Seek immediate medical attention if you suspect a Wellbutrin overdose. Call 911 or your local emergency services. Time is critical in managing the effects of an overdose.
Wellbutrin, or bupropion, is a medication with a relatively narrow therapeutic index. This means the difference between a therapeutic dose and a toxic dose is small. Factors influencing toxicity include the amount ingested, the individual’s weight, metabolism, and the presence of other substances in the body.
There’s no single “fatal dose” applicable to everyone. The severity of an overdose depends on numerous variables. Symptoms can range from mild nausea and agitation to seizures and cardiac arrest. Prompt medical intervention is vital to prevent potentially life-threatening complications. Always store Wellbutrin safely, out of reach of children and others who might accidentally ingest it. Proper medication management is paramount in preventing accidental overdoses.
Remember: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for any concerns about medication or potential overdose.
- Fatal Dose of Wellbutrin: Understanding the Risks
- Wellbutrin’s Mechanism of Action and Potential for Overdose
- Factors Influencing Wellbutrin Toxicity: Dosage, Individual Differences, and Concomitant Medications
- Symptoms of Wellbutrin Overdose: Recognizing the Warning Signs
- Neurological Symptoms
- Gastrointestinal Symptoms
- Cardiovascular Symptoms
- Other Potential Symptoms
- What to Do
- Disclaimer:
- Treatment for Wellbutrin Overdose: Immediate Medical Intervention and Support
- Immediate Actions
- Hospital Treatment
- Post-Overdose Support
- Long-Term Management
- Long-Term Effects and Recovery After a Wellbutrin Overdose
Fatal Dose of Wellbutrin: Understanding the Risks
There’s no single “fatal dose” of Wellbutrin universally applicable. Toxicity depends on individual factors like weight, metabolism, other medications, and the amount ingested. Overdosing on Wellbutrin can be dangerous and even lethal.
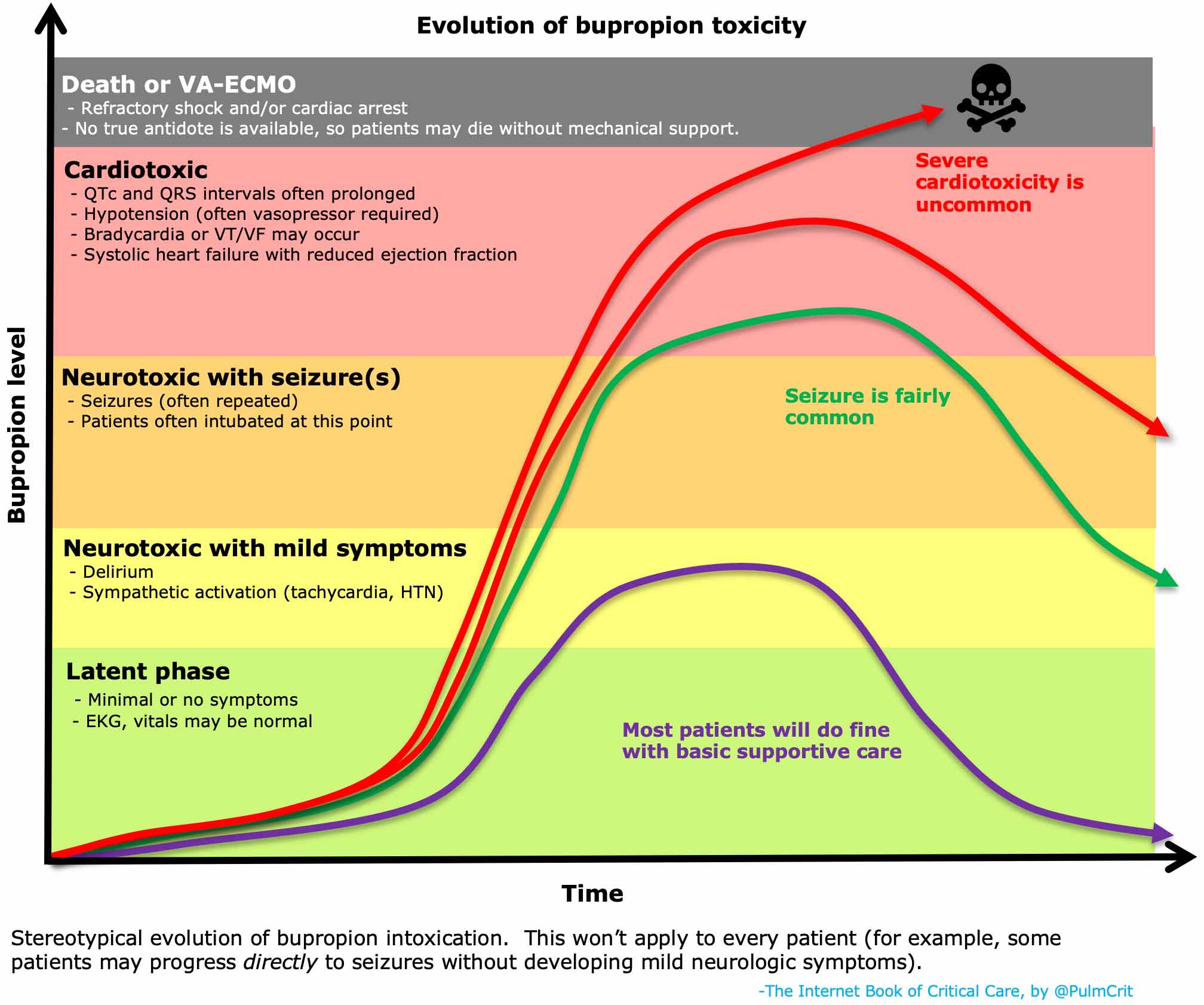
Symptoms of Wellbutrin overdose range from mild to severe, including seizures, rapid heart rate, high blood pressure, and hallucinations. Severe cases may result in coma or death. Immediate medical attention is crucial if you suspect an overdose.
The risk of serious complications increases significantly with higher doses. Taking more than the prescribed amount dramatically elevates your chances of experiencing adverse effects.
| Symptom | Severity | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Nausea, vomiting | Mild | Monitor, contact doctor if persistent |
| Seizures | Severe | Seek immediate medical help |
| Rapid heart rate | Severe | Call emergency services |
| Hallucinations | Severe | Seek immediate medical attention |
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Never change your dosage without consulting them. If you experience concerning side effects, contact your healthcare provider immediately. Open communication with your doctor is key to safe medication management. Never attempt to self-treat or adjust your medication based on online information.
