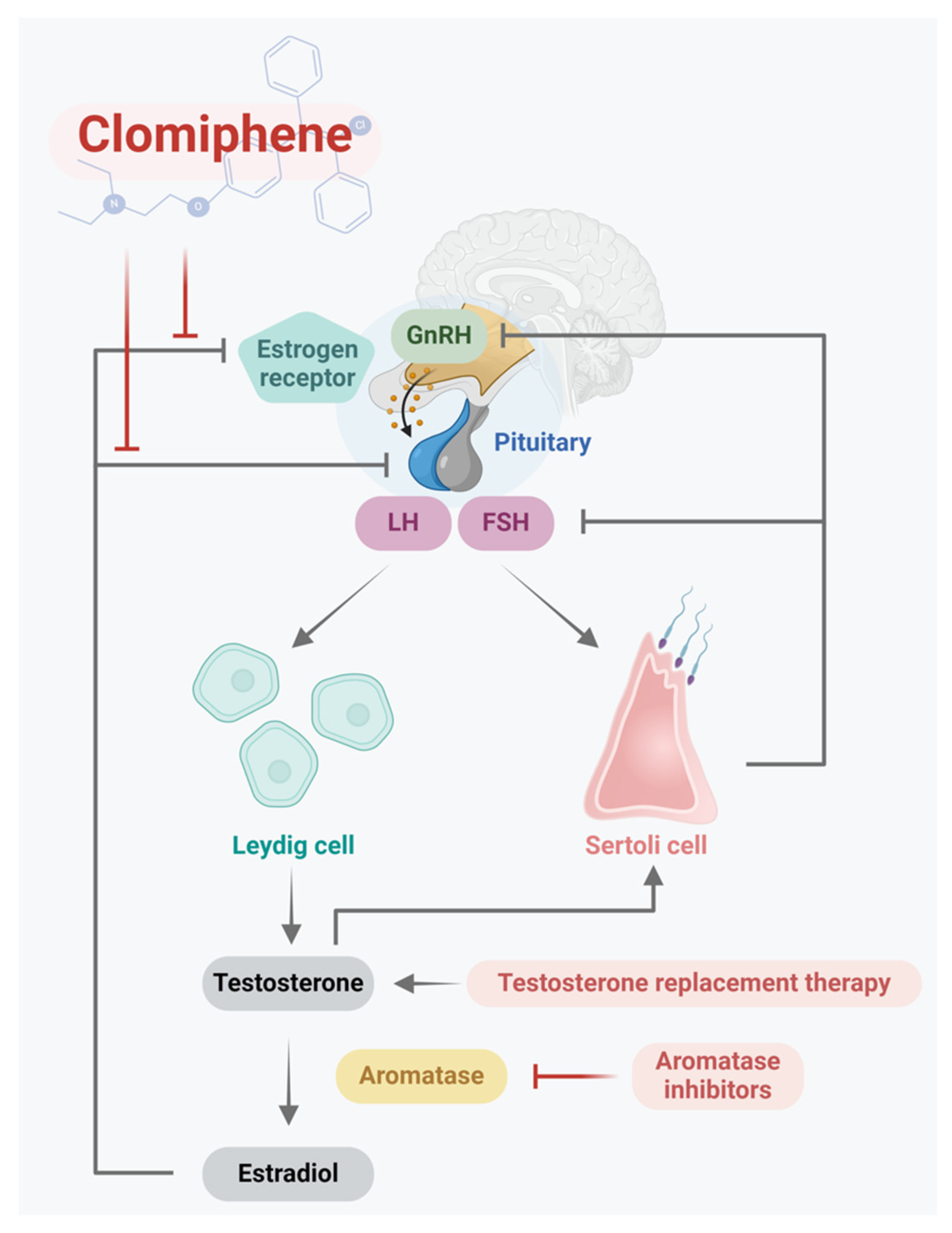
Consider combining Clomid and anastrozole for improved fertility outcomes in men with hypogonadism. This approach targets different aspects of hormonal regulation, potentially enhancing testosterone production while mitigating potential estrogen-related side effects. Specifically, Clomid stimulates the pituitary gland to produce more gonadotropins, which in turn increase testosterone. Anastrozole, an aromatase inhibitor, reduces the conversion of testosterone to estrogen. This dual action can lead to a more balanced hormonal profile.
Remember that individualized dosing is crucial. Typical Clomid dosages range from 25mg to 150mg daily, adjusted based on individual response and hormone levels. Anastrozole is usually prescribed at a lower dose, often starting at 0.5mg per day, to manage estrogen levels without suppressing testosterone production excessively. Frequent blood tests monitor testosterone, estrogen, and luteinizing hormone (LH) levels to ensure optimal treatment.
