Finding the right Risperdal dosage is crucial for effective treatment. Your doctor will determine the appropriate starting dose based on your specific condition and individual needs. Common starting doses for adults range from 1-6 mg daily, often adjusted gradually as needed. Remember, this is a general guideline; individual needs vary significantly.
Children and adolescents will receive different dosages, carefully tailored to their weight and age. Precise dosing instructions will be provided by your child’s physician. Close monitoring of side effects is vital, particularly for younger patients. Always follow your doctor’s prescribed schedule precisely.
Dosage adjustments are common. Your doctor may increase or decrease your dose depending on your response to treatment and the presence of any side effects. Regular check-ups allow for careful monitoring and appropriate modifications. Open communication with your healthcare provider ensures optimal treatment.
Never adjust your Risperdal dosage without consulting your doctor. Sudden changes can have adverse consequences. If you experience any unexpected side effects, report them to your doctor immediately. Your safety and well-being are paramount.
- Dosages of Risperdal: A Detailed Guide
- Risperdal Dosage for Schizophrenia
- Risperdal Dosage for Bipolar Disorder
- Dosage Adjustments
- Maintenance Dosage
- Important Considerations
- Monitoring Side Effects
- Risperdal Dosage for Irritability Associated with Autism
- Adjusting Risperdal Dosage: Factors to Consider
- Patient-Specific Factors
- Response to Treatment
- Dosage Adjustment Strategies
- Specific Considerations for Children and Adolescents
- Risperdal Dosage for Children and Adolescents
- Potential Side Effects and Dosage Adjustments
- Managing Side Effects
- Dosage Adjustments
- Monitoring and Follow-up
- Specific Considerations
- Monitoring Risperdal Treatment
Dosages of Risperdal: A Detailed Guide
Risperdal dosages vary significantly depending on the individual’s condition and response to treatment. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. This guide provides general information; it’s not a substitute for professional medical advice.
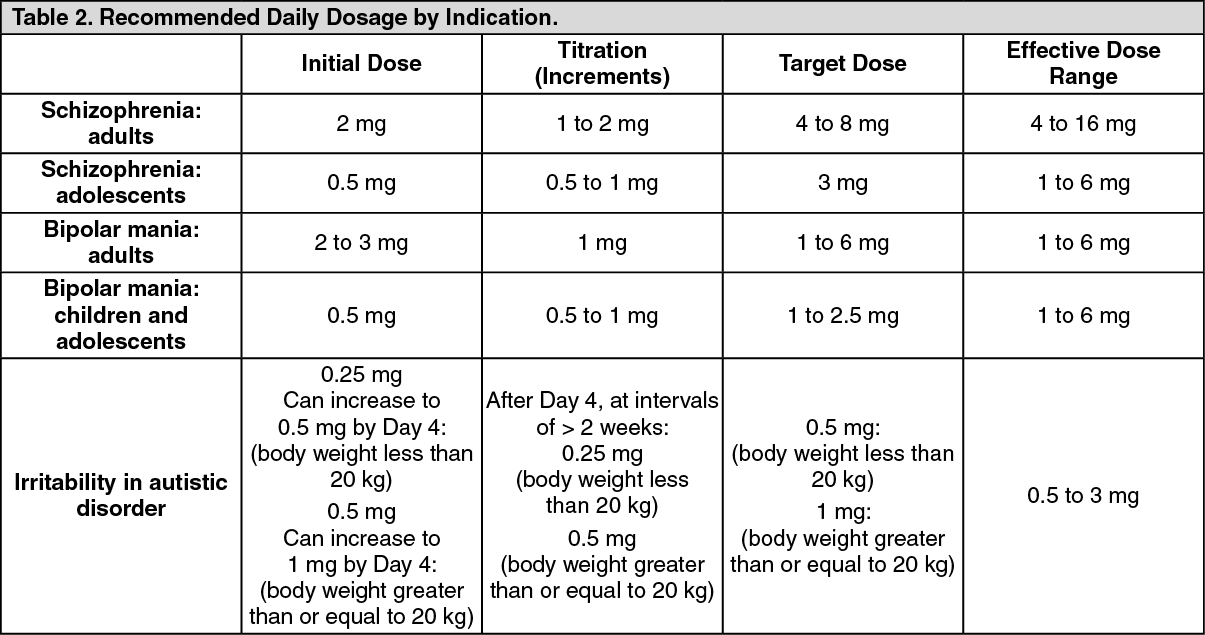
For schizophrenia, the typical starting dose is 2 mg daily, which may be gradually increased to 6 mg daily. Some patients may benefit from higher doses, up to 16 mg daily, while others may require lower doses. Maintenance therapy often involves lower dosages than initial treatment.
In bipolar disorder, Risperdal is often prescribed at lower dosages. A common starting point is 1-3 mg daily, potentially adjusted based on individual response. Dosages for this condition rarely exceed 6 mg daily.
