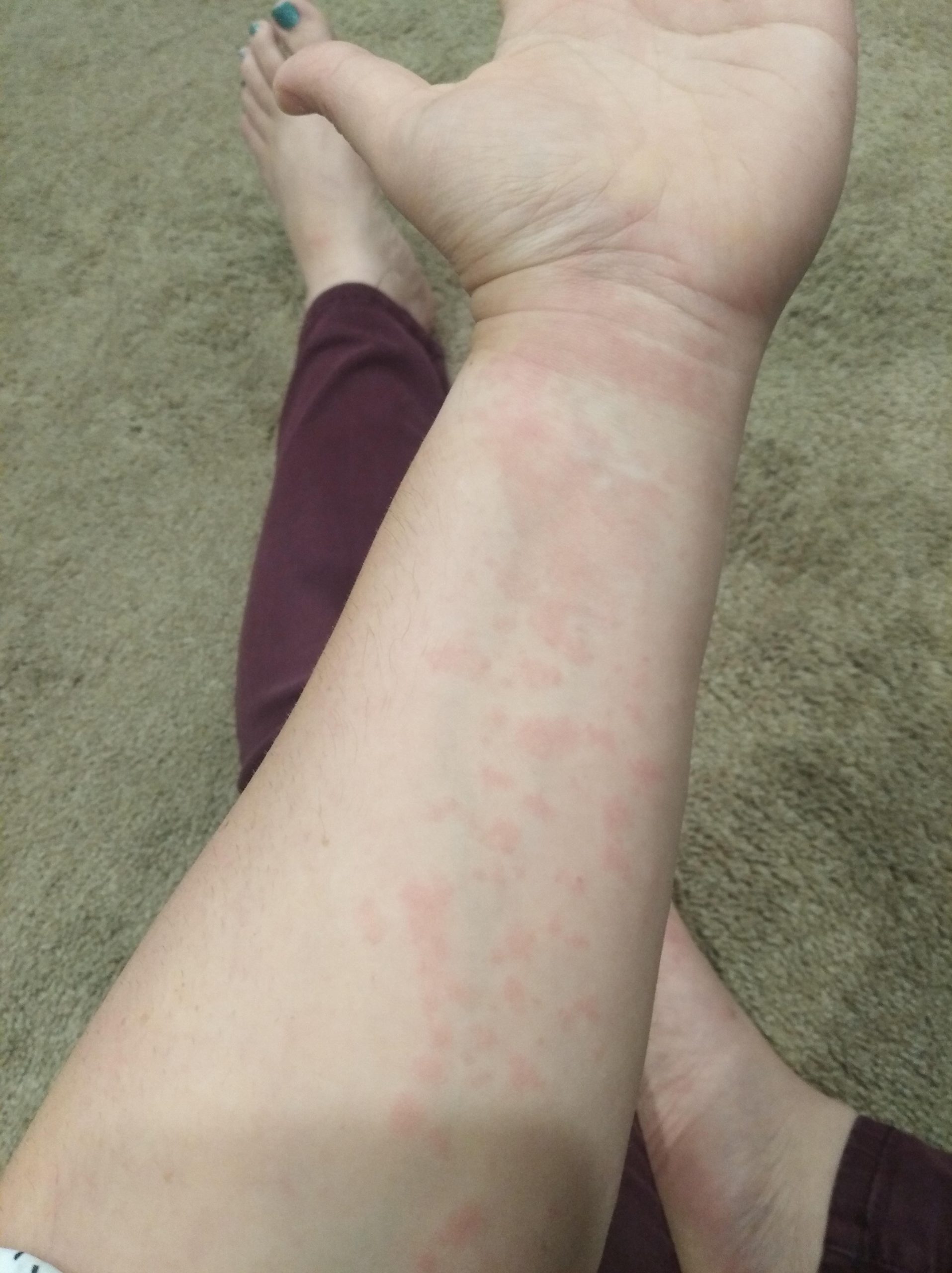
A Flagyl rash usually manifests as a red, itchy, or bumpy skin eruption. It can appear anywhere on your body. Mild rashes often resolve on their own once you stop taking the medication. However, more serious reactions, like Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), are rare but require immediate medical attention. Look for symptoms like widespread blistering, skin peeling, or fever in addition to the rash.
