For uncomplicated UTIs, a common Ciprofloxacin dosage is 250mg twice daily for 3-7 days. Your doctor will determine the precise duration based on your individual needs and the severity of your infection. Always follow your physician’s instructions precisely.
Remember, Ciprofloxacin treats bacterial UTIs, not viral ones. A urine culture can confirm the infection’s cause and guide your treatment. This test is vital for ensuring the antibiotic is appropriate for your specific condition.
Possible side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal pain. Report any severe or persistent side effects to your doctor immediately. Taking Ciprofloxacin with food can help minimize gastrointestinal upset. Staying well-hydrated also aids in medication absorption and helps flush out the infection.
Important Note: This information serves as a general guide only. Never self-medicate. Consult your healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment. They can assess your specific situation and recommend the best course of action, including the correct dosage and duration of Ciprofloxacin.
- Uti Treatment Cipro Dosage
- Standard Dosage
- Factors Affecting Dosage
- Possible Side Effects
- Alternative Antibiotics
- Important Note
- Understanding Ciprofloxacin for UTI Treatment
- Dosage and Administration
- Potential Side Effects
- Important Considerations
- Alternatives to Ciprofloxacin
- Standard Ciprofloxacin Dosage for Uncomplicated UTIs
- Ciprofloxacin Dosage Adjustments for Complicated UTIs
- Potential Side Effects of Ciprofloxacin and What to Watch For
- Gastrointestinal Issues
- Central Nervous System Effects
- Other Potential Side Effects
- When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
- Reporting Side Effects
- Drug Interactions to Consider When Taking Ciprofloxacin
- Alternatives to Ciprofloxacin for UTI Treatment
- When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention During Ciprofloxacin Treatment
- Serious Side Effects Requiring Immediate Attention
Uti Treatment Cipro Dosage
Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) dosage for UTIs depends on several factors, including the severity of the infection, your overall health, and potential drug interactions. Always follow your doctor’s prescribed dosage. Self-treating can be harmful.
Standard Dosage
A common dosage is 250mg or 500mg twice daily for 7-14 days. However, this is a general guideline.
- 7-day course: Often sufficient for uncomplicated UTIs.
- 14-day course: Typically prescribed for more severe or complicated infections.
Factors Affecting Dosage
- Kidney function: Dosage may need adjustment if you have kidney problems. Your doctor will determine the appropriate dose based on your creatinine clearance.
- Type of UTI: The specific bacteria causing the infection influences treatment duration and dosage.
- Age: Dosage adjustments might be necessary for children and the elderly.
- Pregnancy: Cipro is generally avoided during pregnancy due to potential risks to the developing fetus.
Possible Side Effects
Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and headache. Severe side effects are rare but can include tendon rupture, allergic reactions, and Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea. Report any concerning symptoms to your doctor immediately.
Alternative Antibiotics
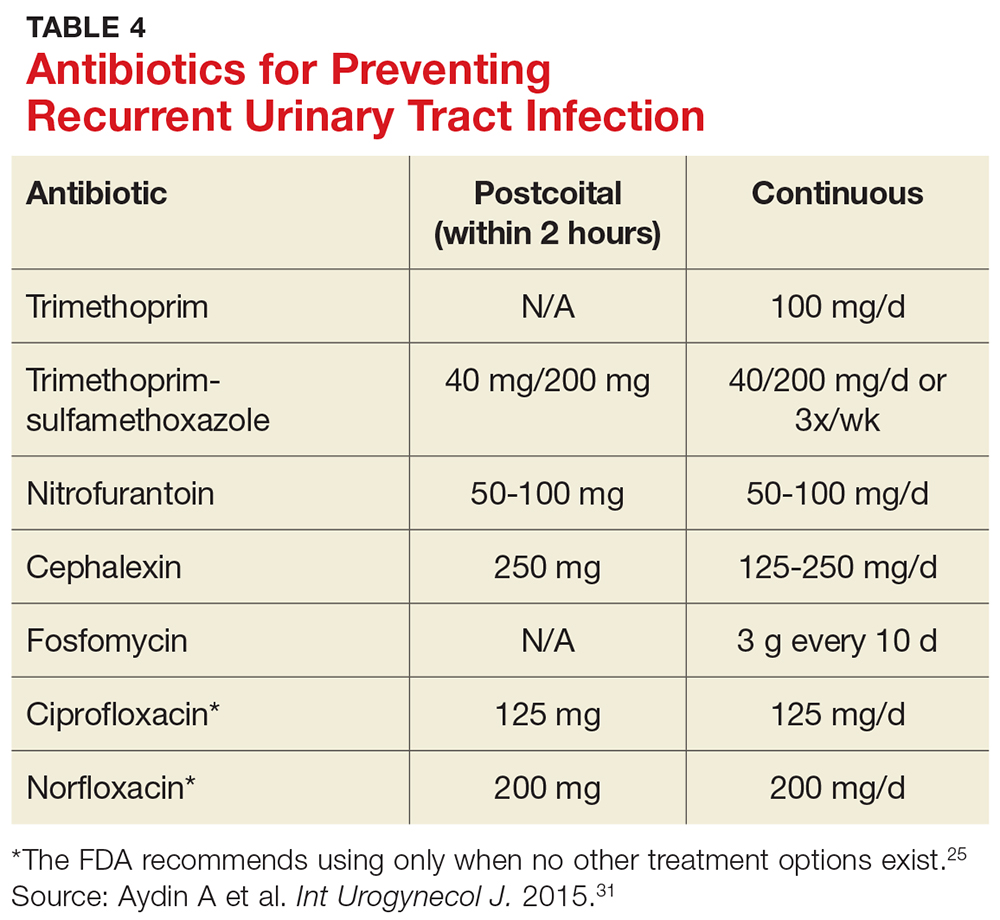
If you’re allergic to Cipro or it’s ineffective, other antibiotics, like nitrofurantoin or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, may be prescribed. Your doctor will choose the best option for your specific situation.
