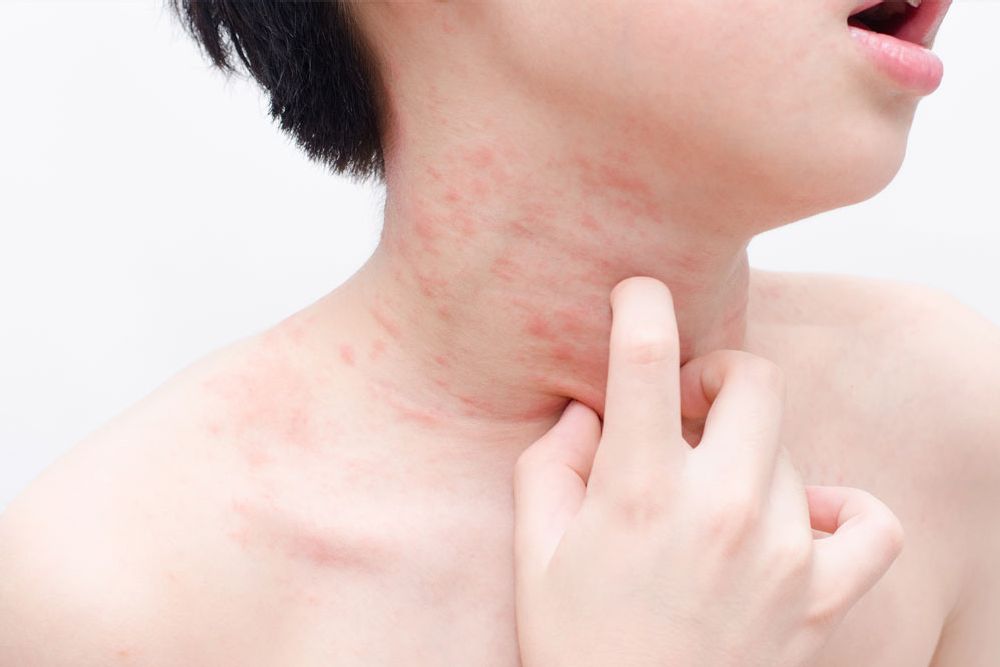
Experienced an amoxicillin rash? First, stop taking the medication immediately. This is crucial; continued use risks worsening the reaction. Then, contact your doctor or seek immediate medical attention if you experience difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or dizziness.
Amoxicillin rashes manifest differently. They can range from mild hives to more severe, blistering reactions. Identifying the rash’s characteristics – location, appearance (e.g., raised, flat, itchy), and associated symptoms – helps your doctor determine the severity and appropriate treatment.
Your doctor will likely recommend antihistamines to alleviate itching and inflammation. In severe cases, corticosteroids might be necessary. They may also suggest alternative antibiotics that won’t trigger the allergic response. Remember to always inform future healthcare providers about this allergy to avoid similar situations.
Prevention is key. Before taking amoxicillin again (if ever prescribed), discuss the allergy with your doctor. They might perform allergy testing to confirm the reaction and assess the risk of future exposure. Detailed medical history is important to manage allergies effectively.
- Amoxicillin Allergy Rash: A Detailed Guide
- Identifying an Amoxicillin Allergy Rash
- Rash Characteristics
- Differentiating from other conditions
- Differentiating Amoxicillin Rash from Other Skin Conditions
- Timing and Associated Symptoms
- Distinguishing Features
- Treatment Options for Amoxicillin-Induced Rash
- Managing Symptoms
- Alternative Antibiotics
- Severe Reactions
- Monitoring and Follow-up
- Medication Summary
- When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
- Prevention Strategies for Future Amoxicillin Reactions
- When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
- Severe Allergic Reaction Symptoms
- Less Severe, but Still Concerning, Symptoms
- Remember:
- Long-Term Management of Amoxicillin Allergy
Amoxicillin Allergy Rash: A Detailed Guide
See a doctor immediately if you develop a rash after taking amoxicillin. This is crucial for diagnosis and treatment.
Amoxicillin rashes range from mild to severe. Mild rashes often appear as itchy, red bumps. Severe reactions can include hives, swelling, and difficulty breathing – requiring immediate medical attention.
Several factors influence rash severity. Your individual sensitivity plays a key role. The dose of amoxicillin and duration of use also contribute.
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination and a review of your medical history. Blood tests may be needed to rule out other conditions.
Treatment focuses on managing symptoms. Antihistamines can alleviate itching. In severe cases, corticosteroids or epinephrine may be necessary.
Prevention involves identifying your allergy. If you’ve experienced an amoxicillin rash, avoid future use. Discuss alternative antibiotics with your doctor.
Always inform your doctor and pharmacist about all your allergies, including medication allergies.
Proper documentation of your allergic reaction is vital for future medical care. Keep records of your symptoms and treatment.
While many experience mild reactions, some develop severe allergic responses. Understanding the potential risks is key to safe medication use.
Remember, prompt medical attention is paramount for any severe allergic reaction. Don’t hesitate to seek immediate care.
Identifying an Amoxicillin Allergy Rash
Examine the rash carefully. Location, appearance, and accompanying symptoms provide crucial clues.
Rash Characteristics
- Timing: Did the rash appear shortly after starting amoxicillin? A reaction usually develops within days, sometimes hours.
- Location: Is it widespread or concentrated in specific areas? Common areas include the torso, face, and extremities.
- Appearance: Note the color (red, pink, hives), texture (raised, flat, bumpy), and shape (circular, blotchy). Take photos for your doctor.
- Itching: Intense itching often accompanies allergic rashes.
- Swelling: Swelling of the face, lips, or tongue indicates a more serious reaction requiring immediate medical attention. This is a sign of angioedema.
Other symptoms to consider alongside the rash:
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Feeling faint or lightheaded
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhea
Differentiating from other conditions
A viral infection can sometimes mimic an amoxicillin allergy. Fever, sore throat, and other cold symptoms help distinguish between the two. If unsure, contact your doctor for proper diagnosis. Non-allergic reactions can also occur. These can cause a less severe rash that disappears once the medication is stopped.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional for any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment and before undertaking a new health care regimen.
Differentiating Amoxicillin Rash from Other Skin Conditions
Amoxicillin rashes typically present as a maculopapular eruption – small, flat, red spots that may become raised. They often appear on the trunk and spread outwards. However, many other skin conditions mimic this, making accurate diagnosis challenging. Pay close attention to timing: an amoxicillin rash usually appears within 1-7 days of starting the antibiotic. This temporal relationship is crucial.
Timing and Associated Symptoms
Consider other symptoms accompanying the rash. Amoxicillin reactions frequently involve itching, but not always. Fever, swelling, and difficulty breathing indicate a more serious allergic reaction requiring immediate medical attention. A simple rash without these additional symptoms is less alarming, but still warrants a doctor’s evaluation.
Distinguishing Features
Measles, rubella, and chickenpox cause rashes with more distinct characteristics: Measles features Koplik’s spots in the mouth before the rash. Rubella often starts on the face and spreads downwards. Chickenpox presents with intensely itchy blisters. Urticaria (hives) presents as raised welts and often appears suddenly. These contrasting features help differentiate them from an amoxicillin reaction. If you experience any skin reaction after taking amoxicillin, consult your doctor for diagnosis and guidance. A medical professional can help determine the cause of your rash.
Treatment Options for Amoxicillin-Induced Rash
First, discontinue amoxicillin immediately. This is the most crucial step in managing the rash. Contact your doctor or allergist for guidance.
Managing Symptoms
Your doctor might recommend antihistamines like diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or cetirizine (Zyrtec) to alleviate itching. For more severe itching or inflammation, topical corticosteroids such as hydrocortisone cream can provide relief. Cool compresses applied to the affected area can also soothe the skin.
Alternative Antibiotics
If the rash was caused by amoxicillin, your doctor will prescribe an alternative antibiotic that doesn’t belong to the penicillin family. Common alternatives include azithromycin or cephalexin. The choice depends on the infection being treated.
Severe Reactions
In rare cases, an amoxicillin rash can indicate a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis). This requires immediate medical attention. Symptoms include difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, or tongue, and a rapid heartbeat. Seek emergency medical care if you experience these symptoms.
Monitoring and Follow-up
Regular follow-up appointments with your doctor are vital to monitor the rash’s healing and ensure the chosen treatment is effective. Your doctor may adjust the treatment plan based on your progress.
Medication Summary
| Medication Type | Examples | Use |
|---|---|---|
| Antihistamine | Diphenhydramine, Cetirizine | Reduce itching |
| Topical Corticosteroid | Hydrocortisone cream | Reduce inflammation |
| Alternative Antibiotic | Azithromycin, Cephalexin | Treat underlying infection |
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Always seek immediate medical attention if you experience any signs of anaphylaxis or if the rash worsens significantly or spreads rapidly.
Prevention Strategies for Future Amoxicillin Reactions
Avoid amoxicillin completely. This is the most reliable way to prevent future reactions. Discuss alternative antibiotics with your doctor.
Inform all healthcare providers of your allergy. Wear a medical alert bracelet or necklace clearly stating your amoxicillin allergy.
Carry an epinephrine auto-injector (EpiPen) if prescribed by your doctor. Know how to use it and when to seek immediate medical attention.
Document all allergic reactions. Keep a detailed record of symptoms, dates, and treatments. Share this information with your doctor and pharmacist.
Discuss allergy testing with your allergist. Skin prick tests or blood tests can help identify the specific component of amoxicillin causing the reaction.
Learn the symptoms of anaphylaxis. Anaphylaxis is a severe, life-threatening allergic reaction requiring immediate medical attention. Recognize symptoms like difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, and a rapid heartbeat.
Always read medication labels carefully. Check for amoxicillin in combination medications. Pay close attention to the ingredients list.
If you experience a mild reaction (rash only), discuss with your physician the possibility of desensitization. This process gradually introduces small doses of amoxicillin to build tolerance, but it carries risks.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
If you experience difficulty breathing, swelling of your face, lips, or tongue, or a severe drop in blood pressure after taking amoxicillin, seek immediate medical help. This indicates a severe allergic reaction, potentially life-threatening.
Severe Allergic Reaction Symptoms
- Hives spreading rapidly across your body
- Wheezing or shortness of breath
- Swelling of your throat or difficulty swallowing
- Rapid heartbeat
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Loss of consciousness
These symptoms require urgent medical care. Call emergency services (911 in the US or your local equivalent) immediately.
Less Severe, but Still Concerning, Symptoms
While not immediately life-threatening, some symptoms warrant a doctor’s visit. These include:
- A widespread rash with significant itching or discomfort.
- Persistent nausea or vomiting.
- High fever.
- Symptoms persisting for more than a few days despite stopping amoxicillin.
Contact your doctor or other healthcare provider if you experience any of these less severe reactions. They can assess your condition and recommend the best course of action.
Remember:
This information is for guidance only and doesn’t replace professional medical advice. Always consult a doctor or other qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns.
Long-Term Management of Amoxicillin Allergy
Avoid amoxicillin and related penicillin antibiotics. This includes ampicillin, dicloxacillin, and piperacillin.
Inform all your healthcare providers of your allergy. Wear a medical alert bracelet or necklace clearly stating your allergy.
Carry an epinephrine auto-injector (like an EpiPen) if your allergy is severe. Learn how to use it properly.
Discuss alternative antibiotics with your doctor. Appropriate substitutes exist for various infections.
If you experience a reaction to a new medication, seek immediate medical attention.
Regularly review your allergy status with your doctor. Allergies can change over time.
Keep a detailed record of any allergic reactions, including symptoms and the medication involved. This helps your doctor effectively manage your allergies in the future.
Understand your allergy symptoms. Knowing what to watch for is key to early intervention.