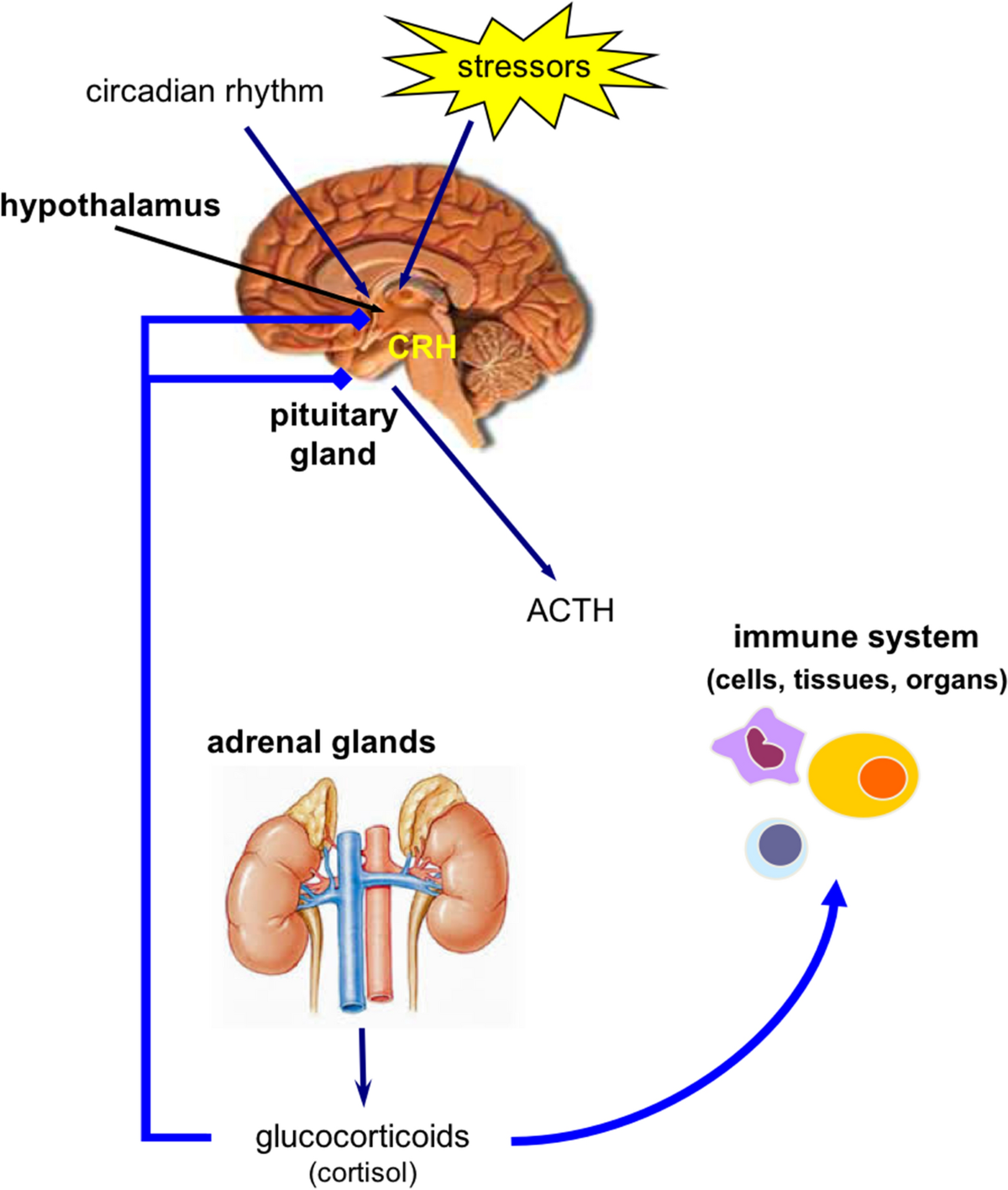
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, can significantly reduce rhinitis symptoms, particularly inflammation. However, it’s crucial to understand its appropriate use and potential side effects. This guide provides clear, practical information to help you make informed decisions.
Short-term prednisone treatment, typically lasting only a few days to a week, often proves effective for managing severe allergic rhinitis flare-ups. This addresses intense symptoms like nasal congestion, sneezing, and itching, offering rapid relief. Remember to follow your doctor’s prescribed dosage meticulously.
Long-term prednisone use for rhinitis is generally avoided due to potential side effects including weight gain, increased blood sugar, and weakened immunity. Your physician will weigh the benefits against these risks, and alternative treatments like nasal corticosteroids or antihistamines might be preferred for ongoing management.
Always discuss your rhinitis treatment plan with your doctor. They can assess your specific condition, considering factors like allergies, other health issues, and medication interactions, to determine the most suitable approach, including whether prednisone is appropriate for you.