Important Note
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of a UTI or any other medical condition.
Understanding Ciprofloxacin for UTI Treatment
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic frequently prescribed for urinary tract infections (UTIs). It targets the bacteria causing the infection, effectively eliminating them. However, remember that antibiotics are most effective when taken correctly. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely regarding dosage and duration.
Dosage and Administration
The typical dosage for uncomplicated UTIs ranges from 250mg to 750mg twice daily for 7-14 days. Your doctor will determine the specific dose based on your individual needs and the severity of your infection. Take Ciprofloxacin with a full glass of water, preferably on an empty stomach to improve absorption. Avoid consuming dairy products or antacids concurrently, as they can interfere with absorption.
Potential Side Effects
While Ciprofloxacin is generally safe and effective, potential side effects include nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Less common side effects may involve tendonitis, and rarely, tendon rupture. Serious allergic reactions are possible, requiring immediate medical attention. Report any concerning symptoms to your doctor immediately.
Important Considerations
Ciprofloxacin is not suitable for all individuals. Pregnant or breastfeeding women, those with a history of tendon problems, or individuals with specific allergies should discuss alternative treatments with their physician. Furthermore, prolonged use of Ciprofloxacin can disrupt gut flora, potentially leading to secondary infections. Your doctor might suggest probiotics to mitigate this risk.
Alternatives to Ciprofloxacin
If Ciprofloxacin isn’t a suitable option, various alternative antibiotics exist for UTI treatment. Your doctor will consider your medical history and the specific bacteria causing your infection to recommend the most appropriate treatment. Discuss your options openly with your physician to find the best course of action for your health.
Standard Ciprofloxacin Dosage for Uncomplicated UTIs
For uncomplicated UTIs, a typical Ciprofloxacin dosage is 250 mg twice daily for three to seven days. This regimen effectively treats most common bacterial causes. The duration depends on individual symptoms and response to treatment; your doctor will determine the optimal length.
Important Note: Always follow your doctor’s specific instructions. They will tailor the dosage and treatment duration to your unique health condition and medical history. Never adjust your medication without consulting your healthcare provider.
Factors influencing dosage may include: kidney function, age, and the severity of the infection. Your doctor will consider these factors when prescribing your Ciprofloxacin. Some individuals may require a different dosage or a longer treatment course.
Potential Side Effects: Common side effects can include diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. More serious, though less frequent, side effects are possible. Inform your doctor immediately if you experience any unusual symptoms or worsening of your condition during treatment.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your physician for diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition.
Ciprofloxacin Dosage Adjustments for Complicated UTIs
For complicated urinary tract infections (UTIs), treatment protocols often deviate from standard regimens. Adjustments depend heavily on the specifics of the infection and patient factors.
Duration: Standard uncomplicated UTI treatment might last 3-7 days. Complicated UTIs frequently require longer courses, often 7-14 days or even longer, depending on the severity and response to therapy. Your doctor will determine the appropriate duration.
Dosage: The usual adult dosage is 250-750 mg twice daily. However, patients with impaired kidney function require dosage reductions to prevent toxicity. Severe infections might necessitate higher doses under close medical supervision.
Specific Patient Factors: Age, weight, and underlying medical conditions (like kidney or liver disease) significantly influence the appropriate Ciprofloxacin dose. Pregnancy also requires careful consideration and often dictates alternative antibiotics.
Example: A patient with moderate renal impairment might receive a reduced dose, perhaps 250 mg twice daily or even once daily, guided by creatinine clearance calculations.
Combination Therapy: In some cases, especially with severe or recurrent infections, doctors prescribe Ciprofloxacin in combination with another antibiotic to broaden antimicrobial coverage and combat resistant bacteria.
Monitoring: Regular monitoring of kidney function and other relevant parameters is crucial during treatment, especially with higher doses or extended durations. This allows for timely adjustments to the treatment plan if needed.
Important Note: This information is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or other qualified healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage and duration of Ciprofloxacin for your specific situation.
Potential Side Effects of Ciprofloxacin and What to Watch For
Ciprofloxacin, while effective, can cause side effects. Monitor yourself closely for any unusual symptoms. If you experience any severe reactions, contact your doctor immediately.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting. These usually are mild and resolve without treatment. However, persistent or severe diarrhea could indicate Clostridium difficile infection, a serious complication requiring medical attention. Drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated.
Central Nervous System Effects
Some people experience dizziness, headaches, or confusion. These effects are usually temporary. Avoid driving or operating machinery if you feel lightheaded or disoriented. Report persistent or worsening neurological symptoms to your healthcare provider.
Other Potential Side Effects
Less common but still possible side effects include tendonitis (inflammation of tendons), particularly in the Achilles tendon, allergic reactions (rash, itching, swelling), and photosensitivity (increased sensitivity to sunlight). Protect yourself from excessive sun exposure while taking Ciprofloxacin.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Seek immediate medical help if you experience:
| Symptom | Action |
|---|---|
| Severe allergic reaction (difficulty breathing, swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat) | Call emergency services immediately. |
| Severe or persistent diarrhea | Contact your doctor. |
| Severe tendon pain or swelling | Stop taking Ciprofloxacin and seek medical advice. |
| Unusual bleeding or bruising | Consult your doctor immediately. |
Reporting Side Effects
Report any side effects, even minor ones, to your doctor or pharmacist. This information helps improve medication safety.
Drug Interactions to Consider When Taking Ciprofloxacin
Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies. Ciprofloxacin interacts with several substances, potentially altering their effects or its own.
Antacids: Taking antacids containing magnesium or aluminum within two hours of ciprofloxacin reduces its absorption. Space out these medications for optimal effectiveness.
Sucralfate: This medication binds to ciprofloxacin, diminishing its absorption. Separate your doses by at least two hours.
Warfarin: Ciprofloxacin can increase the risk of bleeding when taken with warfarin, a blood thinner. Close monitoring of your blood clotting time is crucial.
Theophylline: Ciprofloxacin may increase theophylline levels, potentially leading to side effects like increased heart rate or seizures. Regular monitoring of theophylline levels is recommended.
Caffeine: While not a serious interaction, ciprofloxacin may slightly increase caffeine levels. Observe for increased jitters or anxiety.
NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs): Concurrent use with NSAIDs like ibuprofen or naproxen may increase the risk of seizures or kidney problems. Your doctor might adjust dosages or monitor you carefully.
This information is not exhaustive and doesn’t replace professional medical advice. Always consult your physician or pharmacist for personalized guidance on managing potential drug interactions with ciprofloxacin.
Alternatives to Ciprofloxacin for UTI Treatment
Consider Nitrofurantoin as a first-line option for uncomplicated UTIs. This antibiotic boasts a strong track record and generally causes fewer side effects than Ciprofloxacin.
For more severe infections or those resistant to Nitrofurantoin, your doctor might prescribe:
- Fosfomycin: A single dose treatment offers convenience. It’s generally well-tolerated.
- Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX): A common choice, though resistance is increasing. Your doctor will assess suitability.
- Cephalexin: A cephalosporin antibiotic, effective against many UTI-causing bacteria.
- Amoxicillin-clavulanate: Useful when other options fail, especially if bacterial resistance is suspected.
The best alternative depends on your individual health circumstances and the specific bacteria causing the infection. Always discuss treatment options with your physician to ensure safe and effective management of your UTI. They’ll consider factors like your medical history and allergy profile before deciding on the most appropriate antibiotic.
Remember to complete the full course of any prescribed antibiotic, even if symptoms improve, to prevent recurrence.
If you experience side effects, contact your doctor immediately.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention During Ciprofloxacin Treatment
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following severe side effects: Severe allergic reactions, including difficulty breathing, swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat, and hives. These symptoms can appear suddenly and require urgent medical attention.
Serious Side Effects Requiring Immediate Attention
Seek immediate medical help if you develop signs of tendonitis or tendon rupture, such as pain, swelling, or inflammation around your tendons, particularly in your ankles, wrists, or shoulders. Also, contact your doctor at once if you experience signs of central nervous system problems including seizures, confusion, hallucinations, or unusual anxiety. Severe or persistent diarrhea (possibly indicative of *Clostridium difficile* infection) is another reason for immediate medical attention. Report unexplained weakness, easy bruising or bleeding, or persistent yellowing of your skin or eyes (jaundice) immediately.
Remember, this information is not exhaustive. Always follow your doctor’s instructions and report any concerning symptoms, no matter how minor they may seem, to ensure your safety during treatment.