Fluconazole is the generic name for several brand-name antifungal medications. You’ll find it sold under various brand names depending on your location and the specific pharmaceutical company.
Diflucan is perhaps the most widely recognized brand name for fluconazole. However, other brands exist, and their availability varies geographically. Always check the label to confirm the active ingredient is fluconazole.
Remember to consult your doctor or pharmacist for accurate information about specific brand names available in your region and any potential interactions with other medications. They can provide personalized advice based on your individual health needs and prescription details.
- Fluconazole is Generic for What? A Detailed Guide
- Understanding Fluconazole’s Role as a Generic Drug
- Generic vs. Brand-Name: What’s the Difference?
- Diflucan: The Brand Name Equivalent of Fluconazole
- Specific Fungal Infections Treated by Fluconazole
- Oral and Esophageal Candidiasis
- Vulvovaginal Candidiasis
- Cryptococcal Meningitis
- Systemic Candidiasis
- Other Fungal Infections
- Important Considerations
- Comparing Fluconazole to Other Antifungal Medications
- Oral vs. Intravenous Administration
- Spectrum of Activity
- Side Effects and Drug Interactions
- Cost Considerations
- Specific Infections
- Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition.
- Dosage Forms and Considerations for Fluconazole
- Oral Administration
- Intravenous Administration
- Dosage Adjustments
Fluconazole is Generic for What? A Detailed Guide
Fluconazole is the generic name for Diflucan, a brand-name antifungal medication.
This means that Diflucan contains fluconazole as its active ingredient. Many other pharmaceutical companies produce fluconazole under their own brand names or as a generic medication. The price difference can be substantial, with generic fluconazole often being significantly cheaper.
Fluconazole targets a range of fungal infections. Here’s a breakdown:
- Candidiasis: Fluconazole effectively treats various candidiasis infections, including thrush (oral and vaginal), esophageal candidiasis, and invasive candidiasis.
- Cryptococcal Meningitis: This serious fungal infection affecting the brain and spinal cord responds well to fluconazole treatment.
- Coccidioidomycosis: Fluconazole can be used to treat this fungal infection, particularly in cases where other antifungals are not tolerated.
- Histoplasmosis: Another fungal infection, histoplasmosis, benefits from fluconazole treatment, although other antifungals may be preferred in severe cases.
Important Considerations:
- Dosage: The appropriate dosage of fluconazole varies greatly depending on the specific infection, its severity, and the patient’s health. Always follow your doctor’s prescription instructions precisely.
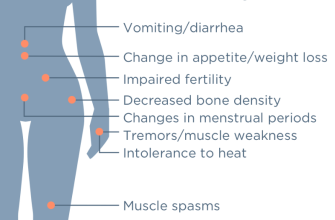
- Side Effects: Like all medications, fluconazole can cause side effects. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and headache. More serious, though less common, side effects are possible. Consult your doctor immediately if you experience any concerning symptoms.
- Drug Interactions: Fluconazole can interact with other medications. Inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are currently taking to prevent potential interactions.
- Allergies: If you have a known allergy to fluconazole or other azole antifungals, inform your doctor before taking this medication.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Fluconazole’s use during pregnancy and breastfeeding requires careful consideration and should be discussed with your doctor to weigh the risks and benefits.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your physician or pharmacist for personalized guidance regarding fluconazole or any medication.
Understanding Fluconazole’s Role as a Generic Drug
Fluconazole is the generic name for Diflucan, a widely prescribed antifungal medication. This means that numerous pharmaceutical companies produce Fluconazole, offering consumers multiple brands at varying prices.
Generic vs. Brand-Name: What’s the Difference?
The key difference lies in the cost. Generic drugs, like Fluconazole, undergo rigorous testing to prove bioequivalence–meaning they have the same active ingredient, dosage form, strength, and route of administration as their brand-name counterparts. This ensures the same therapeutic effect. However, generic manufacturers save on research and marketing costs, leading to significantly lower prices for consumers. This price difference can be substantial, making generic Fluconazole a more affordable treatment option for fungal infections.
Choosing a generic Fluconazole doesn’t compromise quality or efficacy. The FDA strictly regulates both generic and brand-name drugs, guaranteeing safety and effectiveness. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting any medication, including generic Fluconazole, to ensure it’s appropriate for your specific health needs.
Diflucan: The Brand Name Equivalent of Fluconazole
Diflucan is the brand name for the antifungal medication fluconazole. This means Diflucan contains the same active ingredient as fluconazole generic medications.
Both Diflucan and generic fluconazole treat various fungal infections, including yeast infections (like vaginal candidiasis or thrush), ringworm, and athlete’s foot. They work by inhibiting the growth of fungi.
While Diflucan might be more expensive, generic fluconazole offers the same therapeutic benefits at a lower cost. Your doctor can help you determine the best option based on your specific needs and budget. Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment for either medication.
Remember to inform your doctor about any allergies or other medications you are taking before starting treatment with Diflucan or fluconazole.