If you develop a rash, contact your doctor or pharmacist immediately. They can assess the severity of your reaction and recommend appropriate management. This might include stopping Flagyl, applying topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and itching, or taking antihistamines to alleviate discomfort. Your doctor will also rule out more serious conditions.
Prevention involves open communication with your healthcare provider. Discuss your medical history and any allergies. They may be able to suggest alternative antibiotics if a rash is a significant concern. Remember, accurate diagnosis and prompt treatment are vital for the best possible outcome.
Disclaimer: This information is for general knowledge and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your doctor before making any decisions about your medication.
- Flagyl Rash: A Detailed Guide
- Identifying a Flagyl Rash: Symptoms and Appearance
- Causes of Flagyl Rash: Understanding the Allergic Reaction
- Treating a Flagyl Rash: Home Remedies and Medical Interventions
- Preventing Flagyl Rash: Minimizing Your Risk
- When to Seek Medical Attention for a Flagyl Rash: Recognizing Serious Reactions
Flagyl Rash: A Detailed Guide
See your doctor immediately if you develop a rash while taking Flagyl (metronidazole). This is a crucial step in managing potential side effects.
Types of Flagyl Rashes: Flagyl can trigger various reactions, from mild redness to more serious, blistering eruptions. Some rashes are localized, appearing only in certain areas, while others are widespread. Photosensitivity, making skin more sensitive to sunlight, is another possible reaction.
Identifying a Flagyl Rash: Pay close attention to new skin changes. Note the location, size, color, and any accompanying symptoms like itching, burning, or swelling. Take photos to show your doctor.
Managing Flagyl Rash: Your doctor will assess the severity and determine the best course of action. This might include stopping Flagyl immediately, applying topical corticosteroids for inflammation, or using oral antihistamines for itching. In severe cases, hospitalization might be necessary.
Prevention: While not always preventable, minimizing sun exposure during Flagyl treatment can help reduce photosensitivity reactions. Inform your doctor about any pre-existing skin conditions.
Alternative Treatments: If a Flagyl rash occurs, your doctor may recommend alternative antibiotics for your infection. They will select an appropriate replacement based on your individual needs and the nature of the infection.
Important Note: This information is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor before starting or stopping any medication.
Identifying a Flagyl Rash: Symptoms and Appearance
A Flagyl rash typically presents as a red, bumpy rash. It often appears on the torso, but can spread to other areas. The rash might be itchy or cause discomfort. Look for small, raised bumps, possibly resembling hives or small blisters.
Severity varies. Some experience only mild redness, while others develop a more intense, widespread rash. Severe reactions can include blistering or swelling.
Note the timing. The rash usually develops within a few days to a few weeks of starting Flagyl treatment. This timeframe helps distinguish it from other skin conditions.
Other symptoms to watch for include fever, swelling in the face or throat, and difficulty breathing. These indicate a more severe allergic reaction and require immediate medical attention.
If you suspect a Flagyl rash, discontinue use and contact your doctor immediately. Early identification is key to appropriate management and prevention of complications.
Causes of Flagyl Rash: Understanding the Allergic Reaction
Metronidazole, the active ingredient in Flagyl, triggers allergic reactions in some individuals. These reactions manifest as skin rashes, varying in severity from mild to severe.
A direct interaction between metronidazole and your immune system causes this allergic response. Your body mistakenly identifies the drug as a harmful substance, initiating a defensive response. This response involves the release of histamine and other inflammatory chemicals, resulting in the characteristic rash symptoms.
