Yes, Clomid can delay your period. This isn’t uncommon and often reflects the medication working as intended by stimulating ovulation. However, a significantly late period warrants a call to your doctor.
Clomid’s mechanism involves triggering the release of eggs, and this process can disrupt your regular cycle. Expect some variation in your cycle length after taking Clomid. A delay of a few days might be normal, but a delay exceeding a week requires medical attention.
Consider these points: The timing of your ovulation will directly influence when your period arrives. Clomid might cause ovulation later than usual, leading to a late period. Always discuss any significant changes in your cycle with your healthcare provider. They can assess your individual situation and determine the cause of the delay.
Don’t self-diagnose. While a late period can be a side effect of Clomid, other factors could be at play. Schedule an appointment with your doctor if your period is considerably late to rule out other possibilities and ensure your well-being.
- Can Clomid Cause a Late Period?
- Understanding Clomid’s Impact on Your Cycle
- When to Contact Your Doctor
- Managing Expectations
- Possible Causes of Delayed Periods Beyond Clomid
- Understanding Clomid’s Mechanism and Potential Period Delays
- Common Reasons for Late Periods While Taking Clomid
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
- Clomid Dosage and Response
- Underlying Fertility Issues
- Pregnancy
- When to Seek Medical Advice for a Late Period During Clomid Treatment
- Signs Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
- When to Schedule a Follow-up Appointment
- Understanding Potential Causes of Late Periods
Can Clomid Cause a Late Period?
Yes, Clomid can delay your period. This isn’t necessarily a cause for alarm, as it often indicates the medication is working. Clomid stimulates ovulation, and a delayed period frequently signals successful ovulation. However, a significantly late period warrants a doctor’s visit.
Understanding Clomid’s Impact on Your Cycle
Clomid alters hormone levels to encourage egg release. This hormonal shift can affect your menstrual cycle, sometimes causing a delay. The timing of your period after Clomid use depends on several factors, including your individual response to the medication and the dosage prescribed.
When to Contact Your Doctor
While a slightly late period is common with Clomid, a delay exceeding two weeks after your expected period requires medical attention. Additionally, contact your doctor if you experience any unusual symptoms alongside the delayed period, such as severe pelvic pain, significant bleeding or spotting, or other concerning side effects. Your doctor can help determine the cause of the delay and offer the best course of action.
Managing Expectations
Remember, Clomid is a powerful medication and should be taken under strict medical supervision. Open communication with your physician regarding your cycle and any unusual symptoms is paramount for ensuring successful treatment and managing potential side effects.
Possible Causes of Delayed Periods Beyond Clomid
Stress and weight changes can also influence your menstrual cycle. Your doctor can help differentiate between these factors and Clomid’s effects.
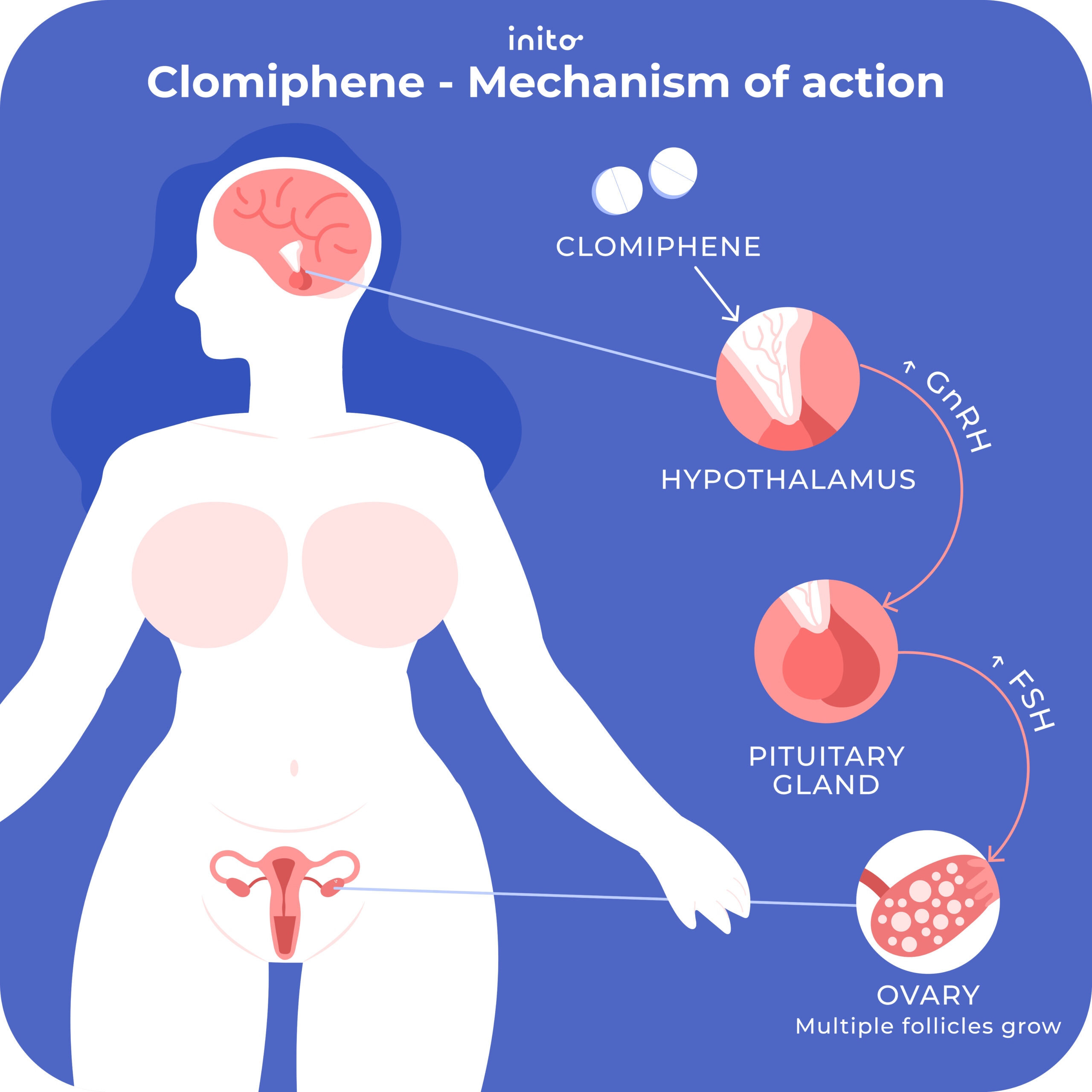
Understanding Clomid’s Mechanism and Potential Period Delays
Clomid, or clomiphene citrate, stimulates your pituitary gland to release more follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). These hormones encourage your ovaries to produce more eggs, increasing your chances of conception. However, this hormonal surge can sometimes disrupt your regular menstrual cycle, causing a late period.
A delayed period after Clomid treatment is a common side effect. The timing of ovulation varies, and a slightly delayed period isn’t always cause for concern. However, a significantly late period (more than a week beyond your expected cycle) warrants contacting your doctor.