This information does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for any concerns regarding Wellbutrin or other medications.
Wellbutrin’s Mechanism of Action and Potential for Overdose
Wellbutrin, or bupropion, primarily works by blocking the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain. This increased neurotransmitter availability affects mood, energy, and focus. However, excessive levels can lead to adverse effects.
Overdosing on Wellbutrin carries significant risks. Symptoms can range from mild (such as nausea, vomiting, and agitation) to severe (seizures, cardiac arrhythmias, and coma). The risk of seizure increases dramatically with higher doses, especially in individuals with a pre-existing seizure disorder or those consuming other drugs that lower the seizure threshold. Cardiac effects are also a major concern.
Factors influencing overdose severity include the amount ingested, individual metabolism, and the presence of other medications or substances. Immediate medical attention is crucial if an overdose is suspected. Treatment typically involves supportive care, such as managing seizures and maintaining cardiovascular stability. Specific antidotes are not readily available.
Always follow your doctor’s prescribed dosage. Never exceed the recommended dose. Openly discuss any concerns about medication with your physician. If you experience unusual symptoms, seek immediate medical help. Proper medication management reduces the chance of an overdose.
This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Consult a healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.
Factors Influencing Wellbutrin Toxicity: Dosage, Individual Differences, and Concomitant Medications
Dosage significantly impacts Wellbutrin toxicity risk. Exceeding the prescribed dose increases the likelihood of adverse effects. Always adhere strictly to your doctor’s instructions. Overdosing, even slightly, can lead to seizures, particularly in individuals predisposed to them.
Individual differences play a crucial role. Factors such as age, weight, liver and kidney function, and genetic predispositions influence how the body metabolizes Wellbutrin. Older adults or those with impaired organ function may experience higher concentrations of the drug, elevating toxicity risk. Genetic variations can affect drug metabolism, leading to unpredictable responses.
Concomitant medications can interact dangerously with Wellbutrin. Specific medications, including MAO inhibitors, certain antidepressants, and some seizure medications, increase the risk of serotonin syndrome or seizures. Always inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking. This allows for careful monitoring and identification of potential interactions before they cause harm.