Several factors influence the likelihood of a Flagyl rash. Genetic predisposition plays a role; some people are inherently more susceptible to drug allergies. Prior exposure to metronidazole or similar medications also increases the risk. The dosage and duration of treatment are relevant; higher doses and longer treatment periods might heighten the chance of a reaction.
| Factor | Influence on Rash Development |
|---|---|
| Genetic Predisposition | Increased susceptibility to drug allergies. |
| Prior Drug Exposure | Higher risk with previous metronidazole or similar drug use. |
| Dosage and Duration | Higher doses and longer treatments increase risk. |
| Liver Function | Impaired liver function may affect drug metabolism, potentially increasing risk. |
Symptoms range from mild itching and redness to widespread hives, blistering, and even more serious reactions. If you experience any rash, discontinue Flagyl and seek medical attention immediately.
Your doctor can diagnose the rash and recommend appropriate management. Treatment may include antihistamines to relieve itching and corticosteroids to reduce inflammation. In severe cases, hospitalization might be necessary.
Treating a Flagyl Rash: Home Remedies and Medical Interventions
First, stop taking Flagyl immediately and contact your doctor. This is crucial for managing the reaction.
For mild discomfort, try cool compresses. Apply a cool, damp cloth to the rash for 15-20 minutes several times a day. This soothes irritated skin.
Oatmeal baths can also provide relief. Add 1-2 cups of colloidal oatmeal to your bathwater. Soak for 15-20 minutes. The oatmeal’s anti-inflammatory properties can help reduce itching and inflammation.
Avoid harsh soaps and lotions. Use gentle, fragrance-free cleansers. Harsh chemicals can worsen the rash.
Loose-fitting clothing allows for better air circulation, reducing irritation. Opt for breathable fabrics like cotton.
Your doctor might prescribe oral antihistamines like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or cetirizine (Zyrtec) to manage itching. These reduce histamine release, a key player in allergic reactions.
In more severe cases, a topical corticosteroid cream might be necessary. This reduces inflammation directly at the rash site. Always follow your doctor’s instructions for application.
Rarely, hospitalization may be required for severe reactions. This involves intravenous fluids and medications to manage the reaction. This is a last resort for very serious cases.
Remember: This information isn’t a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always seek the advice of a medical professional for any questions about your particular circumstances.
Preventing Flagyl Rash: Minimizing Your Risk
Stay hydrated. Drinking plenty of water helps your body flush out medications and reduce the likelihood of a reaction.
Follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Take Flagyl exactly as prescribed – dosage, frequency, and duration are all crucial. Don’t adjust your medication without consulting your physician.
Inform your doctor about allergies and medical history. Mention any prior allergic reactions, especially to antibiotics. A complete medical history allows your doctor to make an informed decision about your treatment.
Monitor yourself for early signs. Be aware of potential symptoms like itching, redness, or swelling. Report any unusual skin changes immediately to your doctor. Early intervention is key.
Consider alternative medications if necessary. If you’ve experienced a Flagyl rash in the past, discuss alternative antibiotic options with your healthcare provider. They can prescribe a different medication with a lower risk of allergic reactions.
Use gentle skin care products. Avoid harsh soaps, lotions, or perfumes that could irritate your skin during treatment. Choose fragrance-free and hypoallergenic products.
Disclaimer: This information is for general knowledge and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.
When to Seek Medical Attention for a Flagyl Rash: Recognizing Serious Reactions
Seek immediate medical attention if your Flagyl rash involves:
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing. This suggests a severe allergic reaction requiring emergency care.
- Swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat. These are hallmark signs of a life-threatening allergic reaction (angioedema).
- Widespread rash covering a large portion of your body. Extensive rash indicates a serious reaction that needs prompt assessment and treatment.
- Blistering or peeling skin. These could signal Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) or toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), extremely serious conditions requiring hospitalization.
- Fever and chills. Combined with a rash, this often suggests a more serious infection or adverse reaction.
- Severe itching or pain. Intolerable discomfort warrants medical evaluation for appropriate management.
Less severe rashes might still need attention. Contact your doctor if you experience:
- A rash that doesn’t improve within a few days of stopping Flagyl.
- A rash accompanied by persistent nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
- A rash that spreads rapidly across your body.
- Any concerning changes in the appearance of your rash (e.g., increased redness, swelling, blistering).
Your doctor can determine the severity of your reaction and recommend the best course of action. Don’t hesitate to seek medical help if you’re unsure whether your rash is serious.