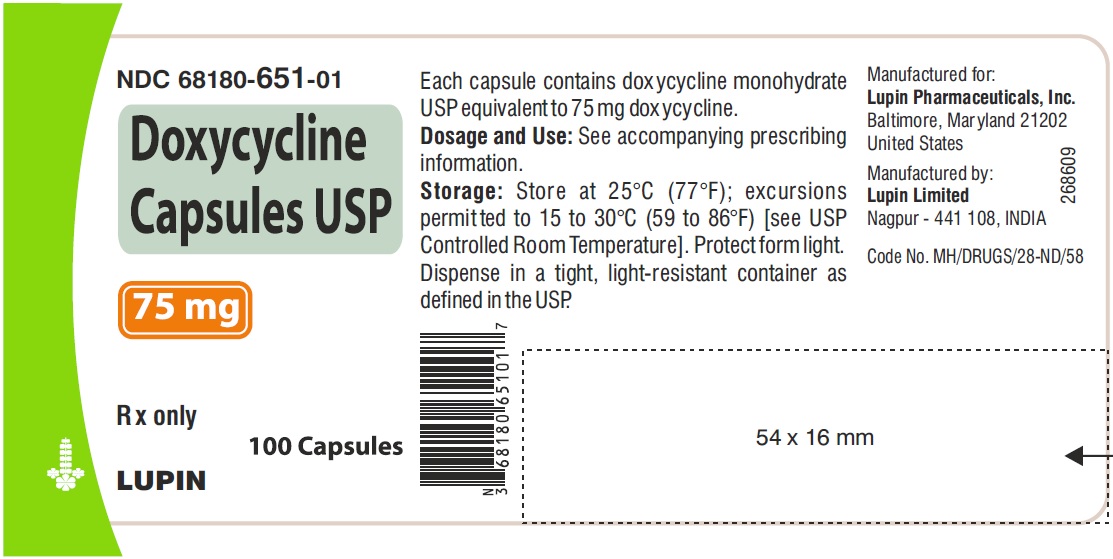
Doxycycline is not the first-line treatment for strep throat. Penicillin or amoxicillin are preferred due to their efficacy and safety profile.
However, if a patient is allergic to penicillin, doxycycline can be a suitable alternative. The typical dosage for adults is 100 mg twice daily for 10 days. Children require a lower dose, determined by weight; always consult a pediatrician for pediatric dosing.
Important Note: This information is for general knowledge only and does not substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a doctor or other qualified healthcare provider before starting any medication, especially antibiotics. They will accurately diagnose your condition and prescribe the appropriate treatment plan based on your individual needs and medical history. Incorrect antibiotic use can lead to antibiotic resistance.
Self-treating strep throat with doxycycline or any other antibiotic without a proper diagnosis can be risky. Seek professional medical care for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
- Dose of Doxycycline for Strep Throat
- Doxycycline: Not a First-Line Treatment for Strep Throat
- Why Avoid Doxycycline for Strep Throat?
- Recommended Treatment Options
- Why Penicillin or Amoxicillin are Preferred for Strep Throat
- Advantages over Doxycycline
- Considerations for Allergic Patients
- When Doxycycline Might Be Considered (Specific Cases)
- Standard Doxycycline Dosage for Bacterial Infections (General Information)
- Potential Side Effects of Doxycycline
- Importance of Completing the Prescribed Course of Antibiotics
- Seeking Professional Medical Advice: The Crucial Step
Dose of Doxycycline for Strep Throat
Doxycycline is not the first-line treatment for strep throat. Penicillin or amoxicillin are preferred.
However, if a patient is allergic to penicillin, doxycycline can be an alternative. A typical adult dose is 100 mg twice daily for 10 days. Children’s dosages vary based on weight and should be determined by a physician. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely.
Important Note: Doxycycline can cause side effects, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and sun sensitivity. Discuss potential side effects with your healthcare provider before taking this medication. Do not take doxycycline if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or have certain kidney or liver conditions.
Always consult your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of strep throat. This information is not a substitute for professional medical advice.
Doxycycline: Not a First-Line Treatment for Strep Throat
Doxycycline isn’t the go-to antibiotic for strep throat. Penicillin or amoxicillin are preferred.
Why Avoid Doxycycline for Strep Throat?
- Resistance: Streptococcus pyogenes, the bacteria causing strep throat, can develop resistance to doxycycline, limiting its effectiveness.
- Side effects: Doxycycline can cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and photosensitivity. While manageable, these side effects might outweigh the benefits in mild strep cases.
- Treatment duration: Longer treatment courses are often needed with doxycycline compared to penicillin or amoxicillin.
Recommended Treatment Options
- Penicillin V: This is usually the first choice. A 10-day course is typical.
- Amoxicillin: A good alternative if penicillin allergy exists. Dosage and duration are similar to penicillin V.
- Other antibiotics: Cephalexin or clindamycin might be used in cases of penicillin allergy, but always under medical supervision.
Always consult your doctor for diagnosis and treatment of strep throat. They can assess your individual needs and prescribe the most appropriate antibiotic. Never self-medicate.
Why Penicillin or Amoxicillin are Preferred for Strep Throat
Penicillin V and amoxicillin remain the first-line treatments for strep throat because of their proven efficacy, safety profile, and affordability. These antibiotics effectively target Streptococcus pyogenes, the bacteria responsible for most strep throat infections. They achieve high blood levels, ensuring the infection is eradicated. Their long history of use provides extensive safety data.
