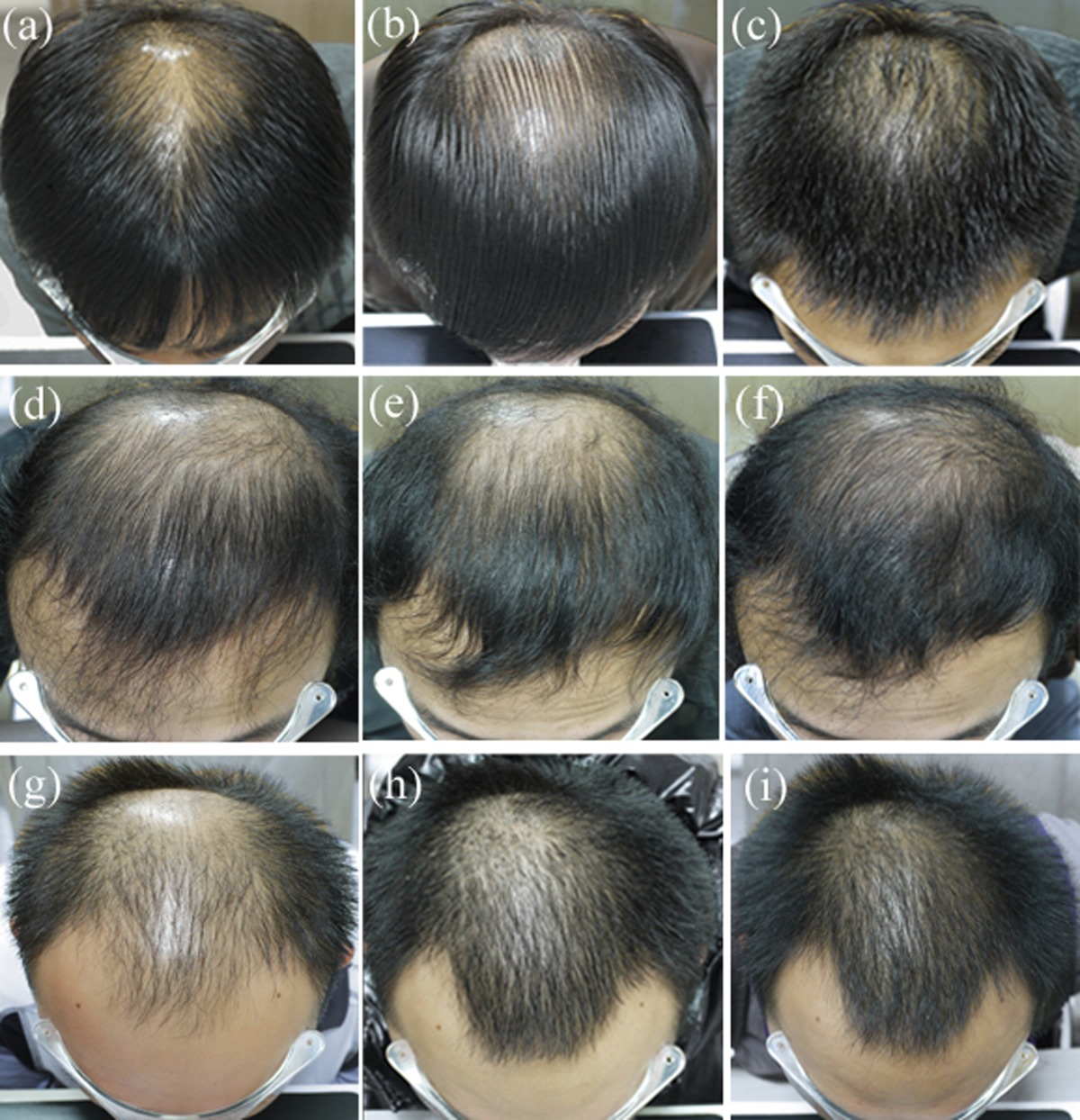
Propecia, or finasteride, can help regrow hair for many men, but its effectiveness varies. Hair regrowth isn’t guaranteed, and results depend on factors like your age, the extent of hair loss, and your overall health. Stopping treatment often leads to hair loss resuming, so consistent use is key.
Studies show significant hair regrowth in a substantial percentage of men using Propecia. However, individual responses differ greatly. You might experience noticeable improvement, minimal change, or no change at all. Consulting a dermatologist or trichologist for personalized advice before starting treatment is crucial to understand your potential outcome and manage expectations.
Important Note: Propecia’s effects are generally maintained only during consistent use. Discontinuing the medication often results in a return to previous hair loss patterns. Discuss long-term management options with your doctor to create a plan that works best for you. They can also help determine if Propecia is the right choice for your individual circumstances.
Before starting any treatment, always seek professional medical guidance. Your doctor can accurately assess your hair loss, discuss potential risks and benefits of Propecia, and recommend the most suitable approach for your specific situation. They’ll consider your medical history and other factors to make informed decisions.