Note: This information is for educational purposes and does not replace professional medical advice. Consult your doctor before starting any new medication.
- Prednisone for Rhinitis: A Detailed Guide
- What is Rhinitis and When is Prednisone Necessary?
- Understanding Prednisone’s Role
- Understanding Prednisone’s Mechanism of Action in Rhinitis
- Dosage and Administration of Prednisone for Rhinitis
- Potential Side Effects and Risks of Prednisone for Rhinitis
- Alternatives to Prednisone for Rhinitis Management
- Other Non-Steroidal Options
- Long-Term Use and Tapering Off Prednisone for Rhinitis
- Managing Long-Term Rhinitis
- Tapering Off Prednisone
- Monitoring for Side Effects
Prednisone for Rhinitis: A Detailed Guide
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, effectively reduces inflammation in the nasal passages, providing relief from rhinitis symptoms. However, it’s not a first-line treatment and should be used under a doctor’s supervision.
When to consider Prednisone: Your doctor may prescribe Prednisone for severe allergic rhinitis, unresponsive to other treatments, or for acute exacerbations causing significant distress. It’s particularly useful for managing symptoms rapidly.
Dosage and Administration: Your doctor determines the correct dose based on your specific needs and the severity of your rhinitis. Typically, a short course (5-10 days) is prescribed. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Never adjust dosage without consulting your physician.
Potential Side Effects: While Prednisone offers significant relief, potential side effects include increased appetite, weight gain, mood changes, insomnia, and increased blood sugar. Long-term use carries more serious risks. Your doctor will discuss these risks with you. Report any unusual symptoms immediately.
Alternative Treatments: Before considering Prednisone, explore first-line treatments like nasal corticosteroids, antihistamines, and saline nasal sprays. These often effectively manage rhinitis without the side effects of Prednisone.
Medication Interactions: Prednisone can interact with other medications. Inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you’re currently taking. This ensures safe and effective treatment.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your doctor or healthcare provider before starting any new medication, including Prednisone, for rhinitis or any other condition.
What is Rhinitis and When is Prednisone Necessary?
Rhinitis is inflammation of the nasal lining, causing stuffy or runny nose, sneezing, and itchiness. Allergic rhinitis stems from allergens like pollen or pet dander, while non-allergic rhinitis has other triggers, such as infections or irritants.
Understanding Prednisone’s Role
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, powerfully reduces inflammation. Doctors prescribe it for severe rhinitis cases unresponsive to other treatments. This includes situations where symptoms significantly impair daily life or when other medications prove ineffective. Specifically, prednisone is often used for acute severe allergic rhinitis flares or for non-allergic rhinitis complicated by sinusitis.
Consider prednisone if your rhinitis symptoms are debilitating, lasting longer than usual, or accompanied by complications like sinus infections. Your doctor will assess your condition and determine if prednisone is appropriate, considering potential side effects. It is generally a short-term treatment for severe cases, not a long-term solution. Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and duration.
Understanding Prednisone’s Mechanism of Action in Rhinitis
Prednisone reduces rhinitis symptoms by suppressing the body’s inflammatory response. It achieves this by binding to intracellular receptors, specifically glucocorticoid receptors, in immune cells like mast cells and lymphocytes.
This binding triggers a cascade of events. Specifically, it influences gene transcription, leading to reduced production of inflammatory mediators such as histamine, leukotrienes, and prostaglandins. These mediators are key players in the allergic reaction causing rhinitis symptoms.
Consequently, the decreased production of these inflammatory molecules leads to less swelling in the nasal passages, reduced mucus production, and a decrease in nasal itching and congestion. This ultimately translates to symptom relief.
Remember, Prednisone doesn’t address the underlying cause of rhinitis, only the symptoms. It’s a powerful anti-inflammatory, however, and provides rapid relief for severe symptoms. Your doctor can advise you on the appropriate use and duration.
Dosage and Administration of Prednisone for Rhinitis
Prednisone dosage for rhinitis varies greatly depending on the severity of your symptoms and your individual response to the medication. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. They will tailor the dosage to your specific needs.
Typically, treatment involves a short course of prednisone, often lasting only a few days to a week. Higher doses might be prescribed initially, followed by a gradual reduction as your symptoms improve.
- Oral Administration: Prednisone is usually taken orally, once or twice daily, with food to minimize stomach upset.
- Dosage Range: Doses typically range from 5mg to 60mg daily, but this significantly depends on your individual case and should be determined by your physician.
Never alter your prescribed dosage or discontinue the medication without consulting your doctor. Sudden cessation can lead to withdrawal symptoms.
- Monitor for Side Effects: Be aware of potential side effects such as increased appetite, weight gain, mood changes, insomnia, and increased blood sugar. Report any concerning side effects to your physician immediately.
- Long-term Use: Prednisone is not intended for long-term use due to potential side effects. Your doctor will determine the shortest effective treatment duration.
- Other Medications: Inform your doctor about all other medications you are currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, as interactions are possible.
Remember, this information is for general knowledge and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult your healthcare professional for personalized guidance on prednisone use for rhinitis.
Potential Side Effects and Risks of Prednisone for Rhinitis
Prednisone, while effective for treating severe rhinitis, carries potential side effects. Understanding these risks helps you make informed decisions with your doctor.
Short-term use usually involves manageable side effects, but long-term use increases the risk of more serious issues. Let’s explore some common concerns:
- Increased Blood Sugar: Prednisone can elevate blood glucose levels, posing a risk for people with diabetes or pre-diabetes. Regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial during treatment.
- Fluid Retention: You may experience swelling in your ankles, feet, or face due to fluid retention. This is often temporary and resolves after stopping the medication.
- Increased Appetite and Weight Gain: Prednisone can stimulate appetite, leading to weight gain if not managed with dietary adjustments. Consult a nutritionist for guidance.
- Mood Changes: Some individuals experience irritability, anxiety, or insomnia. Open communication with your doctor is vital if these occur.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Upset stomach, heartburn, or ulcers can develop. Taking prednisone with food can often mitigate these issues.
- Weakened Immune System: Prednisone suppresses the immune system, making you more susceptible to infections. Avoid contact with sick individuals if possible.
- High Blood Pressure: Prednisone can raise blood pressure. Regular monitoring is important, particularly for those already managing hypertension.
- Osteoporosis (Long-term use): Prolonged prednisone use can thin bones, increasing the risk of fractures. Discuss bone density monitoring with your physician if you’re on long-term treatment.
- Cataracts and Glaucoma (Long-term use): Long-term use can increase the risk of these eye conditions. Regular eye exams are recommended.
Remember: This information is not exhaustive. Always discuss potential side effects and risks with your doctor before starting prednisone. They can assess your individual risk factors and help you manage any side effects that may occur. Regular check-ups during treatment are essential for monitoring your health.
- Communicate openly: Report any concerning symptoms to your doctor immediately.
- Follow prescribed dosage: Never adjust the dosage without consulting your doctor.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: A balanced diet and regular exercise can help mitigate some side effects.
Alternatives to Prednisone for Rhinitis Management
Consider intranasal corticosteroids like fluticasone or mometasone. These offer potent anti-inflammatory action directly at the site of inflammation, often minimizing systemic side effects associated with oral prednisone. They’re available over-the-counter or by prescription, depending on the strength.
Other Non-Steroidal Options
Explore antihistamines, such as cetirizine or fexofenadine. These effectively combat allergic rhinitis symptoms like sneezing and itching. For congestion, you might try a saline nasal spray to rinse nasal passages, naturally clearing irritants. Finally, consider oral decongestants like pseudoephedrine, but use them cautiously and for short periods due to potential rebound congestion.
Immunotherapy, or allergy shots, provides long-term relief by gradually desensitizing you to allergens. While it requires a commitment over several months, it can significantly reduce your reliance on medication. Discuss this option with an allergist.
Lifestyle changes can also make a difference. Identify and avoid triggers, such as pet dander, dust mites, or pollen, through proper cleaning and air filtration. Regular nasal irrigation can also help keep your nasal passages clean.
Long-Term Use and Tapering Off Prednisone for Rhinitis
Prednisone should not be used long-term for rhinitis due to significant side effects. Your doctor will likely prescribe it only for short, intense flare-ups.
Managing Long-Term Rhinitis
If you experience frequent rhinitis, your doctor will explore alternative long-term management options. These commonly include nasal corticosteroids, antihistamines, or immunotherapy. These treatments aim to control symptoms without the risks associated with prolonged prednisone use.
Tapering Off Prednisone
Abruptly stopping prednisone can cause serious withdrawal symptoms. Your doctor will create a tapering schedule, gradually reducing your dose over several days or weeks. This controlled reduction minimizes the risk of rebound inflammation and other withdrawal effects.
| Day | Prednisone Dose (mg) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1-7 | 40 | Example: Starting dose. Adjust based on individual needs. |
| 8-14 | 30 | Reduce by 10mg. Monitor symptoms closely. |
| 15-21 | 20 | Reduce by 10mg. Contact doctor if symptoms worsen. |
| 22-28 | 10 | Reduce by 10mg. Continue monitoring. |
| 29+ | 0 | Complete cessation. Follow-up appointment recommended. |
This is a sample schedule and your doctor will personalize the tapering plan based on your individual response to treatment and overall health.
Monitoring for Side Effects
During the tapering period, carefully monitor for side effects such as increased fatigue, joint pain, or worsening rhinitis symptoms. Report any concerns to your physician immediately. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial for successful tapering and managing your rhinitis.