Advantages over Doxycycline
While doxycycline can treat strep throat, it’s generally reserved for penicillin-allergic patients. Doxycycline’s broader spectrum of activity may increase the risk of developing antibiotic-resistant bacteria compared to penicillin or amoxicillin, which specifically target strep. Furthermore, amoxicillin and penicillin demonstrate better rates of bacterial eradication. Amoxicillin offers better oral bioavailability than doxycycline.
Considerations for Allergic Patients
Penicillin allergy requires careful assessment by a doctor. Alternatives beyond doxycycline exist, such as cephalosporins or clindamycin. A doctor will determine the safest and most effective treatment based on individual health history and allergy specifics. Always discuss treatment options with your healthcare provider to ensure the appropriate antibiotic is selected.
When Doxycycline Might Be Considered (Specific Cases)
Doxycycline isn’t the first-line treatment for strep throat, but it holds a place in specific situations. Doctors may consider it for patients allergic to penicillin or other beta-lactam antibiotics. This allergy necessitates a different antibiotic approach, and doxycycline presents a suitable alternative.
Another scenario involves penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pyogenes. While less common, resistance can develop, rendering penicillin ineffective. In these cases, doxycycline, along with other suitable antibiotics, becomes a viable option. Laboratory testing helps identify resistant strains.
For individuals with severe strep throat complications, like rheumatic fever or post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, a broader-spectrum antibiotic like doxycycline may be used. These severe complications demand aggressive management, and doxycycline’s properties can contribute to the treatment regimen.
Remember, a doctor’s assessment is crucial. They’ll consider your medical history, allergy profile, and the severity of your infection before prescribing any antibiotic. Self-treating strep throat is risky and can lead to complications. Always consult a physician for diagnosis and treatment.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare professional for any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
Standard Doxycycline Dosage for Bacterial Infections (General Information)
Doxycycline dosages vary depending on the specific infection and patient factors. Always follow your doctor’s instructions.
For adults, common dosages range from 100mg to 200mg daily, often split into two doses. Treatment duration typically lasts from 7 to 14 days, depending on the infection’s severity and response to treatment.
Children’s dosages are calculated based on weight and are generally lower than adult dosages. A physician will determine the appropriate dose for a child. Always consult a pediatrician before administering doxycycline to a child.
| Infection Type | Typical Dosage (Adults) | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Pneumonia (certain types) | 100-200mg daily, divided doses | 7-14 days |
| Chlamydia | 100mg twice daily | 7 days |
| Lyme Disease | 200mg daily | 10-21 days |
| Acne | 50-100mg daily | Variable, depending on response |
Note: This table provides general information only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Your doctor will determine the most appropriate dosage and treatment plan for your individual needs. Always discuss potential side effects and drug interactions with your doctor before starting any medication.
Potential Side Effects of Doxycycline
Doxycycline, while effective against many bacterial infections, can cause side effects. These vary in severity and frequency.
Common side effects include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Heartburn
- Loss of appetite
- Vaginal yeast infection
Less common, but still possible, side effects include:
- Photosensitivity (increased sun sensitivity)
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Difficulty sleeping
Serious, though rare, side effects warrant immediate medical attention:
- Severe allergic reactions (difficulty breathing, swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat)
- Signs of liver damage (yellowing of skin or eyes, dark urine, abdominal pain)
- Severe skin reactions (Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis)
- Increased pressure inside the skull (headache, vision changes, confusion)
To minimize potential side effects:
- Take doxycycline with food or milk to reduce stomach upset.
- Use sunscreen and protective clothing when spending time outdoors.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Report any concerning symptoms to your doctor immediately.
This information is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before taking doxycycline or any medication.
Importance of Completing the Prescribed Course of Antibiotics
Finish all your doxycycline, even if you feel better before the prescription runs out. Stopping early allows surviving bacteria to multiply, potentially leading to a more resistant infection that’s harder to treat.
Incomplete treatment increases the risk of complications like rheumatic fever, a serious heart condition. This risk is especially relevant with strep throat.
Antibiotic resistance is a growing concern. Finishing your course helps prevent the development of drug-resistant bacteria, protecting you and others.
Follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. If you have questions about your medication, contact your doctor or pharmacist for clarification.
Consistent antibiotic use according to your physician’s plan maximizes treatment success and minimizes long-term health issues.
Seeking Professional Medical Advice: The Crucial Step
Do not self-treat strep throat. Contact your doctor or a qualified healthcare provider immediately. They will properly diagnose your condition and prescribe the correct antibiotic, including determining the appropriate doxycycline dosage if necessary, considering factors like your age, weight, and overall health.
Your doctor will perform a physical exam and may take a throat swab to confirm the strep infection. This test quickly identifies the bacteria causing your illness, ensuring you receive targeted treatment. Do not rely on home remedies or over-the-counter medications; these may delay proper treatment and potentially worsen the infection.
Accurate diagnosis is paramount. Strep throat symptoms can mimic other illnesses. A professional diagnosis prevents misdiagnosis and subsequent inappropriate treatment. A healthcare professional will also address any potential complications or allergies before prescribing medication.
Following your doctor’s instructions regarding medication dosage and duration is critical for a full recovery. Complete the full course of antibiotics, even if you feel better before finishing the prescribed amount. This prevents the recurrence of infection and reduces antibiotic resistance.
Contact emergency services immediately if you experience difficulty breathing, severe pain, high fever, or swelling in your throat. These could indicate a serious complication requiring urgent medical attention.