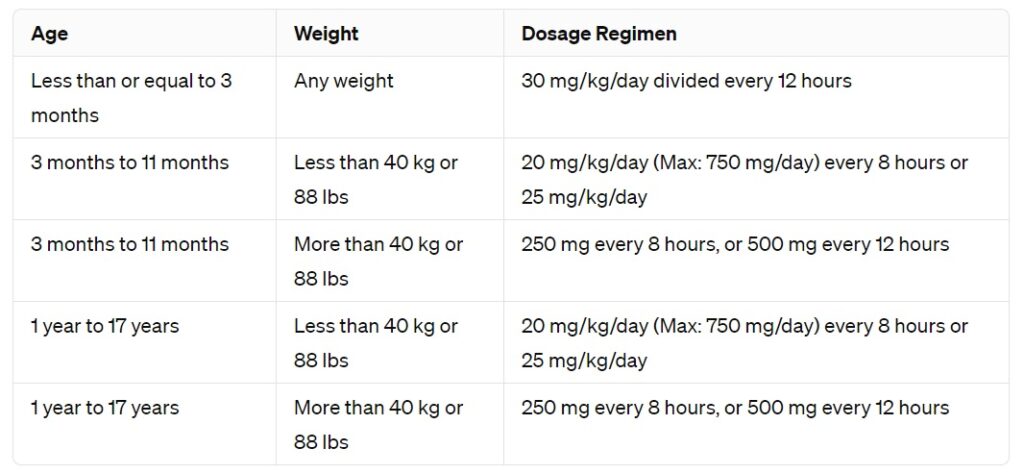
The correct amoxicillin dose for your child depends entirely on their weight and age. Always follow your doctor’s instructions, as they will tailor the prescription to your child’s specific needs. Never guess the dosage; inaccurate dosing can impact treatment effectiveness.
For instance, a typical dosage might range from 20-40 mg per kilogram of body weight per day, administered in two or three divided doses. A doctor will calculate the precise amount based on your child’s weight. This usually translates to a specific number of milliliters or milligrams of the suspension or tablet form.
Always check the medication label carefully and use the measuring device provided (like an oral syringe) to ensure accurate measurement. Never use household spoons, as their volumes are inconsistent. If you have any doubts or questions about the dosage, immediately contact your doctor or pharmacist for clarification.
Remember: This information is for guidance only and does not replace professional medical advice. Consulting your pediatrician is paramount for accurate diagnosis and treatment. They can accurately assess your child’s condition and prescribe the safest and most effective amoxicillin dosage.
- Usual Dose of Amoxicillin for Children
- Determining Your Child’s Weight Accurately
- Calculating the Correct Amoxicillin Dosage Based on Weight
- Understanding Amoxicillin Suspension Concentration
- Administering Amoxicillin Safely and Effectively
- Common Side Effects and When to Contact a Doctor
- Important Considerations and Precautions
- Allergies
- Other Medications
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Missed Doses
- Dental Considerations
- Long-Term Use
- Monitoring
- Storage
Usual Dose of Amoxicillin for Children
Amoxicillin dosage for children depends heavily on their weight and the specific infection being treated. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Generic guidelines are helpful, but a doctor’s assessment is paramount.
Typical dosage ranges: A common starting point is 20-40 mg per kilogram of body weight, divided into two or three doses daily. For example, a 20 kg child might receive 400-800mg per day.
Note: This is just a range; your doctor will determine the appropriate dose for your child’s needs. Factors like age, kidney function, and severity of infection influence the prescription.
Dosage Forms: Amoxicillin comes in various forms, including suspensions (liquids) and chewable tablets, making administration easier for children. Your doctor will choose the best form based on your child’s age and preferences.
Frequency: Amoxicillin is usually given twice or three times daily, depending on the prescribed dosage. Maintaining a consistent schedule is critical for treatment success.
Duration: The treatment course generally lasts for 5 to 10 days. Complete the entire course, even if your child feels better sooner. Stopping early can lead to treatment failure and potential complications.
Side Effects: Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and rash. If you notice any concerning side effects, contact your doctor immediately.
Always consult your pediatrician or family doctor before giving your child any medication, including amoxicillin. They will assess your child’s individual circumstances and provide the correct dosage and administration instructions.
Determining Your Child’s Weight Accurately
Use a reliable, calibrated digital scale designed for infants or children. Ensure the scale is on a level surface and properly zeroed before weighing your child.
Remove your child’s clothing and diaper for the most accurate reading. Heavy clothing or a diaper can significantly affect the weight.
For younger children, consider using a baby scale that measures in grams or ounces for greater precision. For older children, a standard bathroom scale with gram or kilogram measurements works well.
Weigh your child at the same time of day to minimize variations caused by fluid intake or food consumption. Ideally, weigh them before breakfast after eliminating.
Record the weight immediately. Note the units of measurement (kilograms, pounds, grams) to avoid errors in calculation.
If you’re unsure about using a scale, consult your pediatrician or a healthcare professional for assistance. They can provide guidance and ensure the weight is measured correctly.
If you are using a scale that is not digital and requires you to interpret the measurement, be sure you can read the scale accurately.
Calculating the Correct Amoxicillin Dosage Based on Weight
Amoxicillin dosage for children is determined by their weight in kilograms (kg). A common recommendation is 40-50 mg per kilogram of body weight per day, divided into two doses. For example, a 20 kg child would receive 800-1000 mg daily (20 kg x 40 mg/kg = 800 mg; 20 kg x 50 mg/kg = 1000 mg).
