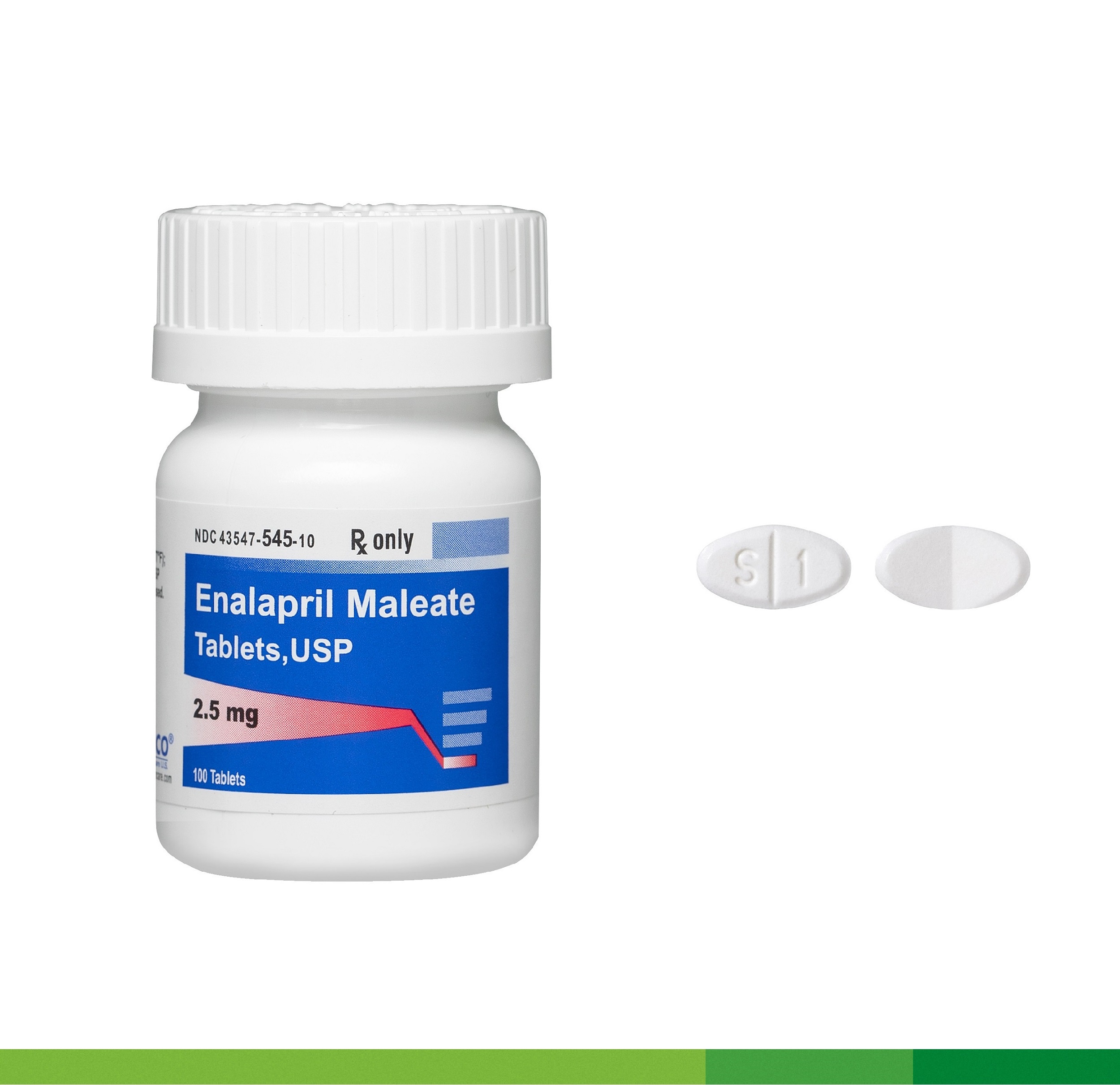
Need to understand Enalapril? Start with dosage: Adults typically begin with 2.5-10mg once daily, adjusted based on blood pressure response and individual needs. Your doctor will determine the right dose for you, so always follow their instructions.
Remember, Enalapril lowers blood pressure. This makes it crucial to monitor your blood pressure regularly, especially during the initial stages of treatment. Report any significant changes or side effects to your physician immediately. Potential side effects include dizziness, fatigue, and a persistent dry cough; some are more common than others.
Always consult your doctor before starting Enalapril, particularly if you have kidney problems, liver disease, or are pregnant or breastfeeding. They can assess your health status and determine the suitability of this medication for you, considering potential drug interactions with other medications you may be taking. This ensures your safety and treatment efficacy.
Proper storage is key. Keep your Enalapril tablets in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture. This helps maintain the medication’s potency and effectiveness throughout its shelf life. Check the expiration date on the packaging and discard any expired tablets.
- Enalapril Tablets: A Detailed Guide
- Understanding Enalapril’s Mechanism of Action
- Common Uses and Indications for Enalapril
- Managing Heart Conditions
- Protecting Kidneys
- Post-Myocardial Infarction Care
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Enalapril
- Potential Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
- More Serious Side Effects
- Drug Interactions: Medications to Avoid with Enalapril
- Precautions and Contraindications for Enalapril Use
- Monitoring and Managing Enalapril Therapy
- When to Contact Your Doctor Regarding Enalapril
- Concerning Side Effects
- Medication Interactions and Adjustments
Enalapril Tablets: A Detailed Guide
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely regarding dosage and administration. Never adjust your dose without consulting them.
Enalapril is an ACE inhibitor, lowering blood pressure by relaxing blood vessels. This eases the strain on your heart and improves blood flow.
Common side effects include dizziness, dry cough, and fatigue. These usually subside as your body adjusts to the medication. Severe side effects, like swelling of the face or throat, require immediate medical attention.
Take enalapril with a full glass of water, ideally at the same time each day. Avoid taking it with grapefruit juice, which can interfere with absorption.
Regular blood pressure monitoring is crucial. Keep your doctor informed about any changes in your health or side effects you experience.
Proper storage is important. Keep tablets in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture. Check the expiration date before each use.
Inform your doctor about all other medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements, as interactions can occur.
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for your next dose. Never double up on doses.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding require special attention. Consult your physician immediately if you become pregnant or are breastfeeding while taking enalapril.
This information does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized guidance about enalapril tablets and their use.
Understanding Enalapril’s Mechanism of Action
Enalapril lowers blood pressure by inhibiting the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). ACE converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor. By blocking this conversion, Enalapril reduces angiotensin II levels.
This decrease in angiotensin II leads to several beneficial effects: blood vessels relax and widen (vasodilation), reducing peripheral resistance. The kidneys also excrete more sodium and water, further lowering blood volume and pressure.
Additionally, Enalapril’s inhibition of ACE prevents the breakdown of bradykinin, a vasodilator. Increased bradykinin contributes to the overall blood pressure-lowering effect. This multifaceted action makes Enalapril a powerful antihypertensive agent.
Remember: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your physician or pharmacist before starting or changing any medication.
Note: Individual responses to Enalapril vary. Your doctor will monitor your blood pressure and adjust your dosage accordingly.
Common Uses and Indications for Enalapril
Enalapril primarily treats high blood pressure (hypertension). Lowering blood pressure reduces your risk of stroke, heart attack, and kidney problems. It’s also highly effective in managing heart failure, improving symptoms like shortness of breath and fatigue by reducing the strain on your heart.
Managing Heart Conditions
Enalapril helps prevent the worsening of heart failure by reducing fluid buildup in the lungs and body. It also slows the progression of heart disease in patients who have already experienced a heart attack. Specifically, it helps prevent the remodeling of the heart muscle after a heart attack, preserving heart function.
Protecting Kidneys
For patients with diabetes and high blood pressure, enalapril offers significant kidney protection. By controlling blood pressure and slowing the progression of diabetic kidney disease, it helps maintain kidney function longer.
Post-Myocardial Infarction Care
After a heart attack, enalapril plays a crucial role in reducing the risk of death and recurrent heart attacks. Its effects on blood pressure and heart function contribute to improved long-term survival and quality of life. Note: Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment.
Remember: This information is for educational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor before starting or changing any medication.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Enalapril
Always follow your doctor’s prescribed dosage. Typical starting doses vary depending on the condition being treated and individual patient factors. For hypertension, a common starting dose is 5-20 mg once daily. This may be adjusted based on blood pressure response. For heart failure, initial doses are usually lower, often starting at 2.5 mg once or twice daily, gradually increased as tolerated.
Take Enalapril exactly as directed. Swallow tablets whole with a glass of water. You can take them with or without food. However, maintaining a consistent schedule improves treatment efficacy.
Missed dose? If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for your next dose. Never double up on doses.
Adjustments: Your doctor will regularly monitor your blood pressure and kidney function, adjusting your dose accordingly. Dosage adjustments are common, particularly in the early stages of treatment and when combined with other medications. Be sure to report any side effects immediately to your healthcare provider.
Special populations: Dosage may need modification for individuals with impaired kidney function or those on dialysis. Older adults may also require lower starting doses and careful monitoring. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should discuss Enalapril use with their doctor.
Important note: This information is for guidance only and does not replace personalized medical advice. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting, stopping, or changing your Enalapril medication.
Potential Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
Enalapril, while generally safe and effective, can cause side effects. The most common include a dry cough, dizziness, and fatigue. This cough often resolves after stopping the medication, but inform your doctor if it persists or is bothersome. Dizziness may improve as your body adjusts; avoid driving or operating machinery until you know how you react.
More Serious Side Effects
Less frequently, but requiring immediate medical attention, are angioedema (swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat), low blood pressure (hypotension), and changes in kidney function. Angioedema is a serious allergic reaction and needs immediate treatment. Hypotension can manifest as lightheadedness or fainting; report any significant drop in blood pressure to your doctor. Regular blood tests can monitor kidney function, especially important for those with pre-existing kidney issues. Changes in potassium levels are possible; your doctor will monitor this through blood tests.
Rare side effects include taste disturbances and skin rashes. Report any unusual symptoms to your physician. Always follow your doctor’s prescribed dosage and instructions. This information doesn’t replace professional medical advice. Consult your doctor if you have concerns or experience any adverse effects.
Drug Interactions: Medications to Avoid with Enalapril
Avoid combining Enalapril with certain medications to prevent potentially harmful effects. Prioritize safety by carefully reviewing your medication list with your doctor or pharmacist.
- Potassium supplements or potassium-sparing diuretics (e.g., spironolactone, amiloride): Enalapril can raise potassium levels. Adding potassium-rich substances increases this risk, potentially causing dangerous hyperkalemia.
- Lithium: Enalapril may reduce lithium excretion, leading to a buildup of lithium in your body and increased risk of lithium toxicity. Close monitoring of lithium levels is necessary if you are taking both medications.
- NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, e.g., ibuprofen, naproxen): NSAIDs can reduce the effectiveness of Enalapril, potentially leading to higher blood pressure. Discuss alternative pain management strategies with your physician.
- Aliskiren (used in treating high blood pressure): Combining Enalapril with aliskiren, particularly in patients with diabetes or impaired kidney function, raises the risk of serious complications like kidney problems and high potassium levels. This combination should generally be avoided.
This is not an exhaustive list. Other medications, including some antacids and certain antibiotics, may also interact with Enalapril. Always inform your healthcare provider of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking, both prescription and over-the-counter.
- Consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting or stopping any medication while taking Enalapril.
- Regularly monitor your blood pressure and potassium levels, as advised by your doctor.
- Report any unusual symptoms, such as muscle weakness, irregular heartbeat, or nausea, to your doctor immediately.
Precautions and Contraindications for Enalapril Use
Before starting Enalapril, inform your doctor about any existing medical conditions. This is especially important for:
- Kidney problems: Enalapril can affect kidney function, requiring careful monitoring, particularly with pre-existing kidney disease.
- Liver problems: Liver impairment can alter Enalapril metabolism, potentially leading to adverse effects. Discuss your liver health with your physician.
- Heart conditions: Certain heart conditions might interact negatively with Enalapril. Your doctor will assess your suitability.
- Diabetes: Enalapril can affect blood sugar levels. Regular monitoring is advised, especially if you have diabetes.
- Hyperkalemia (high potassium levels): Enalapril can increase potassium levels. Your doctor will monitor this through blood tests.
- Pregnancy: Enalapril should generally be avoided during pregnancy, especially in the second and third trimesters. Discuss alternatives with your physician.
- Breastfeeding: The drug’s excretion into breast milk is uncertain, so discuss breastfeeding options with your doctor.
Certain medications can interact with Enalapril. Inform your doctor of all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements. Examples of potentially problematic interactions include:
- Potassium supplements or potassium-sparing diuretics: Increased risk of hyperkalemia.
- Lithium: Enalapril may increase lithium levels.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Reduced Enalapril effectiveness.
Be aware of potential side effects. These can include:
- Dry cough
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Low blood pressure
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any severe side effects, such as swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat (angioedema), difficulty breathing, or chest pain. Regular checkups with your doctor to monitor your blood pressure and kidney function are crucial while taking Enalapril.
Monitoring and Managing Enalapril Therapy
Regularly monitor blood pressure. Aim for consistent readings within your target range, as discussed with your doctor.
Check your potassium levels. Enalapril can raise potassium; your doctor will order blood tests to track this.
Report any symptoms of hyperkalemia immediately. This includes muscle weakness, fatigue, nausea, or irregular heartbeat.
Stay hydrated. Adequate fluid intake helps prevent kidney problems, a potential side effect of Enalapril.
Watch for signs of angioedema. This rare but serious allergic reaction causes facial swelling; seek immediate medical attention if this occurs.
Adjust medication as needed. Your doctor will adjust your dose based on blood pressure readings and potassium levels. Don’t change your dosage without consulting them.
| Symptom | Action |
|---|---|
| Persistent cough | Contact your doctor; they may suggest an alternative medication. |
| Dizziness or lightheadedness | Change positions slowly; avoid sudden movements. |
| Kidney problems (e.g., decreased urine output) | Consult your doctor immediately. |
Maintain a healthy lifestyle. This includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, all of which can support blood pressure control.
Keep all scheduled appointments with your doctor for ongoing monitoring and to discuss any concerns.
When to Contact Your Doctor Regarding Enalapril
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms: severe dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat; difficulty breathing; irregular heartbeat; persistent dry cough; significant changes in your urine output; or muscle weakness or pain.
Concerning Side Effects
Report any unusual side effects to your physician, including but not limited to: persistent nausea or vomiting; yellowing of your skin or eyes; unusual fatigue; unexplained weight loss; or worsening kidney function. These symptoms warrant attention to prevent potential complications.
Medication Interactions and Adjustments
Inform your doctor about all medications you take, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Changes to your Enalapril dose may be necessary if you start or stop taking other medications. Always consult your doctor before making any changes to your medication regimen, even seemingly minor ones.