Potential side effects, while generally manageable, should be discussed with your physician. Clomid can cause visual disturbances, hot flashes, and mood changes. Anastrozole may lead to reduced bone density in long-term use. Open communication with your doctor throughout the treatment is paramount for addressing any concerns and optimizing your therapeutic approach. Regular monitoring allows for timely adjustments to dosage or treatment strategy.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional before starting any medication, including Clomid and anastrozole, to discuss your individual needs and potential risks.
- Clomid and Anastrozole for Men: A Detailed Guide
- Understanding Clomid (Clomiphene Citrate)
- Understanding Anastrozole
- Combined Therapy: Clomid and Anastrozole
- Potential Side Effects and Monitoring
- Important Considerations
- Alternative Treatment Options
- Understanding Clomid’s Role in Male Fertility
- Factors Influencing Clomid’s Efficacy
- Anastrozole: Managing Estrogen Levels in Men on Clomid
- Potential Side Effects and Risks of Combined Clomid and Anastrozole Therapy
- Gynecomastia and Other Concerns
- Specific Recommendations
- Who is a Suitable Candidate for This Combined Therapy?
- Navigating Treatment: Consultation and Monitoring
Clomid and Anastrozole for Men: A Detailed Guide
Consult your doctor before starting any medication, especially Clomid and Anastrozole. They will assess your individual needs and determine the appropriate dosage and monitoring schedule.
Understanding Clomid (Clomiphene Citrate)
Clomid stimulates the pituitary gland to release more follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). Increased LH is key for testosterone production. Common side effects include hot flashes, visual disturbances, and mood changes. Dosage typically ranges from 25mg to 150mg daily, adjusted based on response and bloodwork. Expect to have regular blood tests to monitor your hormone levels.
Understanding Anastrozole
Anastrozole is an aromatase inhibitor. It reduces estrogen conversion from testosterone, leading to potentially higher free testosterone levels. It’s often used in conjunction with Clomid to manage estrogen side effects, such as gynecomastia (breast enlargement). Common side effects include joint pain and decreased libido. Typical dosages range from 0.5mg to 1mg daily, again, adjusted based on individual response and blood tests.
Combined Therapy: Clomid and Anastrozole
Combining Clomid and Anastrozole can be beneficial for men with low testosterone, particularly those experiencing estrogen-related side effects from Clomid alone. Anastrozole helps keep estrogen in check while Clomid boosts testosterone production. However, this combination requires careful monitoring by your doctor.
Potential Side Effects and Monitoring
| Medication | Common Side Effects | Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Clomid | Hot flashes, visual disturbances, mood changes | Testosterone, LH, FSH levels |
| Anastrozole | Joint pain, decreased libido | Estrogen, testosterone levels |
Regular blood tests are crucial to assess your hormone levels and adjust your dosage accordingly. Your doctor will likely monitor your progress through blood tests and physical examinations. Immediately report any concerning side effects to your healthcare provider.
Important Considerations
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Individual responses to Clomid and Anastrozole vary. Never self-medicate. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional to determine the suitability and safety of these medications for your specific situation.
Alternative Treatment Options
Discuss alternative therapies like lifestyle changes (diet, exercise) or other medications with your doctor if this treatment isn’t suitable for you. There might be different approaches to manage your condition.
Understanding Clomid’s Role in Male Fertility
Clomid (clomiphene citrate) increases testosterone production by stimulating the pituitary gland to release more follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). This heightened hormonal activity encourages the testes to produce more sperm. Expect to see improved sperm count, motility, and morphology – all crucial aspects of male fertility. However, Clomid isn’t a guaranteed solution; its effectiveness varies significantly among individuals.
Factors Influencing Clomid’s Efficacy
Response to Clomid depends heavily on the underlying cause of infertility. For men with low testosterone due to hypothalamic-pituitary issues, Clomid often proves beneficial. Conversely, men with primary testicular failure may see limited improvement. Additionally, the prescribed dosage and duration of treatment directly influence outcomes. Your physician will personalize your treatment plan based on your specific needs and test results. Regular monitoring of hormone levels and semen analysis are necessary to assess treatment effectiveness and adjust the regimen accordingly.
Remember, Clomid carries potential side effects, including visual disturbances, hot flashes, and mood swings. Open communication with your doctor about these side effects is key to managing them and ensuring a safe and effective treatment experience. They can help you weigh the potential benefits against the risks before proceeding with Clomid therapy.