Note: This information is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your physician or pharmacist before making any changes to your medication regimen. Seek immediate medical attention if you suspect a Wellbutrin overdose.
Symptoms of Wellbutrin Overdose: Recognizing the Warning Signs
Seek immediate medical attention if you suspect a Wellbutrin overdose. Time is critical.
Neurological Symptoms
- Seizures: These are a serious complication and require immediate emergency care. They can range from brief twitching to prolonged convulsions.
- Tremors: Noticeable shaking or trembling in the hands, arms, or legs.
- Headache: Severe and persistent headache.
- Dizziness: Feeling lightheaded or unsteady.
- Confusion: Difficulty concentrating or thinking clearly.
- Hallucinations: Seeing or hearing things that aren’t there.
Gastrointestinal Symptoms
- Nausea and Vomiting: Persistent feeling of sickness and throwing up.
- Abdominal Pain: Cramps or discomfort in the stomach area.
- Diarrhea: Loose and frequent bowel movements.
Cardiovascular Symptoms
- Rapid Heart Rate: A significantly faster than normal pulse.
- High Blood Pressure: Elevated blood pressure reading.
Other Potential Symptoms
- Agitation: Feeling restless and unable to relax.
- Anxiety: Excessive worry and nervousness.
- Increased Body Temperature: Fever.
- Changes in Sleep Patterns: Insomnia or excessive sleepiness.
What to Do
If you or someone you know experiences any of these symptoms after taking Wellbutrin, immediately call emergency services or your local poison control center. Provide them with details about the medication taken, the amount ingested, and the time of ingestion. Follow their instructions carefully.
Disclaimer:
This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition.
Treatment for Wellbutrin Overdose: Immediate Medical Intervention and Support
Call emergency services immediately (911 in the US or your local equivalent). A Wellbutrin overdose requires immediate medical attention. Delaying treatment can have severe consequences.
Immediate Actions
While waiting for emergency responders, provide them with as much information as possible about the overdose: the amount of Wellbutrin ingested, the time of ingestion, and the individual’s current condition. If possible, collect any remaining medication containers for first responders. Monitor the individual’s breathing, heart rate, and level of consciousness. If they become unconscious, begin CPR if trained.
Hospital Treatment
Upon arrival at the hospital, medical professionals will conduct a thorough assessment. Treatment may involve inducing vomiting (if appropriate), administering activated charcoal to absorb the drug, and managing symptoms like seizures or heart problems. Intensive care might be necessary depending on the severity of the overdose. Close monitoring of vital signs and neurological function is crucial throughout treatment.
Post-Overdose Support
After discharge, access to ongoing mental health support is vital. This may involve counseling, therapy, or participation in support groups to address any underlying issues that may have contributed to the overdose. A follow-up appointment with the prescribing physician or another mental health professional is essential to discuss medication management and relapse prevention strategies. The goal is to create a safe and stable environment for recovery.
Long-Term Management
Medication reconciliation is crucial. Work closely with the healthcare team to review all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to prevent future interactions. Creating a plan for safe medication storage and adherence is critical for successful recovery. A strong support system, including family and friends, is instrumental for long-term success.
Long-Term Effects and Recovery After a Wellbutrin Overdose
Seek immediate medical attention. A Wellbutrin overdose requires prompt professional care to minimize lasting damage.
Long-term effects vary greatly depending on the overdose severity and individual factors. Possible consequences include seizures, cardiac arrhythmias, and prolonged neurological symptoms like cognitive impairment or persistent tremors. Some individuals experience lingering anxiety or depression.
Recovery involves a multifaceted approach. Medical professionals typically monitor vital signs, manage seizures with medication, and provide supportive care. Psychological support, including therapy, is frequently recommended to address potential emotional consequences and aid in recovery. A gradual return to normal activities is essential, guided by medical advice. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to assess progress and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Nutritional support plays a vital role. A balanced diet promotes healing and helps maintain overall health. Sufficient hydration is also important for recovery. Avoiding alcohol and other substances is paramount during this time.
The timeline for complete recovery varies. Some individuals might see significant improvement within weeks, while others might experience lingering effects for months or even longer. Consistent adherence to medical advice and self-care significantly influences the recovery process.
Remember: This information is for general knowledge and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition.