If you’re concerned about the potential link between Topamax and eating disorders, prioritize open communication with your doctor. Discuss your specific concerns and any changes in your appetite or eating habits since starting the medication. Regular monitoring of your weight and overall health is crucial.
Topamax, or topiramate, can sometimes cause side effects like decreased appetite and weight loss. This isn’t true for everyone, but it’s a known possibility. Understanding this potential side effect allows for proactive management. Your physician can help you assess your risk and develop strategies to mitigate potential problems.
Don’t hesitate to report any significant changes in your eating patterns, even seemingly minor ones. This includes increased or decreased food intake, altered food preferences, or obsessive thoughts about food and weight. Early intervention is key to managing any eating disorder symptoms that may develop.
Remember, your doctor is your best resource. They can provide tailored advice, adjust your medication if needed, and refer you to specialists if concerns about an eating disorder arise. Proactive communication ensures your well-being and helps maintain a healthy relationship with food.
- Topamax and Eating Disorders: A Complex Relationship
- Monitoring and Management
- Alternative Strategies
- Topamax’s Mechanism of Action and Potential Weight Loss Effects
- Topamax and Anorexia Nervosa: Risks and Considerations
- Weight Changes and Potential Dangers
- Treatment Focus: Addressing the Root Cause
- Medication Alternatives
- Seeking Professional Help
- Topapx and Bulimia Nervosa: Impact on Purging Behaviors
- Topamax and Binge Eating Disorder: Efficacy and Side Effects
- Managing Topamax Use in Patients with Eating Disorders: Clinical Guidance
Topamax and Eating Disorders: A Complex Relationship
Topamax, while sometimes prescribed off-label for weight management, presents a nuanced relationship with eating disorders. Its weight-loss effect stems from its impact on appetite and metabolism, potentially triggering or exacerbating existing disordered eating patterns. Individuals prone to anorexia or bulimia might misuse Topamax to further restrict calorie intake or purge more easily, believing it assists weight loss. This is extremely dangerous.
Monitoring and Management
Careful monitoring is crucial. Patients prescribed Topamax, especially those with a history of eating disorders, require close observation for changes in eating habits, body image concerns, and weight fluctuations. Regular check-ins with both their prescribing physician and a registered dietitian or therapist specializing in eating disorders are vital. A multidisciplinary approach ensures prompt identification and management of any potential complications.
Alternative Strategies
If weight management is the primary concern, consider safer alternatives. Lifestyle changes like balanced nutrition and increased physical activity offer sustainable, healthier solutions, avoiding the risks associated with Topamax and its potential interaction with eating disorders. Always discuss treatment plans with a healthcare professional experienced in both weight management and eating disorder recovery.
Topamax’s Mechanism of Action and Potential Weight Loss Effects
Topamax (topiramate) primarily works by blocking certain sodium channels in the brain, impacting the release of neurotransmitters like glutamate and GABA. This multifaceted action contributes to its anti-seizure and migraine-prevention properties. A secondary effect, often observed, is weight loss.
This weight loss isn’t fully understood, but it’s thought to be linked to Topamax’s effects on appetite regulation. Specifically, it may decrease appetite and increase feelings of fullness, leading to reduced caloric intake. Some studies suggest Topamax may also influence metabolism, although more research is needed to clarify this aspect.
The degree of weight loss varies significantly between individuals. While some experience substantial weight reduction, others see minimal change or even weight gain. Factors influencing this variation include starting weight, metabolism, diet, and exercise habits. It’s crucial to consult a doctor before using Topamax for weight loss, as it’s not approved for this purpose and carries potential side effects.
Potential side effects, which can be dose-dependent, include fatigue, tingling in the extremities, cognitive difficulties, and kidney stones. Your doctor will carefully weigh the risks and benefits before prescribing Topamax, considering your specific health conditions and overall well-being. They’ll monitor your progress closely and adjust your dosage as needed.
Remember, Topamax is not a magic bullet for weight loss. It should be considered as part of a comprehensive weight management strategy that incorporates a healthy diet and regular exercise. Focus on sustainable lifestyle changes for long-term weight management success. Always prioritize open communication with your doctor to address any concerns and monitor your health effectively.
Topamax and Anorexia Nervosa: Risks and Considerations
Do not use Topamax to treat anorexia nervosa. While Topamax (topiramate) has shown some effects on appetite and weight, its use in anorexia nervosa carries significant risks.
Weight Changes and Potential Dangers
Topamax can cause weight loss, a seemingly positive effect for someone struggling with anorexia. However, this weight loss is often unrelated to improved eating habits and can worsen the underlying eating disorder. It’s crucial to focus on treating the underlying psychological issues of anorexia, not merely addressing the weight symptom.
- Weight loss from Topamax may mask the severity of the anorexia, delaying proper treatment.
- The medication can interact negatively with other medications a patient might be taking for their anorexia.
- Topamax’s side effects, including cognitive impairment and fatigue, can exacerbate the difficulties associated with recovery.
Treatment Focus: Addressing the Root Cause
Effective anorexia treatment centers on comprehensive therapy addressing the psychological roots of the disorder. This typically involves a multidisciplinary team, including:
- Psychiatrists: To address co-occurring mental health conditions.
- Registered dietitians: To create a safe and effective meal plan.
- Therapists: To explore the underlying emotional and behavioral patterns.
Medication Alternatives
Several medications may be helpful in treating co-occurring conditions like depression or anxiety frequently associated with anorexia. However, their use should be carefully considered and overseen by a medical professional specializing in eating disorders. A psychiatrist can determine the most appropriate medication based on the individual’s needs and health status. They will closely monitor the patient for any adverse reactions and ensure the medication is beneficial and not detrimental to their recovery.
Seeking Professional Help
If you or someone you know is struggling with anorexia, seek professional help immediately. Early intervention improves the chances of successful recovery. A qualified eating disorder specialist can provide a tailored treatment plan that includes therapy, nutritional guidance, and, if necessary, appropriate medication for related mental health conditions. Don’t hesitate to reach out for support.
Topapx and Bulimia Nervosa: Impact on Purging Behaviors
Topamax, or topiramate, may influence bulimia nervosa by affecting appetite and potentially reducing the frequency of purging behaviors. Studies suggest a possible correlation between Topamax use and decreased binge-purge cycles in some individuals.
However, it’s crucial to understand that Topamax isn’t a guaranteed cure for bulimia. Its impact varies significantly between patients. Some individuals experience a noticeable reduction in purging episodes, while others see no change or even an increase in binge eating.
Weight changes are a common side effect of Topamax, which can both positively and negatively influence bulimic behaviors. Weight loss might initially reduce the urge to purge, but it can also exacerbate existing body image issues and trigger further disordered eating.
Importantly, Topamax should never be considered a standalone treatment for bulimia nervosa. It’s vital to combine medication with comprehensive therapy, including cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and nutritional counseling. This multi-pronged approach addresses the underlying psychological and behavioral aspects of the disorder for the most effective outcome.
Patients considering Topamax for bulimia should discuss potential benefits and risks with their psychiatrist and therapist. Close monitoring of weight, eating patterns, and mental health is necessary throughout treatment. Regular check-ins allow healthcare professionals to adjust medication or therapy as needed, ensuring optimal patient care.
Remember, recovery from bulimia is a complex process requiring individualized care. The success of Topamax in managing purging behaviors depends on a tailored treatment plan that incorporates medication, therapy, and ongoing support.