This daily dose is then split into two administrations. Thus, an 800 mg daily dose becomes 400 mg twice a day; a 1000 mg dose becomes 500 mg twice a day. Always follow your doctor’s specific instructions, as individual needs may vary.
Important Note: This is a general guideline. Your doctor will consider factors like the child’s age, overall health, and the specific infection being treated when determining the appropriate dosage. Always follow your doctor’s prescription and carefully read the medication information provided.
Never adjust the dosage without consulting your pediatrician. Incorrect dosage can affect treatment efficacy. If you have any questions or concerns about your child’s amoxicillin dosage, contact your doctor or pharmacist.
You can use an online dosage calculator to help you, but always verify the calculation with your doctor or pharmacist before administering the medication.
Understanding Amoxicillin Suspension Concentration
Amoxicillin suspensions come in various concentrations. Common concentrations are 125 mg/5 mL and 250 mg/5 mL. This means each 5 milliliters (mL) of the 125 mg/5 mL suspension contains 125 milligrams (mg) of amoxicillin, while the 250 mg/5 mL suspension contains 250 mg per 5 mL.
Always check the label on your child’s prescription to confirm the exact concentration. The prescription will specify the total dosage and frequency, allowing you to calculate the correct amount of suspension to administer.
Incorrect measurement can lead to underdosing or overdosing, impacting treatment effectiveness. Accurate measurement using a calibrated oral syringe or medication cup is crucial.
| Concentration | Amoxicillin per 5 mL | Dosage Calculation Example (500 mg total daily dose, divided into two administrations) |
|---|---|---|
| 125 mg/5 mL | 125 mg | 20 mL (2 x 10 mL) per day |
| 250 mg/5 mL | 250 mg | 10 mL (2 x 5 mL) per day |
Consult your pediatrician or pharmacist if you have any questions regarding dosage or the concentration of your child’s amoxicillin suspension. They can provide tailored guidance based on your child’s weight, age, and specific medical needs. Never hesitate to ask for clarification.
Administering Amoxicillin Safely and Effectively
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. Measure the dose using the provided measuring device, not a household spoon. Inaccurate measurement can lead to ineffective treatment or adverse effects.
Give amoxicillin with food or milk to minimize stomach upset. This is especially important for younger children. Administering it after a meal is usually recommended.
Ensure your child completes the entire course of medication, even if symptoms improve before the prescription ends. Stopping early can lead to antibiotic resistance and recurrence of the infection.
Store amoxicillin liquid in the refrigerator. Discard any leftover medication after the expiration date. Shake well before each dose to ensure even distribution of the medicine.
Monitor your child for allergic reactions, such as rash, hives, swelling, or difficulty breathing. Contact your doctor immediately if any of these occur. These reactions can be serious.
If your child vomits shortly after taking the medication, contact your doctor to determine if a replacement dose is needed. Don’t simply give a second dose without guidance.
Keep amoxicillin out of your child’s reach. Accidental ingestion can be harmful. Proper storage is crucial for safety.
Talk to your pharmacist or doctor if you have any questions or concerns about administering amoxicillin to your child. They are your best resources for accurate information.
This information is for general guidance only and does not replace advice from a healthcare professional. Always consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized instructions.
Common Side Effects and When to Contact a Doctor
Most children tolerate amoxicillin well, but some experience side effects. Common ones include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and a rash. These usually are mild and resolve without treatment.
However, some side effects require immediate medical attention. Contact your doctor immediately if your child develops:
- Severe diarrhea, especially if it’s watery or bloody.
- Difficulty breathing or wheezing.
- Swelling of the face, lips, or tongue (angioedema).
- A severe rash, including hives or blisters.
- Yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice).
- Dark urine.
- Unusual bleeding or bruising.
- Persistent vomiting.
Less common, but still important to note, are side effects like:
- Vaginal yeast infection.
- Thrush (oral yeast infection).
While these milder side effects usually clear up on their own, mention them to your doctor during your next appointment. Early identification can prevent potential complications.
Remember, this information is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding amoxicillin dosage and monitor your child closely for any adverse reactions.
Important Considerations and Precautions
Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely. The correct amoxicillin dosage depends on your child’s weight, age, and the specific infection being treated.
Allergies
- Tell your doctor if your child has any allergies, particularly penicillin allergies. Amoxicillin is a penicillin antibiotic, and allergic reactions can range from mild skin rashes to severe, life-threatening anaphylaxis.
- Monitor your child for signs of an allergic reaction such as hives, swelling, difficulty breathing, or dizziness. Seek immediate medical attention if these occur.
Other Medications
Inform your doctor about all other medications your child is taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Some medications can interact with amoxicillin.
Gastrointestinal Issues
- Amoxicillin can sometimes cause diarrhea or nausea. If your child experiences severe or persistent diarrhea, contact your doctor immediately, as this could indicate a serious condition like Clostridium difficile infection.
- Administering amoxicillin with food may reduce gastrointestinal upset. However, always check with your doctor for specific recommendations.
Missed Doses
- Give the missed dose as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for the next dose. Then, skip the missed dose and continue with the regular schedule.
- Never double the dose to make up for a missed one.
Dental Considerations
Amoxicillin can stain teeth, especially in young children. Good oral hygiene is crucial during treatment. Ensure your child brushes and flosses regularly.
Long-Term Use
Prolonged amoxicillin use can disrupt the balance of good bacteria in the gut and increase the risk of fungal infections. Your doctor will assess the need for long-term treatment and adjust the course accordingly.
Monitoring
Closely monitor your child’s response to the medication. Report any unusual symptoms or lack of improvement to your doctor promptly.
Storage
Store amoxicillin as directed on the label, usually in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture.