Sildenafil citrate is the active ingredient in Viagra, a medication primarily used to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) in men. It achieves this by increasing blood flow to the penis, facilitating an erection.
This effect stems from its action as a phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitor. PDE5 enzymes normally break down cyclic GMP, a molecule crucial for penile erection. By inhibiting PDE5, sildenafil allows cyclic GMP to persist, leading to vasodilation and improved blood flow.
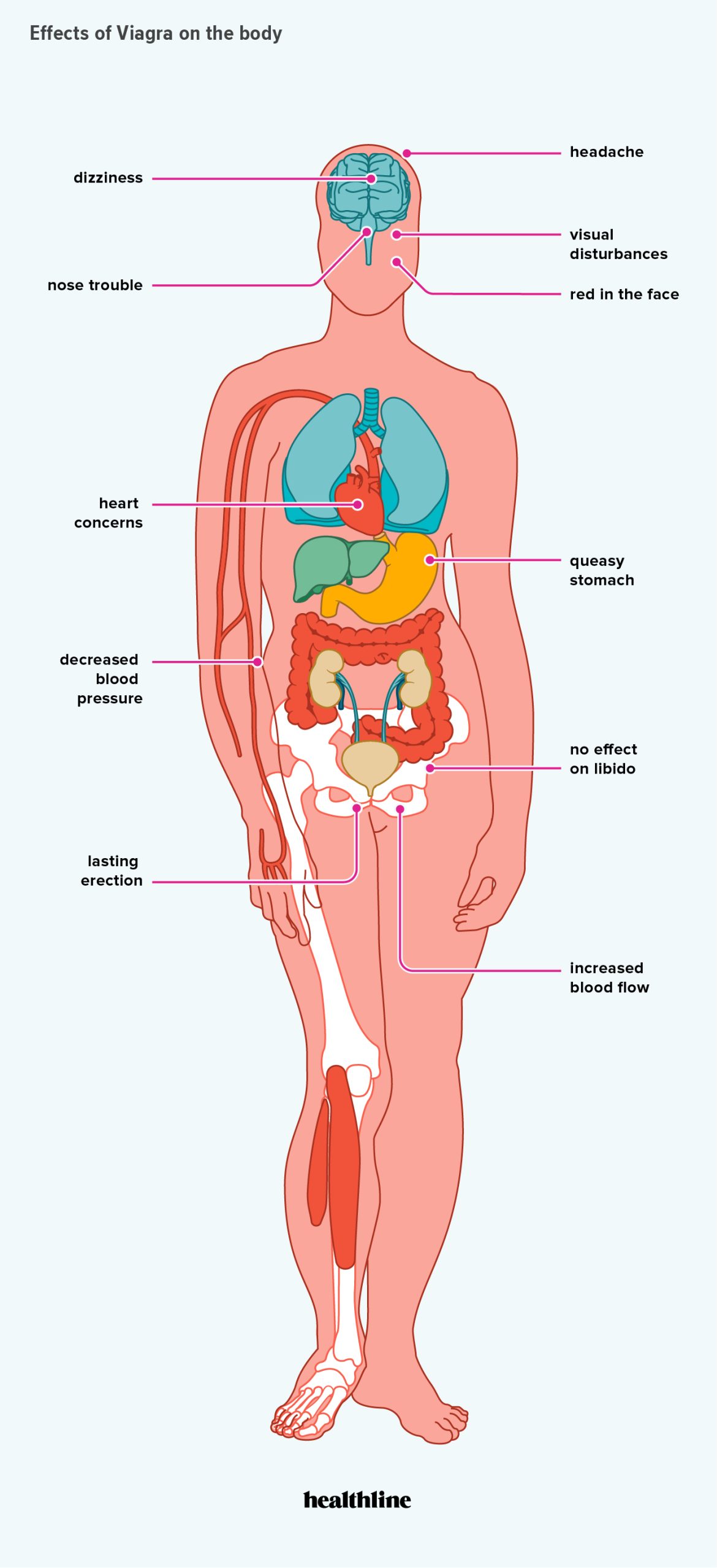
Important Note: Sildenafil is a prescription medication. Consult your doctor before use, as it’s not suitable for everyone. Potential side effects include headache, flushing, nasal congestion, and visual disturbances. The medication interacts with certain other drugs, so be transparent with your doctor about your complete medical history.
Beyond ED, sildenafil also finds application in treating pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), a condition marked by high blood pressure in the arteries leading to the lungs. Its mechanism of action in PAH is similar to its effect on erectile function: it promotes vasodilation and improves blood flow.
- Define Sildenafil Citrate
- Mechanism of Action
- Uses and Considerations
- Dosage Information
- Other Medications Containing Sildenafil Citrate
- What is Sildenafil Citrate?
- How Sildenafil Citrate Works
- Beyond Erectile Dysfunction
- How Sildenafil Citrate Works
- Medical Uses of Sildenafil Citrate
- Erectile Dysfunction Treatment
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Treatment
- Other Uses
- Important Note:
- Side Effects and Precautions
- Common Side Effects
- Less Common, but Still Important Side Effects
- Precautions
- Sildenafil Citrate: Dosage and Administration
- Adjusting the Dosage
- Important Considerations
Define Sildenafil Citrate
Sildenafil citrate is the active ingredient in Viagra and several other medications. It’s a phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitor. This means it works by increasing blood flow to the penis, facilitating an erection.
Mechanism of Action
Sildenafil citrate blocks PDE5, an enzyme that breaks down cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). Higher cGMP levels relax the smooth muscles in the blood vessels of the penis, leading to increased blood flow and, consequently, an erection. This action requires sexual stimulation to trigger the process.