Specific Fungal Infections Treated by Fluconazole
Fluconazole effectively targets a range of fungal infections. It’s a powerful tool in managing several common conditions.
Oral and Esophageal Candidiasis
Fluconazole successfully treats Candida infections affecting the mouth (oral thrush) and esophagus (esophageal candidiasis). These infections often present with white patches and discomfort. Treatment duration varies depending on severity, typically ranging from 7 to 14 days.
Vulvovaginal Candidiasis
This common yeast infection is effectively treated with fluconazole. A single dose often suffices, though more prolonged therapy may be necessary for recurrent infections. Always consult a doctor for diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Cryptococcal Meningitis
Fluconazole is a cornerstone of treatment for this serious fungal infection of the brain and spinal cord. This requires a longer treatment course, often several weeks or months, under close medical supervision.
Systemic Candidiasis
In cases of invasive Candida infections spreading throughout the body, fluconazole may be part of a broader treatment strategy. The dosage and duration are highly dependent on the severity and location of the infection.
Other Fungal Infections
Fluconazole also shows efficacy against certain dermatophyte infections, such as tinea cruris (jock itch) and tinea corporis (ringworm), though other antifungals might be preferred for these conditions. It may also be used in the treatment of onychomycosis (nail fungus), although treatment may be lengthy.
Important Considerations
| Infection | Typical Treatment Duration | Dosage |
|---|---|---|
| Oral/Esophageal Candidiasis | 7-14 days | Varies depending on severity and patient factors. |
| Vulvovaginal Candidiasis | Single dose or 3-7 days | Varies depending on severity and patient factors. |
| Cryptococcal Meningitis | Several weeks to months | Varies depending on severity and patient factors. Requires close medical monitoring. |
| Systemic Candidiasis | Varies greatly | Highly individualized; requires close medical supervision. |
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of any fungal infection.
Comparing Fluconazole to Other Antifungal Medications
Fluconazole, a triazole antifungal, targets a specific enzyme in fungal cells. This differs from other classes like echinocandins (caspofungin, micafungin, anidulafungin), which inhibit fungal cell wall synthesis, or polyenes (amphotericin B, nystatin), which target fungal cell membranes. Choosing the right antifungal depends heavily on the specific fungal infection and patient factors.
Oral vs. Intravenous Administration
Fluconazole offers oral bioavailability, a significant advantage over some antifungals requiring intravenous administration. This makes it convenient for treating less severe infections. However, for serious systemic infections, intravenous options like amphotericin B might be necessary for quicker and higher drug concentration in the bloodstream.
Spectrum of Activity
Fluconazole is effective against Candida species and some dermatophytes, but its activity against other fungi, such as Aspergillus, is limited. Amphotericicin B boasts broader activity against a wider range of fungi, including Aspergillus and Cryptococcus. Echinocandins are particularly effective against Aspergillus species but show less activity against Candida than fluconazole.
Side Effects and Drug Interactions
Fluconazole’s side effects are generally mild, often involving gastrointestinal upset. However, it can interact with certain medications, including some statins and oral contraceptives. Amphotericicin B, on the other hand, can cause nephrotoxicity (kidney damage) and infusion-related reactions. Each medication’s potential side effects and drug interactions must be carefully considered before prescribing.
Cost Considerations
Fluconazole is generally more affordable than other antifungals, making it a cost-effective option for many infections. However, cost shouldn’t be the sole determining factor; the most appropriate antifungal should always be chosen based on the severity of the infection and the patient’s overall health.
Specific Infections
For instance, treating oral thrush (Candida infection) might favor fluconazole’s convenient oral formulation. Conversely, treating invasive aspergillosis (Aspergillus infection) often requires the broader-spectrum activity and potentially higher concentrations achieved with an echinocandin or amphotericin B. Your doctor should determine the best antifungal for your specific condition.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition.
Dosage Forms and Considerations for Fluconazole
Fluconazole is available in several forms, including oral tablets (200mg), oral suspension (as a liquid), and intravenous solutions. The specific dosage form will depend on your individual needs and the severity of your infection. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely.
Oral Administration
Oral tablets are generally easy to take with water, but remember to take them as directed. Absorption may vary slightly depending on food intake; your doctor will advise if adjustments are necessary. The liquid suspension is useful for those who find swallowing tablets difficult. Shake the bottle well before each dose to ensure even distribution.
Intravenous Administration
The intravenous (IV) form is usually reserved for severe infections or when oral administration isn’t feasible. This form is administered by a healthcare professional and requires careful monitoring. The medication should be diluted properly before administering to avoid adverse reactions.
Dosage Adjustments
Your doctor will determine the appropriate dose and duration of treatment. The dosage might need adjustments based on factors such as your kidney function and the specific fungal infection being treated. People with impaired kidney function often require lower doses or less frequent administration to prevent medication buildup. Always inform your doctor about any pre-existing health conditions or medications you’re currently taking, especially those that may impact kidney or liver function.