Anastrozole: Managing Estrogen Levels in Men on Clomid
Anastrozole, an aromatase inhibitor, directly reduces estrogen production. This is particularly helpful for men using Clomid, a fertility drug that can sometimes increase estrogen levels, leading to side effects like gynecomastia (breast enlargement) or reduced libido.
Doctors often prescribe anastrozole alongside Clomid to maintain estrogen within a healthy range. The dosage of anastrozole is individualized and depends on factors like your age, overall health, and response to Clomid. Typical dosages range from 0.5mg to 1mg daily, often taken every other day or even less frequently.
Close monitoring of estrogen levels through blood tests is critical. Regular checkups allow your doctor to adjust the anastrozole dosage accordingly, preventing both excessively high and low estrogen levels. This approach ensures you receive the benefits of Clomid while minimizing potential side effects.
Common side effects of anastrozole include joint pain and decreased bone density. Open communication with your physician is key to managing these potential issues. They can help determine if the benefits of managing estrogen outweigh these risks. Consider discussing lifestyle adjustments, such as weight-bearing exercise, to support bone health.
Remember, anastrozole should only be used under the direct supervision of a physician. Self-medicating with anastrozole or Clomid is dangerous and can have severe consequences. Always discuss potential benefits and risks before starting any medication.
Potential Side Effects and Risks of Combined Clomid and Anastrozole Therapy
Combining Clomid and Anastrozole carries potential side effects, demanding careful monitoring. Clomid, primarily, can cause visual disturbances like blurred vision or light sensitivity. Headaches and hot flashes are also common. More seriously, it might increase the risk of blood clots. Remember to report any unusual symptoms immediately.
Gynecomastia and Other Concerns
Anastrozole, designed to lower estrogen, can sometimes lead to reduced libido and decreased bone density. A significant concern is gynecomastia (breast enlargement) – a side effect experienced by some men. Both medications can affect liver function, so regular blood tests are recommended to monitor liver enzymes. Furthermore, this combination therapy may influence cholesterol levels. Your doctor should carefully assess your risk profile before prescribing this treatment.
Specific Recommendations
Before starting combined Clomid and Anastrozole therapy, discuss potential risks and benefits thoroughly with your doctor. Regular check-ups are vital for monitoring your progress and detecting any potential complications early. Open communication with your healthcare provider is key to ensuring your safety and well-being throughout the treatment.
Who is a Suitable Candidate for This Combined Therapy?
Men with low testosterone levels (hypogonadism) unresponsive to Clomid alone are often good candidates. This combination is particularly beneficial for those experiencing:
- High estrogen levels alongside low testosterone.
- Failure to respond adequately to Clomid monotherapy.
- Infertility issues related to low testosterone and/or high estrogen.
However, this therapy isn’t suitable for everyone. Consider these factors:
- Liver function: Both Clomid and Anastrozole can affect liver health. Individuals with pre-existing liver conditions should avoid this combination.
- Cardiovascular health: Anastrozole can impact cholesterol levels; men with cardiovascular disease should discuss this therapy with their doctor carefully.
- Existing medical conditions: Certain other health problems may interact negatively with these medications. Full disclosure of your medical history is crucial.
- Drug interactions: These medications can interact with other drugs you are taking. Inform your physician about all medications and supplements you use.
- Age and general health: Older men or those with significant health challenges may have a higher risk of side effects.
Before starting this therapy, a thorough medical evaluation, including blood tests to assess hormone levels and liver function, is necessary. Your doctor will determine if this approach is safe and appropriate for your individual circumstances and will closely monitor your progress during treatment.
Navigating Treatment: Consultation and Monitoring
Schedule a consultation with a reproductive endocrinologist or urologist experienced in male infertility. Discuss your medical history, including any pre-existing conditions. They will perform a physical exam and order necessary blood tests, including hormone levels (testosterone, FSH, LH, estradiol) and semen analysis.
Expect regular monitoring throughout treatment. Blood tests will track your hormone levels, ensuring the Clomid and anastrozole dosages remain appropriate and safe. Frequent semen analyses will assess sperm count, motility, and morphology, providing insights into treatment efficacy. Your doctor might adjust medication based on these results.
Open communication with your physician is paramount. Report any side effects immediately, such as headaches, visual disturbances, or hot flashes. Discuss your concerns and questions freely. Active participation in your treatment plan maximizes its success.
Understand that treatment response varies. Some men respond well within a few cycles; others may require adjustments or a longer treatment duration. Patience and consistent adherence to the prescribed regimen are key. Remain proactive in your communication to achieve the best possible outcome.
Following treatment, continue scheduled follow-up appointments to monitor your hormone levels and semen analysis. This post-treatment monitoring helps ensure long-term health and assesses the long-term effects of the medication.