Uses and Considerations
Primarily used to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) in men, sildenafil citrate also treats pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). However, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional before using sildenafil citrate. It’s not suitable for everyone, and potential side effects include headache, flushing, nasal congestion, and visual disturbances. People with certain heart conditions, low blood pressure, or taking specific medications should avoid it.
Dosage Information
| Condition | Typical Starting Dose | Maximum Dose |
|---|---|---|
| Erectile Dysfunction | 50 mg | 100 mg |
| Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension | 20 mg three times daily | 80 mg three times daily |
Note: Dosage adjustments are frequently needed based on individual responses and potential side effects. Always follow your doctor’s instructions.
Other Medications Containing Sildenafil Citrate
Several generic versions of sildenafil citrate exist. These are available under various brand names and should be obtained only with a doctor’s prescription.
What is Sildenafil Citrate?
Sildenafil citrate is the active ingredient in Viagra, a medication primarily used to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) in men. It works by increasing blood flow to the penis, facilitating an erection in response to sexual stimulation. This happens because sildenafil inhibits a specific enzyme, phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5), which regulates blood vessel dilation.
How Sildenafil Citrate Works
PDE5’s inhibition allows for higher levels of cyclic GMP, a molecule crucial for smooth muscle relaxation in the penis. This relaxation allows increased blood flow, leading to penile engorgement and erection. Importantly, sildenafil only works with sexual stimulation; it doesn’t cause spontaneous erections.
Beyond Erectile Dysfunction
Note: While primarily known for treating ED, sildenafil citrate also finds application in treating pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), a condition causing high blood pressure in the arteries leading to the lungs. In PAH, sildenafil’s vasodilatory properties improve blood flow to the lungs. Always consult a doctor before using sildenafil, regardless of the intended use. Dosage and potential side effects vary based on the condition being treated and individual health factors.
How Sildenafil Citrate Works
Sildenafil citrate targets a specific enzyme called phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5). PDE5 breaks down a crucial messenger molecule called cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP).
By inhibiting PDE5, sildenafil allows cGMP levels to rise. Increased cGMP relaxes the muscles in the blood vessels of the penis, increasing blood flow.
This increased blood flow is responsible for achieving and maintaining an erection. Importantly, sexual stimulation is still required; sildenafil doesn’t cause erections on its own.
The drug’s effects typically last for 4-5 hours. Dosage and individual factors influence the duration and intensity of the effects. Consult your doctor to find the right dose for you.
Note: Sildenafil citrate requires a prescription. Always follow your doctor’s instructions and discuss any potential side effects or drug interactions.
In short: Sildenafil citrate enhances the effects of sexual stimulation by increasing blood flow to the penis via PDE5 inhibition.
Medical Uses of Sildenafil Citrate
Sildenafil citrate, primarily known by the brand name Viagra, treats erectile dysfunction (ED) by increasing blood flow to the penis. This allows for firmer, easier erections.
Erectile Dysfunction Treatment
Doctors prescribe sildenafil for men experiencing difficulties achieving or maintaining an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual intercourse. It’s crucial to consult a physician before use, as underlying health conditions may influence treatment.
- Dosage varies depending on individual needs and response.
- It’s not suitable for all men, particularly those with certain heart conditions.
- Side effects, though generally mild, include headaches, flushing, and nasal congestion.
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Treatment
Beyond ED, sildenafil also treats pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). PAH involves abnormally high blood pressure in the arteries leading to the lungs. Sildenafil helps relax and widen these blood vessels, improving blood flow and reducing strain on the heart.
Other Uses
- Raynaud’s phenomenon: Sildenafil can improve blood flow to fingers and toes affected by this condition, reducing pain and discomfort.
- Exercise-induced hypoxia: Some studies suggest it may help improve exercise tolerance in individuals with certain lung conditions.
Important Note:
Always seek professional medical advice before using sildenafil citrate, regardless of intended use. A doctor can assess your health status, determine appropriate dosage, and address any potential interactions with other medications. Self-medication is discouraged.
Side Effects and Precautions
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience chest pain, irregular heartbeat, or sudden vision loss. These are serious side effects requiring prompt medical intervention.
Common Side Effects
Many experience mild side effects like headaches, facial flushing, nasal congestion, and indigestion. These usually subside within a few hours. Drink plenty of water to help alleviate some of these symptoms. If they persist or worsen, consult your doctor.
Less Common, but Still Important Side Effects
Less frequently reported side effects include dizziness, muscle aches, back pain, and visual disturbances (besides sudden vision loss). If you notice any unusual changes in your vision, hearing, or sensitivity to light, contact your doctor immediately. Be aware that prolonged or high-dose use can increase the likelihood of these.
Note: This medication can interact with other drugs, particularly nitrates. Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to avoid potentially dangerous interactions.
Precautions
Avoid alcohol consumption while taking sildenafil citrate, as it can increase the risk of side effects. Refrain from driving or operating machinery if you feel dizzy or lightheaded. If you have a history of heart disease, high blood pressure, or stroke, discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor before using sildenafil citrate. Pre-existing eye conditions also require careful consideration. Follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and frequency.
Sildenafil Citrate: Dosage and Administration
The typical starting dose for sildenafil citrate is 50 mg taken orally, approximately one hour before sexual activity. This dose can be adjusted based on individual response and tolerance. Your doctor will guide you on the appropriate dosage.
Adjusting the Dosage
Depending on efficacy and side effects, your doctor may increase the dose to a maximum of 100 mg or decrease it to 25 mg. Never exceed the prescribed dosage. The drug should be taken only as needed, not more than once daily.
Important Considerations
Avoid taking sildenafil with grapefruit or grapefruit juice, as it can increase blood levels of the medication, potentially leading to side effects. Inform your doctor about all medications you are currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, as interactions are possible. Alcohol consumption can reduce the effectiveness of sildenafil. Consult your physician for personalized advice on dosage and administration.