For irritability associated with autism spectrum disorder, dosages are generally lower, typically starting at 0.5 mg daily and titrated upwards, but rarely exceeding 16 mg daily. Careful monitoring is critical.
Dosage adjustments should be made gradually to minimize side effects. Common side effects include weight gain, drowsiness, and movement disorders. Your physician will closely monitor your progress and adjust your dosage as needed.
For elderly patients and those with impaired renal or hepatic function, lower starting doses and slower titration are often recommended due to increased risk of side effects.
Never abruptly stop taking Risperdal without consulting your doctor. Stopping abruptly can lead to withdrawal symptoms. Your doctor will guide you on a safe and gradual discontinuation process if needed.
Remember, this information is for educational purposes only. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice regarding Risperdal dosage and treatment.
Risperdal Dosage for Schizophrenia
Treatment typically begins with a low dose, often 2 mg daily, gradually increased based on individual response and tolerability. Doctors closely monitor patients for efficacy and side effects.
Typical starting dose: 2-4 mg daily.
Maintenance dose: This varies greatly, ranging from 4 mg to 16 mg daily, or even higher in some cases. The appropriate dosage depends on several factors, including the severity of symptoms, patient response, and potential side effects.
Dose adjustments: Increases are usually made in increments of 1-2 mg every 1-2 days, with careful monitoring. The goal is to find the lowest effective dose that manages symptoms.
Maximum dose: While Risperdal has a high maximum dose, exceeding 16 mg daily is infrequent and usually only considered in severe cases unresponsive to lower doses. This decision requires careful consideration by a psychiatrist.
Important Note: This information is for general knowledge only and should not be considered medical advice. Dosage and treatment should always be determined and managed by a qualified healthcare professional. They will assess individual needs and adjust the medication accordingly. Regular monitoring is vital.
Risperdal Dosage for Bipolar Disorder
Treatment for bipolar disorder with Risperdal (risperidone) typically begins with a low dose and is gradually increased as needed. Initial doses often range from 1 to 3 mg daily, taken once or twice a day. Your doctor will carefully monitor your response and adjust the dosage accordingly.
Dosage Adjustments
Dosage adjustments depend on individual response and tolerance. Higher doses, up to 6 mg daily, may be used for some patients, but this requires careful monitoring for side effects. The maximum recommended daily dose is generally 16 mg, though this is rarely reached.
Maintenance Dosage
Once the optimal dose is achieved to control symptoms, a maintenance dose is established to prevent relapse. This can vary greatly from individual to individual. Your physician will guide you through the appropriate maintenance strategy.
Important Considerations
| Factor | Impact on Dosage |
|---|---|
| Patient Age | Lower starting doses are often recommended for older adults. |
| Other Medications | Interactions with other medications can influence Risperdal dosage. Full disclosure of all medications is crucial. |
| Kidney or Liver Function | Impaired kidney or liver function may require dose adjustments. |
Monitoring Side Effects
Regular monitoring for side effects is paramount. Common side effects include weight gain, drowsiness, dizziness, and movement disorders. Report any concerning side effects to your doctor immediately. They may adjust the dosage or consider alternative treatment options.
Risperdal Dosage for Irritability Associated with Autism
Risperdal (risperidone) is sometimes prescribed off-label to manage irritability in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder. Dosage is highly individualized and depends on factors like age, weight, and the severity of symptoms. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely.
Typically, treatment begins with a low dose and gradually increases as needed, under close medical supervision. The process involves careful monitoring for both efficacy and potential side effects.
- Initial Dosage: For children and adolescents, a starting dose might be 0.25mg to 0.5mg once or twice daily.
- Dosage Increases: Increases are usually small increments, often 0.5mg per day or less. Doctors carefully assess the response and side effects before adjusting the dose. The maximum daily dose varies depending on patient factors and is determined by the prescribing physician.
- Maintenance Dosage: The maintenance dose will be the lowest effective dose that manages irritability while minimizing side effects.
Important Considerations:
- Regular monitoring of weight and height is necessary, as Risperdal can cause weight gain.
- Close observation for extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) like muscle stiffness, tremors, or involuntary movements is vital.
- Blood tests may be recommended to monitor blood sugar and lipid levels.
- Risperdal is not a first-line treatment for irritability in autism and should only be used after other interventions have been considered.
- Always discuss potential side effects with your doctor and immediately report any concerning changes in your child’s behavior or health.
This information is for educational purposes only and should not substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage and treatment plan for your specific situation.
Adjusting Risperdal Dosage: Factors to Consider
Always adjust Risperdal dosage under the close supervision of a psychiatrist or other qualified healthcare professional. Never alter your dosage independently.
Patient-Specific Factors
- Age: Dosage adjustments are frequently needed based on age, particularly in children and older adults. Lower starting doses are often prescribed for these groups.
- Weight: Body weight significantly influences medication metabolism. Higher weight may necessitate higher doses, while lower weight may require lower doses.
- Kidney and Liver Function: Impaired kidney or liver function can affect how the body processes Risperdal. Dosage modifications are commonly required to prevent adverse effects.
- Other Medications: Interactions with other drugs can alter Risperdal’s effectiveness and side effects. Your doctor needs a complete medication list to manage potential conflicts.
- Pre-existing medical conditions: Certain medical conditions such as cardiovascular disease or diabetes might influence the decision on dosage and require close monitoring.
Response to Treatment
- Symptom Improvement: Dosage increases might be considered if symptoms are inadequately controlled at the current dose. However, increases should be gradual.
- Side Effects: If side effects are significant, the doctor may reduce the dosage or adjust the medication schedule. Common side effects include weight gain, drowsiness, and movement disorders.
- Monitoring: Regular blood tests and clinical assessments are crucial to monitor both effectiveness and potential adverse effects. Adjustments are often guided by these results.
Dosage Adjustment Strategies
Dosages are typically adjusted gradually, usually in small increments, to optimize therapeutic benefit and minimize side effects. Your doctor will create a personalized plan, taking into account all the factors mentioned above. Open communication with your healthcare provider about any symptoms, concerns, or improvements is essential for successful Risperdal management.
Specific Considerations for Children and Adolescents
Treatment for children and adolescents requires extra care due to their ongoing development. The starting dose is typically lower, and increases are made gradually under strict medical supervision. Regular monitoring for growth and development is critical.
Risperdal Dosage for Children and Adolescents
Risperdal dosage for children and adolescents varies significantly depending on the specific condition being treated, the individual’s weight, and their response to medication. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely.
For autism spectrum disorder, initial dosages typically range from 0.25 mg to 0.5 mg daily, gradually increasing as needed under medical supervision. The maximum recommended daily dose is generally 4 mg.
In treating irritability associated with autistic disorder, initial dosages are often lower, starting at 0.5 mg daily and incrementally increasing based on the child’s response and tolerance. Again, close monitoring by a healthcare professional is crucial.
For schizophrenia in adolescents, starting doses are usually lower than those for adults, often beginning at 0.5 mg to 1 mg daily. The maximum dose may vary, depending on individual needs and response to treatment.
Remember, precise dosing instructions will come directly from your child’s psychiatrist or pediatrician. Regular monitoring of potential side effects is necessary. Immediately report any concerning symptoms to your healthcare provider. Dosage adjustments are common during treatment and depend on clinical response.
This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with your child’s doctor before starting or changing any medication.
Potential Side Effects and Dosage Adjustments
Risperdal, like other antipsychotics, can cause side effects. Common ones include weight gain, drowsiness, dizziness, and tremors. Less common, but serious, side effects include tardive dyskinesia (involuntary movements), neuroleptic malignant syndrome (a rare but potentially fatal condition), and increased risk of diabetes. Monitor for these carefully.
Managing Side Effects
If you experience side effects, contact your doctor immediately. They may adjust your dosage or prescribe medication to manage specific symptoms. For example, weight gain might be addressed through dietary changes and exercise, while drowsiness could be mitigated with a modified dosing schedule. Remember, open communication with your healthcare provider is key.
Dosage Adjustments
Dosage adjustments are typically made gradually. Your doctor will carefully monitor your response to treatment and adjust your dose accordingly. Factors influencing dosage include your age, weight, overall health, and response to the medication. Never change your dosage without consulting your doctor. Starting with a low dose and gradually increasing it is standard practice to minimize side effects.
Monitoring and Follow-up
Regular blood tests may be necessary to monitor for potential side effects and ensure your treatment is effective. Consistent follow-up appointments with your psychiatrist are also important. These check-ups allow your doctor to assess your progress, adjust your medication as needed, and address any concerns you may have. Active participation in your treatment plan is crucial for optimal results.
Specific Considerations
Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as heart problems or seizures, may require careful monitoring and dosage adjustments. Always inform your doctor about your complete medical history, including any current medications you are taking. This allows for a tailored treatment plan that minimizes potential risks.
Monitoring Risperdal Treatment
Regularly monitor weight, blood pressure, and blood sugar levels. Check these at least monthly, especially during the initial phases of treatment.
Closely observe for signs of tardive dyskinesia (TD), a potentially irreversible movement disorder. Look for involuntary movements of the face, mouth, or limbs. Report any unusual movements to your doctor immediately.
Track potential side effects such as drowsiness, dizziness, or constipation. Document frequency and severity to help your doctor adjust medication if needed. Consider keeping a journal to record observations.
Monitor for metabolic changes, such as increased cholesterol or triglycerides. Regular blood tests are necessary to detect these. Discuss lifestyle modifications with your doctor to manage these risks.
Assess the effectiveness of Risperdal in managing symptoms. Work closely with your healthcare provider to evaluate improvement in target symptoms and adjust dosage as needed. Open communication is vital.
Remember: This information is for guidance only. Always follow your doctor’s specific instructions and attend all scheduled appointments. They will tailor monitoring to your individual needs and circumstances.
Consult your doctor or pharmacist for any concerns or questions about your Risperdal treatment.