Several factors contribute to period irregularities while taking Clomid. The increased hormone levels directly influence the timing of your cycle. Additionally, successful ovulation doesn’t guarantee a timely period; implantation and hormonal changes following conception also play a role. A late period might signal pregnancy, but it’s equally possible it’s simply a side effect of the medication.
Your doctor will consider your specific circumstances, including the dosage of Clomid, your overall health, and your cycle history when evaluating a late period. They will likely perform tests, such as a pregnancy test and blood work, to determine the cause and recommend the appropriate next steps. Open communication with your doctor is key throughout your treatment.
Remember, this information is for educational purposes only and doesn’t substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Common Reasons for Late Periods While Taking Clomid
A late period while on Clomid doesn’t automatically signal a problem. Several factors can contribute to this. Successful ovulation, the primary goal of Clomid, sometimes delays your period by a few days. This is because the timing of ovulation and subsequent menstruation varies naturally. Expect your period to arrive anywhere from 12 to 16 days after ovulation.
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
OHSS is a more serious complication, causing the ovaries to swell. Mild OHSS might only cause a slight delay, while severe cases require medical attention. Symptoms include bloating, abdominal pain, and nausea. If you experience these, contact your doctor immediately.
Clomid Dosage and Response
Your body’s response to Clomid is unique. Higher doses or a particularly sensitive response can affect your cycle length. Your doctor carefully monitors your progress and adjusts your dosage accordingly. Discuss any concerns about your cycle regularity with them.
Underlying Fertility Issues
Clomid addresses certain fertility problems, but other conditions can interfere with regular menstruation. Conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid problems can influence your cycle, even with Clomid treatment. Your doctor considers these factors when developing a treatment plan.
Pregnancy
A late period is often a very early sign of pregnancy. Clomid aims to increase chances of conception. Take a pregnancy test if your period is significantly late, especially if you’ve experienced other pregnancy symptoms.
When to Seek Medical Advice for a Late Period During Clomid Treatment
Contact your doctor immediately if your period is more than 7 days late after completing your Clomid cycle. This is especially important if you experienced any unusual symptoms during treatment.
Signs Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
- Severe pelvic pain
- Significant abdominal bloating or distension
- Fever or chills
- Vaginal bleeding outside of your expected period, especially heavy bleeding
- Severe nausea or vomiting
- Shortness of breath
These symptoms could indicate potential complications requiring prompt medical intervention.
When to Schedule a Follow-up Appointment
- If your period is 5-7 days late, schedule a consultation to discuss your situation and potential next steps.
- If you experience mild symptoms like breast tenderness or mood swings, monitoring is often sufficient, but let your doctor know.
- Always inform your doctor of any medication changes or other relevant health updates during your Clomid treatment.
Open communication with your doctor is key for successful Clomid treatment and managing potential complications. Don’t hesitate to reach out with any concerns, even minor ones. Early detection and intervention can improve outcomes.
Understanding Potential Causes of Late Periods
A late period during Clomid treatment can result from several factors, including successful ovulation (leading to pregnancy), ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), or simply a hormonal imbalance. Your doctor can perform tests to determine the cause and recommend appropriate management.