Yes, doxycycline hyclate is a common and effective treatment for chlamydia. A typical course involves taking 100mg twice daily for seven days. This antibiotic directly targets the bacteria responsible for the infection.
However, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment. Self-treating can be dangerous; a doctor will perform tests to confirm chlamydia and rule out other conditions. They can also discuss potential side effects and ensure the medication is appropriate for your individual health situation.
Doxycycline hyclate is generally well-tolerated, but some common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Rarely, more serious side effects may occur. Always report any adverse reactions to your doctor immediately. Following your doctor’s instructions meticulously is key for successful treatment and preventing complications. Complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if you start feeling better before the seven days are up, to fully eliminate the infection.
Remember, untreated chlamydia can lead to serious health problems, including pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women and infertility in both men and women. Prompt treatment is vital for preventing long-term consequences.
- Can Doxycycline Hyclate Treat Chlamydia?
- Dosage and Treatment Duration
- Potential Side Effects
- Alternatives and Considerations
- Important Note:
- Doxycycline Hyclate: A Common Treatment for Chlamydia
- Important Considerations Before Starting Treatment
- Potential Side Effects
- Alternative Treatments and Considerations for Chlamydia
- Seeking Medical Attention for Chlamydia Infection
- Finding a Doctor
- What to Expect
- After Treatment
- Protecting Your Health
- Additional Resources
Can Doxycycline Hyclate Treat Chlamydia?
Yes, doxycycline hyclate is a common and highly effective treatment for chlamydia infections. It’s a broad-spectrum antibiotic that targets the bacteria responsible for this sexually transmitted infection.
Dosage and Treatment Duration
Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage and treatment duration, typically 7 days of once- or twice-daily doses. Precise instructions are crucial for successful eradication of the infection. Failure to complete the full course of medication may lead to reinfection or antibiotic resistance.
Potential Side Effects
While generally well-tolerated, doxycycline hyclate can cause side effects. Common ones include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and heartburn. More serious, though rarer, side effects include increased sensitivity to sunlight and yeast infections. Report any concerning symptoms to your healthcare provider immediately.
Alternatives and Considerations
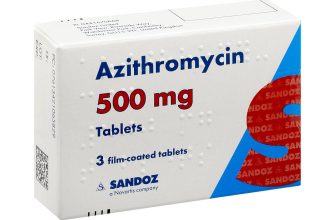
Azithromycin is another antibiotic used to treat chlamydia. Your doctor will consider your medical history and potential drug interactions when choosing the most suitable option. Always discuss your treatment options thoroughly with your doctor before starting any medication. They can assess your individual needs and ensure you receive appropriate care. Regular testing and safe sexual practices remain vital in preventing chlamydia reinfection.
Important Note:
Doxycycline hyclate is a prescription medication. Self-treating can be dangerous and may delay proper diagnosis and treatment of other potential health issues. Seek professional medical advice for chlamydia and other STIs.
Doxycycline Hyclate: A Common Treatment for Chlamydia
Yes, doxycycline hyclate is a frequently prescribed antibiotic for chlamydia infections. Doctors typically recommend a 7-day course of treatment, taking one 100mg capsule twice daily. Complete the full course, even if symptoms disappear sooner; this prevents reinfection and ensures complete eradication of the bacteria.
Important Considerations Before Starting Treatment
Before beginning doxycycline hyclate, inform your doctor about any existing medical conditions, particularly pregnancy, breastfeeding, or allergies to tetracyclines. Doxycycline may interact with certain medications, such as antacids or anticoagulants. Your doctor will assess potential drug interactions and adjust your treatment plan accordingly. Certain contraindications exist, so open communication with your healthcare provider is key.
Potential Side Effects
While generally well-tolerated, doxycycline hyclate can cause side effects. These may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and photosensitivity (increased sun sensitivity). Less common side effects include yeast infections and esophageal irritation. Contact your doctor immediately if you experience severe side effects.
Alternative Treatments and Considerations for Chlamydia
Azithromycin is another effective antibiotic commonly used to treat chlamydia. It’s a single-dose treatment, offering convenience compared to doxycycline’s longer course.
Choosing the right antibiotic depends on several factors. Your doctor will consider:
- Your overall health.
- Any potential drug interactions with other medications you take.
- Pregnancy or breastfeeding status – certain antibiotics are safer than others during these times.
- Severity of the infection.
Treatment for chlamydia must be completed as directed, even if you feel better before finishing the course. Stopping early can lead to antibiotic resistance and treatment failure.
Retesting after treatment is crucial to confirm successful eradication. Your healthcare provider will schedule a follow-up appointment for testing, usually a few weeks after completing the antibiotic course.
Sexual partners should also be tested and treated simultaneously to prevent re-infection. Open communication with partners is vital for successful treatment and preventing the spread of infection.
Untreated chlamydia can lead to serious complications, including pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women and epididymitis in men. Both can lead to infertility. Early detection and treatment are critical to avoid these complications.
- Contact your doctor immediately if you experience symptoms of chlamydia or suspect infection.
- Practice safe sex, including consistent condom use, to reduce your risk of contracting sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- Regular STI screenings are recommended, especially if you are sexually active.
Seeking Medical Attention for Chlamydia Infection
See a doctor immediately if you suspect a chlamydia infection. Early diagnosis is key to preventing complications.
Finding a Doctor
Your primary care physician is a good starting point. Many clinics offer rapid testing and treatment, often without an appointment. You can also search online for sexually transmitted infection (STI) clinics in your area. Some pharmacies provide testing services; check their websites or call to confirm.
What to Expect
Your doctor will likely ask about your symptoms, sexual history, and risk factors. Testing usually involves a urine sample or a swab from the cervix or urethra. Depending on the clinic, you may receive your results the same day or within a few days. Treatment usually involves a course of antibiotics like doxycycline, prescribed by your healthcare provider.
After Treatment
Complete your entire course of antibiotics, even if symptoms disappear. Inform your sexual partners so they can also get tested and treated. Follow-up testing is recommended to confirm successful treatment. Practice safe sex to prevent future infections.
Protecting Your Health
Regular STI screenings are crucial for maintaining sexual health. Open communication with your partner(s) about sexual health and safe sex practices is vital. Remember, chlamydia is treatable, and early intervention ensures better outcomes.
Additional Resources
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) website offers comprehensive information on chlamydia and other STIs. Your local health department can also provide valuable resources and support.