- Does Hair Grow Back With Propecia?
- Who Benefits Most?
- What to Expect:
- Important Considerations:
- Propecia’s Role in Hair Regrowth
- Understanding Propecia’s Mechanism of Action
- Who is a Suitable Candidate for Propecia?
- Specific Requirements and Considerations
- Expected Results and Timeframe for Hair Regrowth
- What to Expect
- Individual Variations
- Maintaining Results
- Consult Your Doctor
- Potential Side Effects and Risks Associated with Propecia
- Comparing Propecia to Other Hair Loss Treatments
- Minoxidil (Rogaine)
- Hair Transplantation
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
- Maintaining Hair Growth After Propecia Treatment
Does Hair Grow Back With Propecia?
Yes, Propecia (finasteride) can regrow hair for many men. However, it’s crucial to understand that results vary.
Who Benefits Most?
- Men with mild to moderate male pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia).
- Men who start treatment early, before significant hair loss occurs.
- Men who consistently take the medication as prescribed.
Propecia works by inhibiting the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone that contributes to hair follicle miniaturization and hair loss. This allows for the potential regrowth of miniaturized hairs and prevents further hair loss for many users.
What to Expect:
- Initial Results: You might see some hair regrowth within three to six months, but it’s usually gradual.
- Maximum Results: Optimal results typically take a year or more to become apparent.
- Maintenance: Continued use is necessary to maintain any hair regrowth achieved. Stopping treatment often leads to hair loss resuming.
- Individual Variation: Response to Propecia is highly individual. Some men experience significant regrowth, others see only minimal improvement, and some see no change at all.
Important Considerations:
- Side Effects: Potential side effects include decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and decreased ejaculate volume. These are generally mild and temporary for most men but warrant discussion with a doctor.
- Consultation: Before starting Propecia, consult a dermatologist or healthcare professional to discuss your hair loss and determine if this medication is right for you.
- Alternative Treatments: Other hair loss treatments, such as minoxidil (Rogaine), hair transplantation, or low-level laser therapy, may be considered alone or in conjunction with Propecia. Your doctor can help determine the best approach for your specific needs.
Propecia’s Role in Hair Regrowth
Propecia doesn’t miraculously create new hair follicles. Instead, it helps existing miniaturized follicles to grow stronger and larger, producing thicker hairs. This process leads to noticeable improvement in hair density and appearance for many who use it.
Understanding Propecia’s Mechanism of Action
Propecia, containing finasteride, works by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase. This enzyme converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone strongly linked to male pattern baldness.
By blocking 5-alpha-reductase, Propecia significantly reduces DHT levels in the scalp. Lower DHT levels slow hair miniaturization–the process where hair follicles shrink, producing thinner, weaker hairs.
This reduction in DHT allows for the potential regrowth of existing miniaturized hair follicles and maintenance of existing larger, healthier follicles. The effects are most pronounced in men with mild to moderate hair loss.
It’s crucial to remember Propecia’s effects are generally maintained only during continued use. Stopping treatment typically leads to a gradual return to the previous hair loss pattern.
Individual responses vary; some men experience significant hair regrowth, while others see only modest improvement or stabilization of hair loss. Results depend on factors like age, genetic predisposition, and duration of treatment.
Who is a Suitable Candidate for Propecia?
Men experiencing male pattern baldness, specifically androgenetic alopecia, are generally suitable candidates. This means you’re experiencing hair thinning or receding hairline, typically on the crown and temples. Propecia is most effective for men who are still relatively young and have not yet experienced significant hair loss. Optimal results are often seen in men aged 18-41.
Specific Requirements and Considerations
You should be in good overall health. Discuss any existing medical conditions with your doctor before starting Propecia, as it may interact with certain medications. Pregnant women and children should avoid contact with Propecia, as it can cause birth defects. If you’re planning on fathering a child, discuss the risks with your doctor. Finally, remember that Propecia works best when started early and continued consistently. Regular blood tests may be required for monitoring. Results vary greatly depending on genetics and individual response. It is not a cure for baldness, but can help slow or stop hair loss in many cases.
Expected Results and Timeframe for Hair Regrowth
Propecia, or finasteride, helps many men regrow hair, but results vary. Expect gradual improvement, not overnight miracles. You might see some initial shedding before new growth appears, which is normal. Don’t get discouraged!
What to Expect
Most men notice improvement within 3-6 months of consistent use. Significant changes usually appear after a year. Continued use is key for maintaining results. Hair growth may slow down after the first two years, but most men retain the benefits of treatment with continued use.
Individual Variations
Your personal response depends on factors like age, genetics, and the extent of hair loss. Some men experience substantial regrowth, others see modest improvements. Some may not see any changes at all. Open communication with your doctor is vital to assess your progress.
| Timeframe | Expected Results |
|---|---|
| 3-6 months | Possible initial shedding, some men may notice subtle improvements. |
| 6-12 months | Noticeable hair regrowth for many users. |
| 12+ months | Maintenance phase; continued regrowth but at a slower rate. |
Maintaining Results
Stopping Propecia typically leads to hair loss resuming at the previous rate. Continued use is usually needed to maintain the gains achieved. Discuss long-term treatment plans with your doctor. This should include regular monitoring of your progress and any potential side effects.
Consult Your Doctor
Propecia isn’t a solution for everyone. Your physician can determine if it’s appropriate for you and monitor your progress. They can also advise on alternative treatments if needed.
Potential Side Effects and Risks Associated with Propecia
Propecia, while effective for many, carries potential side effects. The most common include decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and ejaculation problems. These typically affect a minority of users, and often resolve upon cessation of treatment. However, some men experience these issues persistently.
Less common, but serious, side effects include gynecomastia (breast enlargement) and depression. Reports of these are relatively infrequent, but warrant immediate medical attention if experienced.
Important Note: Propecia is not intended for women or children due to the potential risk of birth defects. Women who are pregnant or might become pregnant should avoid contact with crushed or broken Propecia tablets.
Before starting Propecia, consult your doctor. They can assess your suitability for the medication and discuss potential risks and benefits specific to your health profile. Open communication with your physician is critical for managing any side effects that may arise.
Regular check-ups are recommended while taking Propecia to monitor for any adverse reactions. Your doctor can adjust the treatment plan or suggest alternatives if necessary.
Comparing Propecia to Other Hair Loss Treatments
Propecia (finasteride) is a powerful medication, but it’s not the only option for hair loss. Let’s compare it to other common treatments to help you decide what’s right for you.
Minoxidil (Rogaine)
- Mechanism: Stimulates hair growth directly on the scalp.
- Application: Topical solution or foam.
- Pros: Available over-the-counter, relatively mild side effects.
- Cons: Less effective than finasteride for many, requires consistent application for results.
- Comparison to Propecia: While effective for some, Minoxidil generally produces less dramatic hair regrowth than Propecia, particularly in cases of advanced male pattern baldness. Often used in conjunction with Propecia for maximized results.
Hair Transplantation
- Mechanism: Moves hair follicles from a donor area to balding areas.
- Application: Surgical procedure.
- Pros: Permanent results in the transplanted area.
- Cons: Expensive, requires downtime for recovery, potential for scarring.
- Comparison to Propecia: A very different approach. Propecia prevents further hair loss and may stimulate regrowth, whereas hair transplantation directly addresses existing baldness. Often a good choice *after* trying medication like Propecia, or for individuals with significant hair loss.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
- Mechanism: Uses low-level lasers to stimulate hair follicles.
- Application: At-home devices or in-clinic treatments.
- Pros: Non-invasive, relatively painless.
- Cons: Limited evidence of effectiveness compared to medication, can be costly.
- Comparison to Propecia: LLLT is often considered an adjunct therapy, meaning it can be used alongside Propecia or Minoxidil to potentially boost results. It’s not a standalone solution for most individuals experiencing significant hair loss.
Choosing the right treatment depends on several factors, including the severity of your hair loss, your budget, and your personal preferences. Consult a dermatologist or hair loss specialist for personalized advice.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
- Mechanism: Involves injecting concentrated platelets from your own blood into the scalp.
- Application: Injections administered by a medical professional.
- Pros: Relatively minimally invasive, uses your body’s natural healing processes.
- Cons: Effectiveness is still under investigation; multiple treatments are usually needed, and it’s not a cure for hair loss.
- Comparison to Propecia: Similar to LLLT, often used as a supplementary treatment alongside medication, offering potential benefits when added to a broader hair loss management plan.
Maintaining Hair Growth After Propecia Treatment
Continue taking Propecia as prescribed by your doctor. Consistent use is key to maintaining results.
Adopt a healthy lifestyle. This includes a balanced diet rich in protein and vitamins, regular exercise, and sufficient sleep. These contribute to overall hair health.
Manage stress levels. High stress can negatively impact hair growth. Explore stress-reduction techniques like meditation or yoga.
Consider minoxidil (Rogaine). Used in conjunction with Propecia, it can enhance hair growth and reduce shedding. Always consult your doctor before starting any new medication.
Maintain good hair hygiene. Use gentle shampoos and conditioners, and avoid harsh styling products that can damage your hair.
Schedule regular check-ups with your dermatologist or doctor. They can monitor your progress and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
Be patient. Results take time, and hair growth isn’t always linear. Maintain a positive outlook and continue following your doctor’s recommendations.
Explore low-level laser therapy (LLLT). Some studies suggest LLLT can stimulate hair follicles and promote growth. Discuss this option with your doctor.
Avoid aggressive hair styling techniques. Reduce the use of heat styling tools and avoid tight hairstyles that can pull on your hair and cause damage.