Start with a low dose, typically 5-20mg daily, under your doctor’s guidance. This initial dose will target inflammation effectively while minimizing potential side effects. The specific starting dose depends greatly on your individual condition and severity of inflammation.
Dosage adjustments are common. Your physician will carefully monitor your progress and may increase the dose gradually if needed to achieve optimal anti-inflammatory results. Remember, increasing the dose should always be done under medical supervision, never independently.
Tapering off Prednisone is crucial to prevent rebound inflammation and other withdrawal symptoms. Your doctor will create a personalized tapering schedule, gradually decreasing your daily dose over several weeks or months. This slow reduction is vital for a safe transition.
Specific conditions require specific approaches. For example, autoimmune diseases often need higher doses and longer treatment periods than acute inflammatory conditions. Always follow your doctor’s prescribed regimen, tailored precisely to your medical history and current health needs.
Side effects are a real concern. Monitor for common side effects such as weight gain, mood changes, increased blood sugar, and fluid retention. Open communication with your doctor about any adverse reactions is paramount for safe and effective treatment.
- Prednisone Inflammation Dosage: A Detailed Guide
- Understanding Prednisone’s Role in Inflammation
- How Prednisone Affects the Body
- Dosage and Individual Responses
- Dosage Considerations Based on Inflammatory Condition
- Potential Side Effects and Management Strategies
- Common Side Effects
- Managing Side Effects
- Severe Side Effects
- Tapering Off Prednisone: A Safe Approach
Prednisone Inflammation Dosage: A Detailed Guide
Dosage depends entirely on the specific inflammation, its severity, and your individual health. Always follow your doctor’s prescription. There is no one-size-fits-all answer.
Common starting doses for adults often range from 5mg to 60mg daily, usually administered once daily in the morning. Higher doses might be necessary for severe inflammation, such as in cases of severe allergic reactions or autoimmune disorders. Lower doses are typical for less severe conditions like arthritis.
Important Note: Higher doses typically require a slow tapering-off process to avoid adrenal suppression and other side effects. Your doctor will create a personalized tapering schedule, gradually reducing your Prednisone intake over weeks or months. Abruptly stopping Prednisone can be harmful.
Specific conditions and dosage: Dosage varies significantly depending on the condition. For example, asthma might warrant a lower dose than a severe inflammatory bowel disease flare-up. Your doctor will carefully consider your medical history and current health to determine the appropriate starting dose and treatment plan.
Potential side effects include weight gain, increased blood sugar, mood changes, and increased risk of infections. Open communication with your physician about any side effects is paramount to managing your treatment effectively. Regular monitoring of blood pressure and blood sugar levels is often recommended, particularly with higher doses and extended treatment periods.
Children’s dosages are significantly lower and are always determined by a pediatrician considering the child’s weight and specific condition. Children’s treatment requires close supervision and monitoring for side effects.
This guide provides general information only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your physician or a qualified healthcare professional before starting, stopping, or changing your Prednisone dosage. They will assess your individual needs and create a safe and effective treatment plan.
Understanding Prednisone’s Role in Inflammation
Prednisone, a corticosteroid, powerfully reduces inflammation by acting on your body’s immune system. It works by decreasing the production of inflammatory substances like cytokines and prostaglandins, which cause swelling, pain, and redness. This suppression reduces the severity of inflammatory responses.
How Prednisone Affects the Body
Prednisone mimics the effects of cortisol, a hormone naturally produced by your adrenal glands. By increasing cortisol levels, it dampens your immune response, thereby reducing inflammation. The specific mechanism involves binding to receptors in cells, triggering changes in gene expression that lead to the decreased production of inflammatory mediators. This process significantly affects various inflammatory conditions, from allergies to autoimmune diseases.
Dosage and Individual Responses
Your doctor will determine the appropriate prednisone dosage based on your specific condition, its severity, and your overall health. Remember, individual responses to prednisone vary. Factors like age, weight, and the specific inflammatory process all influence how your body reacts. Close monitoring is necessary to adjust the dosage and minimize side effects.
Dosage Considerations Based on Inflammatory Condition
Prednisone dosage significantly varies depending on the specific inflammatory condition. For rheumatoid arthritis, initial daily doses often range from 7.5 to 60 mg, gradually tapering down as symptoms improve. Remember, this is a general guideline; your doctor will personalize your treatment.
In cases of lupus, the starting dose might be similar, but the maintenance dose and duration are highly individualized, guided by disease activity and response to treatment. Regular blood tests are crucial to monitor for side effects.
Asthma requires a different approach. Prednisone is usually prescribed for short bursts, often at higher doses (like 40-60 mg daily for a few days) during acute exacerbations to rapidly control inflammation. Long-term use isn’t generally recommended.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, may necessitate higher initial doses, possibly even exceeding 60mg daily, although this is less common. Treatment strategy hinges on individual disease severity and response. Again, close medical supervision is key.
Allergic reactions might only need a short course of low-dose prednisone, perhaps 20-40 mg daily for a few days, to manage inflammation and symptoms. The physician determines the appropriate duration and dose.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions meticulously. They will tailor the dosage and duration to your specific needs and carefully monitor your progress. Never alter your prednisone regimen without consulting your healthcare provider.
Potential Side Effects and Management Strategies
Prednisone, while effective for inflammation, carries potential side effects. Understanding these and employing management strategies is key to a safe treatment.
Common Side Effects
- Increased appetite and weight gain: Monitor your diet and calorie intake. Consider regular exercise to counteract this. Consult your doctor about nutritional guidance.
- Fluid retention (edema): Reduce salt intake. Wear compression stockings if advised by your doctor. Regular monitoring of weight is helpful.
- Mood changes (irritability, anxiety, depression): Open communication with your doctor is vital. They might adjust your dosage or recommend supportive therapies.
- Insomnia: Take your dose earlier in the day. Establish a relaxing bedtime routine. Discuss sleep aids with your doctor if needed.
- Increased blood sugar: Regular blood sugar monitoring is essential, especially if you have diabetes. Dietary adjustments might be necessary. Your doctor will guide you.
- Increased blood pressure: Regular monitoring is critical. Lifestyle changes, such as dietary adjustments and exercise, can help. Medication adjustments may be needed.
- Weakened bones (osteoporosis): Maintain adequate calcium and vitamin D intake. Weight-bearing exercise is beneficial. Your physician might recommend bone density testing.
- Increased risk of infection: Practice good hygiene and avoid contact with sick individuals. Report any signs of infection to your doctor immediately.
Managing Side Effects
- Dosage adjustment: Your doctor will carefully manage your dosage to minimize side effects while maximizing therapeutic benefits. They may prescribe the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration.
- Alternative therapies: In some cases, your doctor might integrate alternative therapies, like physical therapy or other anti-inflammatory medications, to minimize prednisone’s dosage and related side effects.
- Gradual tapering: Sudden cessation of prednisone can cause serious withdrawal symptoms. Your doctor will gradually reduce your dosage over time to prevent this.
- Regular monitoring: Regular check-ups with your physician are crucial for monitoring blood pressure, blood sugar, and other relevant parameters.
Severe Side Effects
While uncommon, severe side effects warrant immediate medical attention. These include severe allergic reactions (rash, swelling, difficulty breathing), stomach ulcers, and pancreatitis. Contact your doctor or seek immediate medical care if you experience these symptoms.
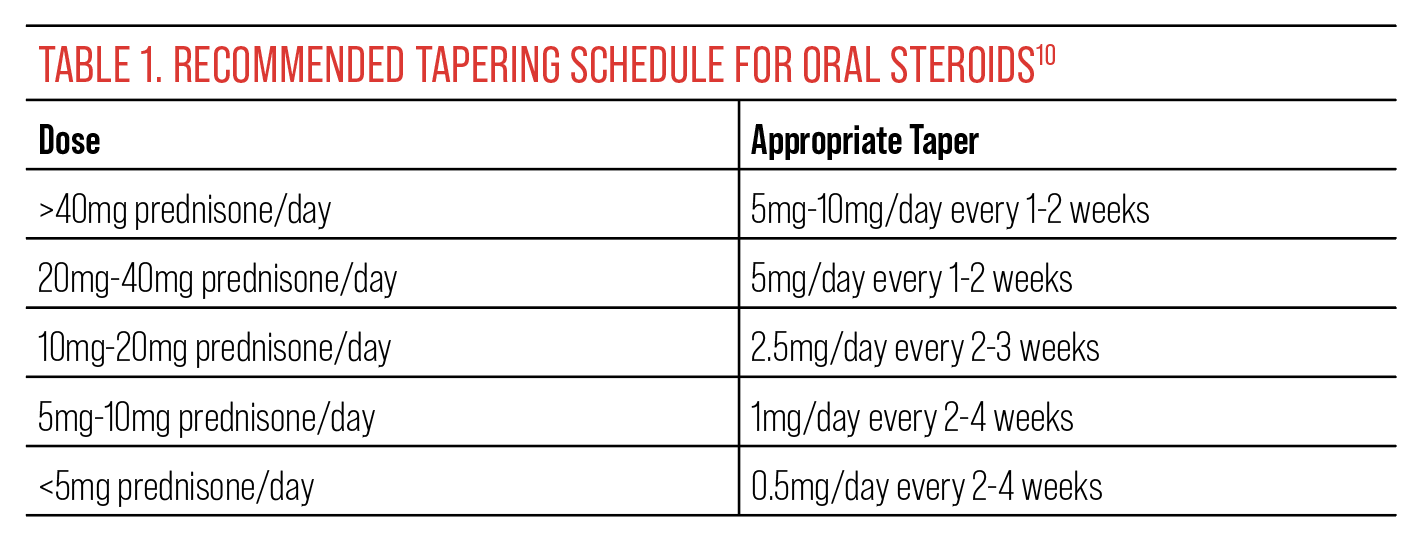
Tapering Off Prednisone: A Safe Approach
Never stop Prednisone suddenly. Your doctor will create a personalized tapering schedule, usually decreasing your dose gradually over weeks or months. This prevents adrenal insufficiency, a serious complication.
Common tapering schedules involve reducing your dose by 5-10mg every few days or weeks, depending on your initial dosage and your body’s response. Smaller reductions are often used for higher initial doses.
Monitor for withdrawal symptoms like fatigue, muscle weakness, joint pain, nausea, or dizziness. Report these symptoms immediately to your doctor. They might adjust your tapering schedule to minimize discomfort.
During the tapering process, maintain close communication with your doctor. Regular blood tests can monitor your adrenal function and help ensure a safe reduction of Prednisone. This proactive approach helps prevent complications and supports your overall health.
Remember, adherence to the prescribed schedule is key to successfully and safely reducing your Prednisone dosage. Your doctor’s guidance is your best resource throughout this process. Consistency is crucial for a positive outcome.
If you experience any concerning symptoms, contact your doctor promptly. They will help manage your withdrawal symptoms and ensure you remain comfortable and healthy.