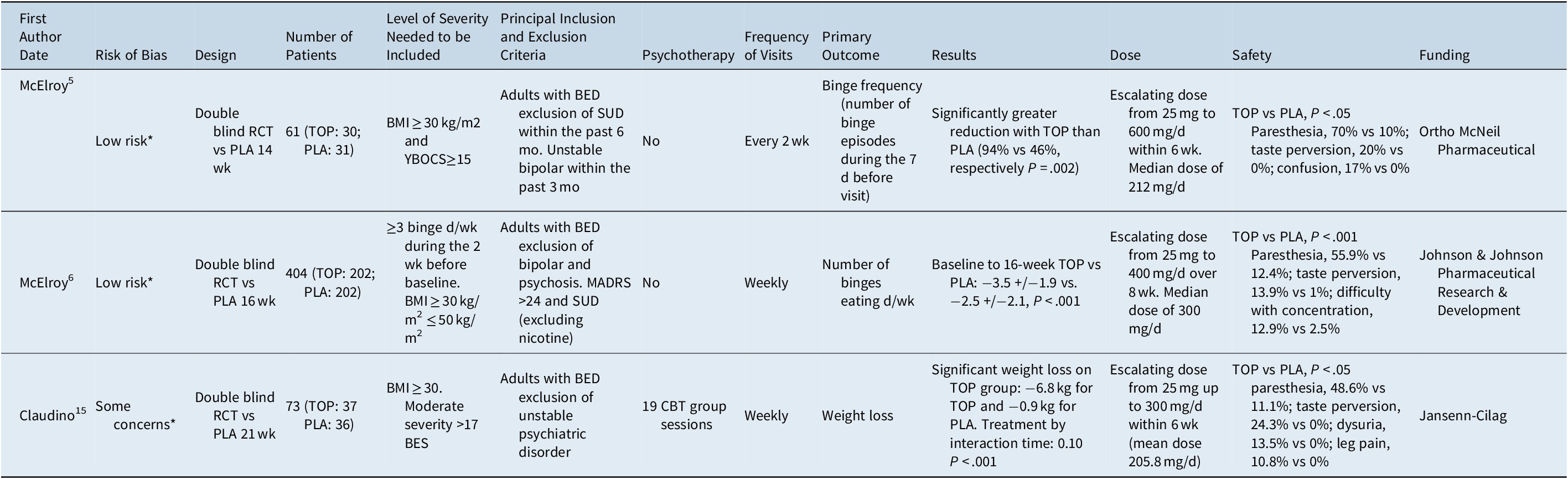
Topamax and Binge Eating Disorder: Efficacy and Side Effects
Topamax (topiramate) shows some promise in treating binge eating disorder (BED), but its use isn’t without potential drawbacks. Studies suggest it may reduce binge eating episodes and associated weight gain in certain individuals. However, the degree of benefit varies considerably.
One study showed a statistically significant reduction in binge eating frequency compared to a placebo group. Another demonstrated a positive effect on weight loss among BED patients taking Topamax, though the weight loss was modest. These findings aren’t universally replicated across all research, and more extensive trials are needed for definitive conclusions.
Side effects are a significant consideration. Commonly reported side effects include paresthesia (tingling or numbness), weight loss, cognitive impairment (including difficulty with concentration and memory), and kidney stones. The risk of kidney stones increases with higher doses. Gastrointestinal issues such as nausea and diarrhea also occur.
Important Note: Topamax is not FDA-approved specifically for BED. Its use in this context is considered off-label. A doctor should carefully weigh the potential benefits against the individual’s risk of side effects before prescribing it for BED.
Recommendations: If considering Topamax for BED, discuss all potential benefits and risks with your doctor or psychiatrist. They can assess your specific situation and determine if it’s an appropriate treatment option for you. Regular monitoring for side effects is also crucial.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Consult with a healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.
Managing Topamax Use in Patients with Eating Disorders: Clinical Guidance
Closely monitor patients for weight changes and electrolyte imbalances. Regular blood tests are crucial, especially potassium and sodium levels. Adjust Topamax dosage cautiously, prioritizing patient safety and stability. Consider a slower titration schedule to minimize side effects.
Regularly assess the patient’s eating patterns and mental health. Utilize validated eating disorder assessment tools to track progress objectively. Collaboration with a registered dietitian is recommended to address nutritional deficiencies and support healthy eating habits.
Provide comprehensive education about Topamax side effects, including potential weight loss and appetite suppression. Equip patients with strategies to manage these side effects, such as frequent small meals and adequate hydration. Encourage open communication about any concerns or changes in their condition.
Integrate Topamax management into a broader treatment plan addressing the underlying eating disorder. This plan should include therapy focused on cognitive behavioral techniques and other appropriate interventions for their specific eating disorder diagnosis. Regular multidisciplinary team meetings are valuable for coordinated care.
Document all medication changes, patient responses, and treatment plan modifications meticulously. Maintain clear and concise records for effective communication and continuity of care.
Recognize that individual responses to Topamax vary. Adjust treatment based on the patient’s specific needs and response, prioritizing their overall well-being.